Digital twin technology offers a dynamic, real-time simulation of manufacturing processes, enabling predictive maintenance and operational optimization beyond static CAD modeling's detailed 3D design capabilities. Unlike CAD models, which primarily focus on the geometric representation of products, digital twins integrate sensor data and analytics to mirror actual production environments, enhancing decision-making and reducing downtime. Explore more about how digital twins revolutionize manufacturing efficiency and innovation.
Why it is important
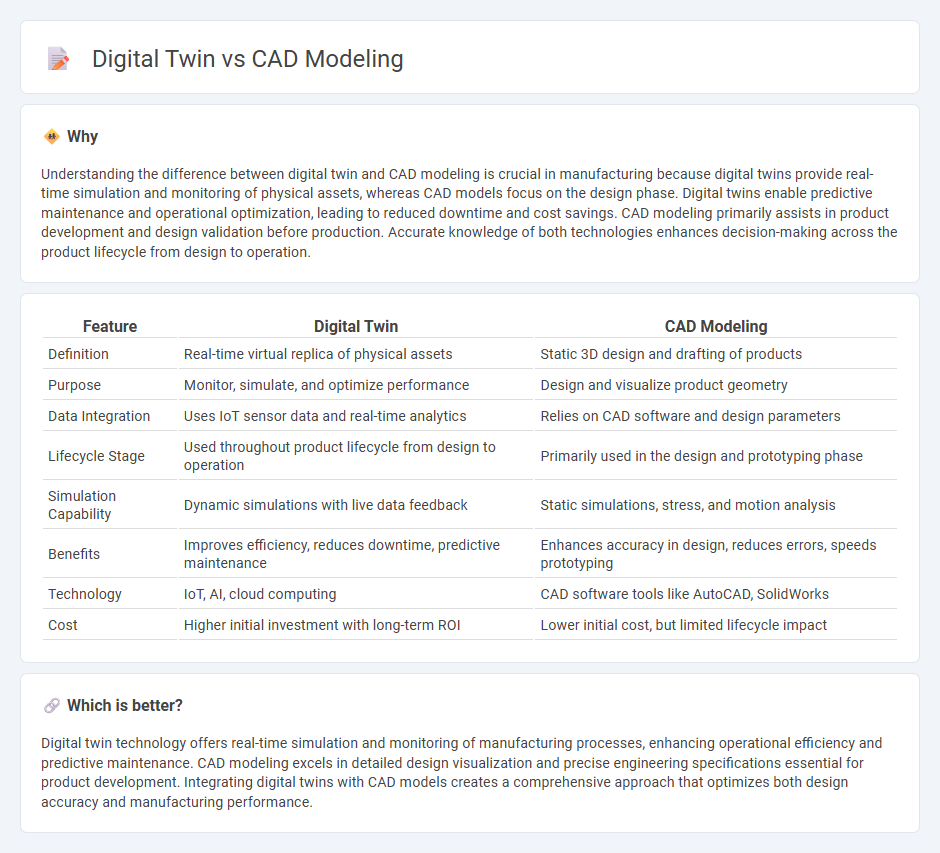
Understanding the difference between digital twin and CAD modeling is crucial in manufacturing because digital twins provide real-time simulation and monitoring of physical assets, whereas CAD models focus on the design phase. Digital twins enable predictive maintenance and operational optimization, leading to reduced downtime and cost savings. CAD modeling primarily assists in product development and design validation before production. Accurate knowledge of both technologies enhances decision-making across the product lifecycle from design to operation.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Twin | CAD Modeling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time virtual replica of physical assets | Static 3D design and drafting of products |
| Purpose | Monitor, simulate, and optimize performance | Design and visualize product geometry |
| Data Integration | Uses IoT sensor data and real-time analytics | Relies on CAD software and design parameters |
| Lifecycle Stage | Used throughout product lifecycle from design to operation | Primarily used in the design and prototyping phase |
| Simulation Capability | Dynamic simulations with live data feedback | Static simulations, stress, and motion analysis |
| Benefits | Improves efficiency, reduces downtime, predictive maintenance | Enhances accuracy in design, reduces errors, speeds prototyping |
| Technology | IoT, AI, cloud computing | CAD software tools like AutoCAD, SolidWorks |
| Cost | Higher initial investment with long-term ROI | Lower initial cost, but limited lifecycle impact |
Which is better?
Digital twin technology offers real-time simulation and monitoring of manufacturing processes, enhancing operational efficiency and predictive maintenance. CAD modeling excels in detailed design visualization and precise engineering specifications essential for product development. Integrating digital twins with CAD models creates a comprehensive approach that optimizes both design accuracy and manufacturing performance.
Connection
Digital twin technology and CAD modeling are intrinsically connected through their shared foundation in creating precise, digital representations of physical manufacturing assets. CAD models serve as the initial blueprint, providing detailed geometric and structural data that digital twins use to simulate real-time operations, monitor performance, and predict maintenance needs. This integration enhances product design accuracy, optimizes manufacturing processes, and enables dynamic, data-driven decision-making on the factory floor.
Key Terms
3D Geometry
CAD modeling creates precise 3D geometry for design and manufacturing processes, focusing on detailed representations of parts and assemblies. Digital twins integrate 3D geometry with real-time data and sensor inputs to simulate the actual behavior and performance of physical assets. Explore more to understand how combining both enhances product lifecycle management and operational efficiency.
Real-time Simulation
CAD modeling creates static 3D representations of physical objects, primarily used for design and manufacturing planning. Digital twins extend this concept by integrating real-time simulation data from IoT sensors, enabling continuous monitoring and predictive analysis of asset performance. Explore how real-time simulation enhances operational efficiency and decision-making in digital twin technology.
Data Synchronization
CAD modeling provides precise geometric representations of products, enabling detailed design and engineering visualization. Digital twins extend beyond static models by integrating real-time data synchronization from sensors and IoT devices, ensuring continuous alignment between the physical asset and its virtual counterpart. Explore how advanced data synchronization enhances predictive maintenance and operational efficiency in digital twin applications.
Source and External Links
What is CAD modeling? Comparing design software for 3D printing - CAD modeling is the process of creating realistic computer models of parts and assemblies for digital manufacturing and simulation, enabling faster, cost-efficient prototyping and design iteration.
All About Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Modeling - Xometry - CAD modeling uses specialized software to create precise digital representations of real-world objects, streamlining the conceptualization, visualization, and analysis of complex designs across various industries.
Computer-aided design - Wikipedia - CAD refers to the use of computers to assist in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of designs, forming a core part of digital product development in engineering and design fields.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com