Smart factories leverage advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and automation to optimize production processes, enhance real-time data analysis, and improve operational efficiency compared to traditional methods. Lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste, reducing costs, and streamlining workflows by continuously improving processes and maximizing value for customers. Discover how integrating smart factory principles with lean manufacturing can transform industrial productivity and competitiveness.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between smart factory and lean manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and technology integration. Smart factories leverage IoT, AI, and automation to create highly connected and adaptable manufacturing environments. Lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing value through streamlined processes and continuous improvement. Distinguishing these approaches enables manufacturers to strategically implement innovations that align with their operational goals and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
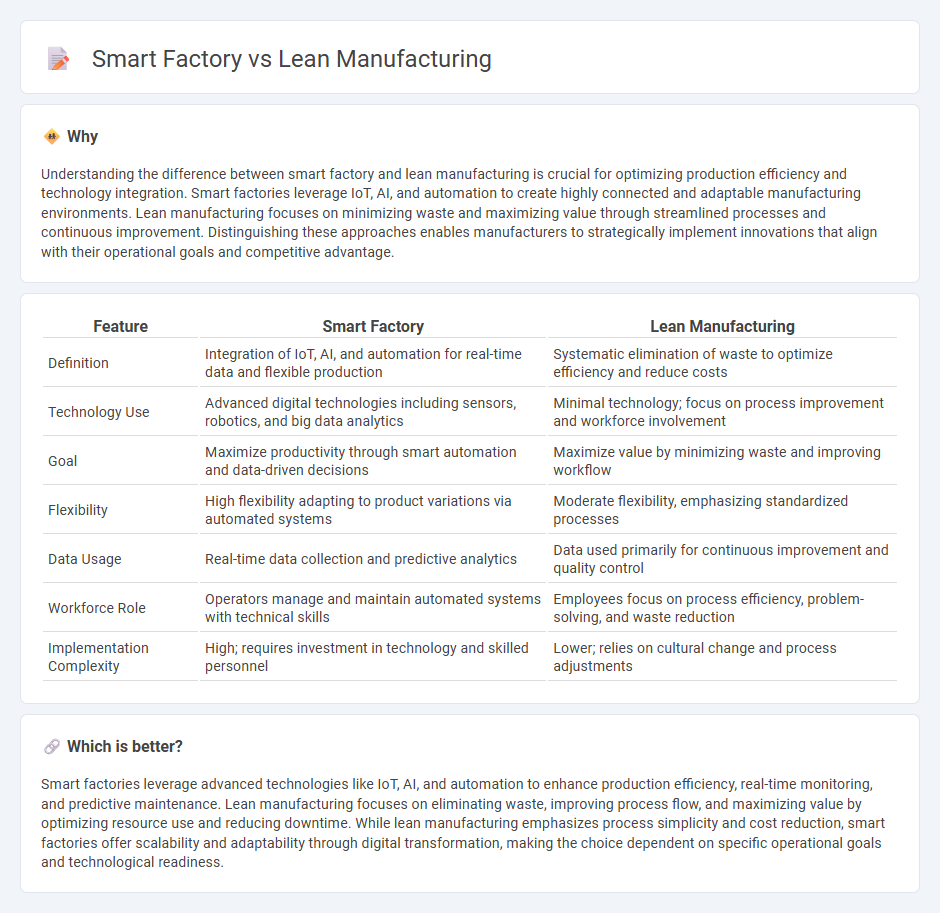
| Feature | Smart Factory | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of IoT, AI, and automation for real-time data and flexible production | Systematic elimination of waste to optimize efficiency and reduce costs |
| Technology Use | Advanced digital technologies including sensors, robotics, and big data analytics | Minimal technology; focus on process improvement and workforce involvement |
| Goal | Maximize productivity through smart automation and data-driven decisions | Maximize value by minimizing waste and improving workflow |
| Flexibility | High flexibility adapting to product variations via automated systems | Moderate flexibility, emphasizing standardized processes |
| Data Usage | Real-time data collection and predictive analytics | Data used primarily for continuous improvement and quality control |
| Workforce Role | Operators manage and maintain automated systems with technical skills | Employees focus on process efficiency, problem-solving, and waste reduction |
| Implementation Complexity | High; requires investment in technology and skilled personnel | Lower; relies on cultural change and process adjustments |
Which is better?
Smart factories leverage advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and automation to enhance production efficiency, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance. Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste, improving process flow, and maximizing value by optimizing resource use and reducing downtime. While lean manufacturing emphasizes process simplicity and cost reduction, smart factories offer scalability and adaptability through digital transformation, making the choice dependent on specific operational goals and technological readiness.
Connection
Smart factories integrate advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and automation to optimize production processes, while lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste and improving efficiency. Together, they enhance operational agility by enabling real-time data-driven decision-making and continuous process improvement. This synergy results in higher productivity, reduced costs, and improved product quality in manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Waste Reduction (Lean Manufacturing)
Lean manufacturing targets waste reduction by eliminating non-value-added activities through techniques like Just-In-Time, 5S, and Kaizen, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs. Smart factories leverage advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and real-time data analytics to monitor, predict, and autonomously minimize waste throughout the production process. Discover how integrating lean principles with smart factory innovations can revolutionize waste reduction strategies.
Automation (Smart Factory)
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction and process efficiency using human-driven methods and simple automation, while smart factories leverage advanced automation technologies like AI, IoT, and robotics to enable real-time data exchange, self-optimization, and predictive maintenance. Smart factory automation enhances flexibility and responsiveness, allowing for adaptive production lines and minimizing downtime through intelligent decision-making systems. Explore further to understand how smart factory automation is transforming modern manufacturing landscapes.
Real-Time Data (Smart Factory)
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction and process efficiency through standardized workflows, while smart factories leverage real-time data analytics and IoT sensors to optimize operations dynamically. Real-time data enables predictive maintenance, rapid decision-making, and adaptive supply chain management, driving higher productivity and reduced downtime. Explore how integrating real-time data transforms manufacturing approaches for a competitive edge in Industry 4.0.
Source and External Links
Lean manufacturing - Wikipedia - Lean manufacturing is a method focused on reducing production system times and supplier/customer response times by minimizing activities that do not add customer value, originating from the Toyota Production System and targeting the elimination of seven types of waste.
What is Lean Manufacturing? | Definition from TechTarget - Lean manufacturing is a methodology that minimizes waste and maximizes productivity, focusing on customer value and continuous improvement, widely adopted by companies across various industries.
What is Lean Manufacturing and the 5 Principles Used? - TWI - Lean manufacturing streamlines processes to eliminate waste and maximize productivity, operating on five core principles: value, value stream, flow, pull, and perfection.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com