Decentralized manufacturing disperses production across multiple locations, enhancing flexibility and reducing lead times, while continuous manufacturing focuses on an uninterrupted production flow to optimize efficiency and consistency. Both approaches leverage advanced technologies like IoT and AI to streamline operations and improve quality control. Discover how these manufacturing strategies transform industrial processes and drive competitive advantage.
Why it is important
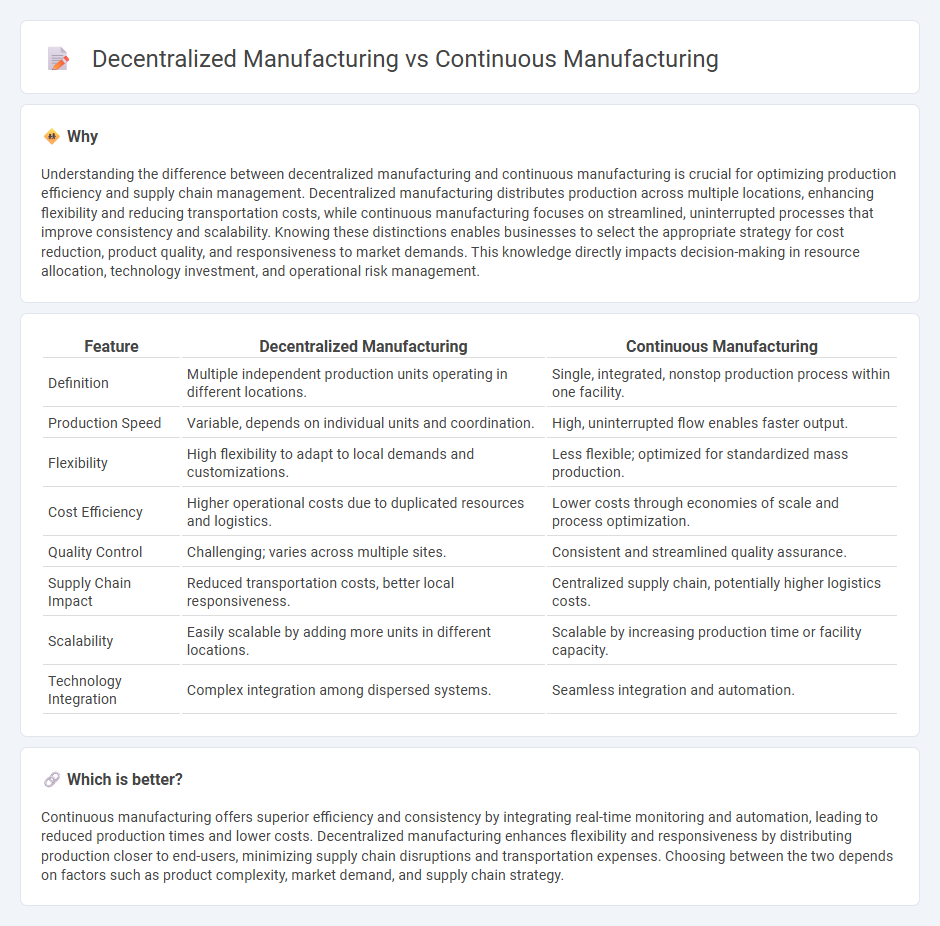
Understanding the difference between decentralized manufacturing and continuous manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and supply chain management. Decentralized manufacturing distributes production across multiple locations, enhancing flexibility and reducing transportation costs, while continuous manufacturing focuses on streamlined, uninterrupted processes that improve consistency and scalability. Knowing these distinctions enables businesses to select the appropriate strategy for cost reduction, product quality, and responsiveness to market demands. This knowledge directly impacts decision-making in resource allocation, technology investment, and operational risk management.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Manufacturing | Continuous Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple independent production units operating in different locations. | Single, integrated, nonstop production process within one facility. |
| Production Speed | Variable, depends on individual units and coordination. | High, uninterrupted flow enables faster output. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility to adapt to local demands and customizations. | Less flexible; optimized for standardized mass production. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher operational costs due to duplicated resources and logistics. | Lower costs through economies of scale and process optimization. |
| Quality Control | Challenging; varies across multiple sites. | Consistent and streamlined quality assurance. |
| Supply Chain Impact | Reduced transportation costs, better local responsiveness. | Centralized supply chain, potentially higher logistics costs. |
| Scalability | Easily scalable by adding more units in different locations. | Scalable by increasing production time or facility capacity. |
| Technology Integration | Complex integration among dispersed systems. | Seamless integration and automation. |
Which is better?
Continuous manufacturing offers superior efficiency and consistency by integrating real-time monitoring and automation, leading to reduced production times and lower costs. Decentralized manufacturing enhances flexibility and responsiveness by distributing production closer to end-users, minimizing supply chain disruptions and transportation expenses. Choosing between the two depends on factors such as product complexity, market demand, and supply chain strategy.
Connection
Decentralized manufacturing leverages localized production units to enhance responsiveness and reduce supply chain disruptions, while continuous manufacturing integrates real-time data and automation for efficient, uninterrupted production processes. The synergy between decentralized and continuous manufacturing allows for scalable, flexible operations with improved quality control and reduced lead times. Advanced IoT sensors and AI-driven analytics facilitate seamless coordination across distributed facilities, optimizing resource use and boosting overall productivity.
Key Terms
Production Flow
Continuous manufacturing streamlines production flow through an unbroken, automated process that reduces lead times and enhances product consistency, leveraging real-time data for optimal efficiency. Decentralized manufacturing distributes production across multiple locations, allowing localized responsiveness and flexibility but potentially introducing complexities in coordination and inventory management. Explore deeper insights into how production flow dynamics impact efficiency and scalability in both manufacturing models.
Facility Location
Continuous manufacturing centralizes production in large-scale facilities designed for uninterrupted processes, optimizing efficiency and minimizing downtime. Decentralized manufacturing distributes production across multiple smaller facilities closer to end markets, reducing transportation costs and increasing responsiveness. Explore the strategic impact of facility location on manufacturing efficiency and supply chain resilience to understand which approach best suits your business needs.
Supply Chain Integration
Continuous manufacturing streamlines supply chain integration by enabling real-time data flow and consistent production output, reducing lead times and inventory costs. Decentralized manufacturing enhances supply chain resilience through localized production, minimizing transportation delays and adapting swiftly to regional demand shifts. Explore further to understand how integrating these manufacturing models can optimize your supply chain strategies.
Source and External Links
Continuous Manufacturing and How To Do It -- Katana - Continuous manufacturing is a 24/7 production process where raw materials like gases, liquids, powders, or slurries are continuously processed in one location through chemical or physical means to produce finished products without interruption, commonly used in industries such as oil refining and pharmaceuticals.
Continuous Manufacturing: Batch to the Future - Continuous manufacturing improves drug quality by shortening production times, reducing human error with automated monitoring, enabling flexible batch sizes, and minimizing waste and shortages compared to traditional batch processes.
Continuous production - Wikipedia - Continuous production is a flow method to manufacture materials without interruption, typically running 24/7 with rare maintenance shutdowns, involving continuous movement and treatment of materials, contrasted with batch production.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com