Cloud manufacturing leverages advanced cloud computing technologies to streamline production processes, enable real-time data sharing, and enhance collaboration across distributed facilities. Lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste, optimizing workflows, and improving product quality through continuous process improvement and efficient resource management. Explore how integrating cloud-based solutions with lean principles can drive innovation and operational excellence in modern manufacturing.
Why it is important
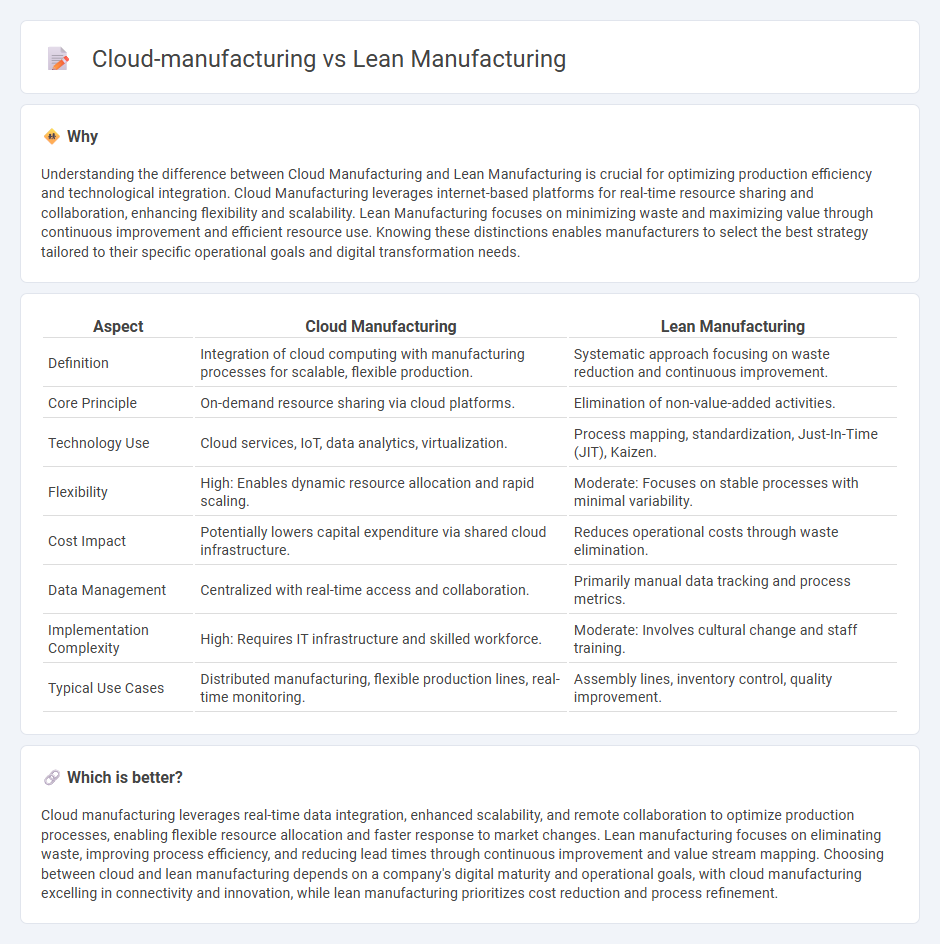
Understanding the difference between Cloud Manufacturing and Lean Manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and technological integration. Cloud Manufacturing leverages internet-based platforms for real-time resource sharing and collaboration, enhancing flexibility and scalability. Lean Manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing value through continuous improvement and efficient resource use. Knowing these distinctions enables manufacturers to select the best strategy tailored to their specific operational goals and digital transformation needs.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cloud Manufacturing | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of cloud computing with manufacturing processes for scalable, flexible production. | Systematic approach focusing on waste reduction and continuous improvement. |
| Core Principle | On-demand resource sharing via cloud platforms. | Elimination of non-value-added activities. |
| Technology Use | Cloud services, IoT, data analytics, virtualization. | Process mapping, standardization, Just-In-Time (JIT), Kaizen. |
| Flexibility | High: Enables dynamic resource allocation and rapid scaling. | Moderate: Focuses on stable processes with minimal variability. |
| Cost Impact | Potentially lowers capital expenditure via shared cloud infrastructure. | Reduces operational costs through waste elimination. |
| Data Management | Centralized with real-time access and collaboration. | Primarily manual data tracking and process metrics. |
| Implementation Complexity | High: Requires IT infrastructure and skilled workforce. | Moderate: Involves cultural change and staff training. |
| Typical Use Cases | Distributed manufacturing, flexible production lines, real-time monitoring. | Assembly lines, inventory control, quality improvement. |
Which is better?
Cloud manufacturing leverages real-time data integration, enhanced scalability, and remote collaboration to optimize production processes, enabling flexible resource allocation and faster response to market changes. Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste, improving process efficiency, and reducing lead times through continuous improvement and value stream mapping. Choosing between cloud and lean manufacturing depends on a company's digital maturity and operational goals, with cloud manufacturing excelling in connectivity and innovation, while lean manufacturing prioritizes cost reduction and process refinement.
Connection
Cloud manufacturing integrates digital technologies and real-time data sharing to optimize production processes, aligning closely with Lean manufacturing principles that aim to minimize waste and enhance efficiency. By leveraging cloud platforms, manufacturers can achieve greater transparency, rapid responsiveness, and streamlined workflows, all key components of Lean methodologies. This synergy enables dynamic resource allocation and continuous improvement, leading to reduced lead times and cost savings.
Key Terms
Waste reduction vs. Resource virtualization
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction by streamlining production processes, eliminating non-value-added activities, and improving operational efficiency to minimize excess inventory, defects, and waiting times. Cloud manufacturing leverages resource virtualization, enabling distributed manufacturing capabilities, flexible resource allocation, and real-time data sharing to optimize production scalability and responsiveness. Explore the transformative impact of these approaches on modern manufacturing systems to enhance productivity and sustainability.
Just-in-time (JIT) vs. On-demand production
Lean manufacturing emphasizes Just-in-time (JIT) production to minimize inventory and reduce waste by producing goods only as needed, enhancing operational efficiency. Cloud manufacturing leverages digital platforms to enable On-demand production, allowing for real-time resource allocation and flexible scaling based on customer demand. Explore how these advanced methodologies transform manufacturing agility and responsiveness today.
Kaizen (continuous improvement) vs. Cyber-physical integration
Lean manufacturing emphasizes Kaizen, a continuous improvement methodology that reduces waste and optimizes processes through incremental changes and employee involvement. Cloud-manufacturing integrates cyber-physical systems, enabling real-time data analytics, remote monitoring, and adaptive production flexibility to enhance operational efficiency. Explore how combining Kaizen principles with cloud-manufacturing technologies can revolutionize industrial productivity.
Source and External Links
Lean manufacturing - Lean manufacturing is a method focused on reducing production and response times by eliminating waste and inefficiencies, originally developed from Toyota's Production System and emphasizing continuous improvement and just-in-time manufacturing.
What is Lean Manufacturing? | Definition from TechTarget - Lean manufacturing aims to minimize waste and maximize productivity by focusing on activities that add value for the customer, based on principles like Kaizen and widely applied in industries beyond manufacturing.
What is Lean Manufacturing and the 5 Principles Used? - TWI - Lean manufacturing revolves around five core principles: value, value stream, flow, pull, and perfection, and seeks to make workflows efficient while eliminating waste across processes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com