Digital twins provide a virtual replica of physical manufacturing processes, enabling real-time simulations and predictive analytics to optimize production efficiency. Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) manage and monitor work-in-progress on the factory floor, ensuring compliance and traceability. Explore how integrating digital twins with MES can revolutionize manufacturing operations and drive smarter decision-making.
Why it is important
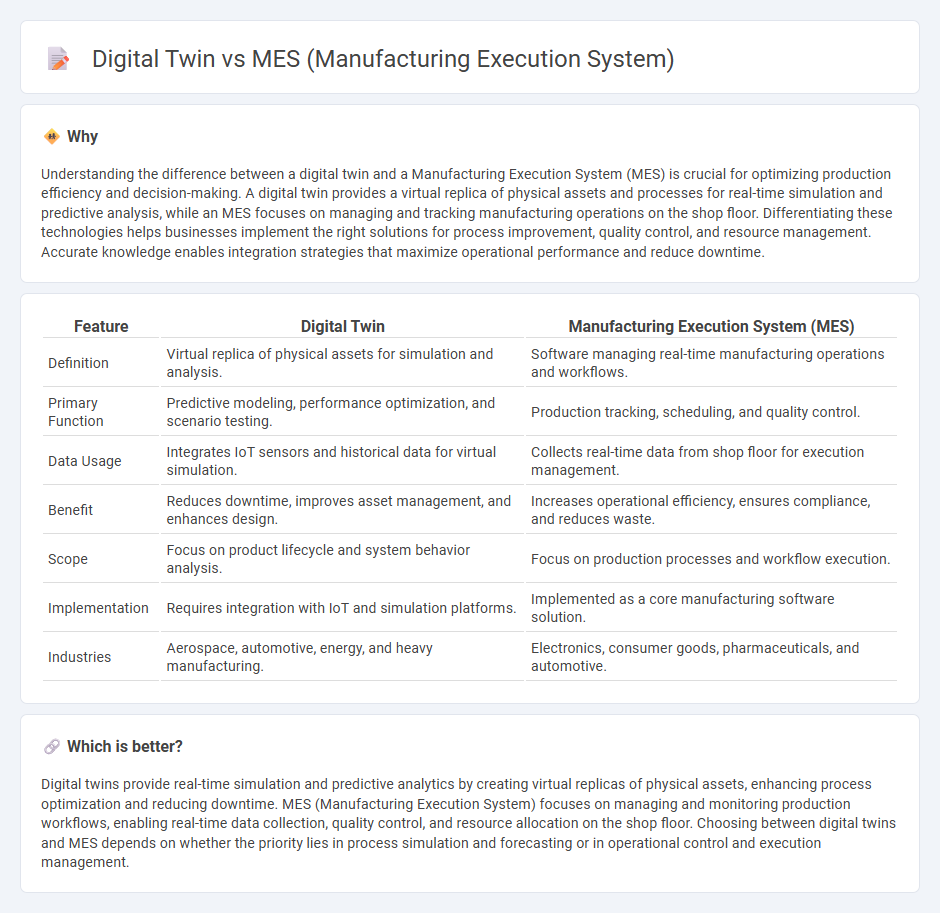
Understanding the difference between a digital twin and a Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and decision-making. A digital twin provides a virtual replica of physical assets and processes for real-time simulation and predictive analysis, while an MES focuses on managing and tracking manufacturing operations on the shop floor. Differentiating these technologies helps businesses implement the right solutions for process improvement, quality control, and resource management. Accurate knowledge enables integration strategies that maximize operational performance and reduce downtime.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Twin | Manufacturing Execution System (MES) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual replica of physical assets for simulation and analysis. | Software managing real-time manufacturing operations and workflows. |
| Primary Function | Predictive modeling, performance optimization, and scenario testing. | Production tracking, scheduling, and quality control. |
| Data Usage | Integrates IoT sensors and historical data for virtual simulation. | Collects real-time data from shop floor for execution management. |
| Benefit | Reduces downtime, improves asset management, and enhances design. | Increases operational efficiency, ensures compliance, and reduces waste. |
| Scope | Focus on product lifecycle and system behavior analysis. | Focus on production processes and workflow execution. |
| Implementation | Requires integration with IoT and simulation platforms. | Implemented as a core manufacturing software solution. |
| Industries | Aerospace, automotive, energy, and heavy manufacturing. | Electronics, consumer goods, pharmaceuticals, and automotive. |
Which is better?
Digital twins provide real-time simulation and predictive analytics by creating virtual replicas of physical assets, enhancing process optimization and reducing downtime. MES (Manufacturing Execution System) focuses on managing and monitoring production workflows, enabling real-time data collection, quality control, and resource allocation on the shop floor. Choosing between digital twins and MES depends on whether the priority lies in process simulation and forecasting or in operational control and execution management.
Connection
Digital twin technology and Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) are interconnected by enabling real-time simulation and control of manufacturing processes. The digital twin creates a virtual replica of physical assets, which MES utilizes to monitor production workflows, optimize resource allocation, and improve process efficiency. Integrating these systems enhances predictive maintenance, reduces downtime, and facilitates data-driven decision-making in smart manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Real-time Data Management
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) centralizes real-time production data to monitor and control manufacturing processes, ensuring operational efficiency and quality compliance. Digital twin technology creates a virtual replica of physical assets, providing continuous real-time data synchronization for predictive analysis and scenario simulation. Discover how integrating MES with digital twins enhances real-time data management and drives smart manufacturing innovation.
Virtual Simulation
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) primarily monitor and control real-time production processes, while digital twins offer virtual simulation by creating dynamic, real-world replicas of manufacturing environments for predictive analysis and optimization. Digital twins enable detailed scenario testing without interrupting actual operations, enhancing decision-making through immersive virtual insights. Explore how integrating MES with digital twin technology revolutionizes manufacturing efficiency and innovation.
Production Optimization
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) provides real-time data tracking and control over production processes, enabling immediate adjustments to improve efficiency and reduce downtime. Digital twins create a virtual replica of physical assets and production lines, allowing simulation and predictive analysis to optimize workflows and foresee potential bottlenecks. Explore the advantages of integrating MES and digital twins for superior production optimization strategies.
Source and External Links
Manufacturing execution system - Wikipedia - MES are computerized systems that track, document, and control production operations in real time, enabling optimization of processes, quality management, resource scheduling, and integration with ERP systems to enhance manufacturing efficiency and transparency.
What is a Manufacturing Execution System (MES)? - IBM - An MES is software that monitors and controls manufacturing on the shop floor, providing real-time visibility and data to optimize production planning, quality assurance, inventory management, and improve overall equipment effectiveness.
The MES Beginners Guide | Rockwell Automation - MES tracks real-time production data across the manufacturing lifecycle and equipment, helping businesses monitor product genealogy, performance, and work in progress to optimize operations effectively.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com