Edge computing enhances manufacturing efficiency by processing data locally on devices, reducing latency and improving real-time decision-making in factories. Industrial IoT platforms integrate connected sensors and machinery to enable centralized monitoring, predictive maintenance, and streamlined operations across multiple sites. Discover how combining edge computing with Industrial IoT platforms transforms modern manufacturing workflows.
Why it is important
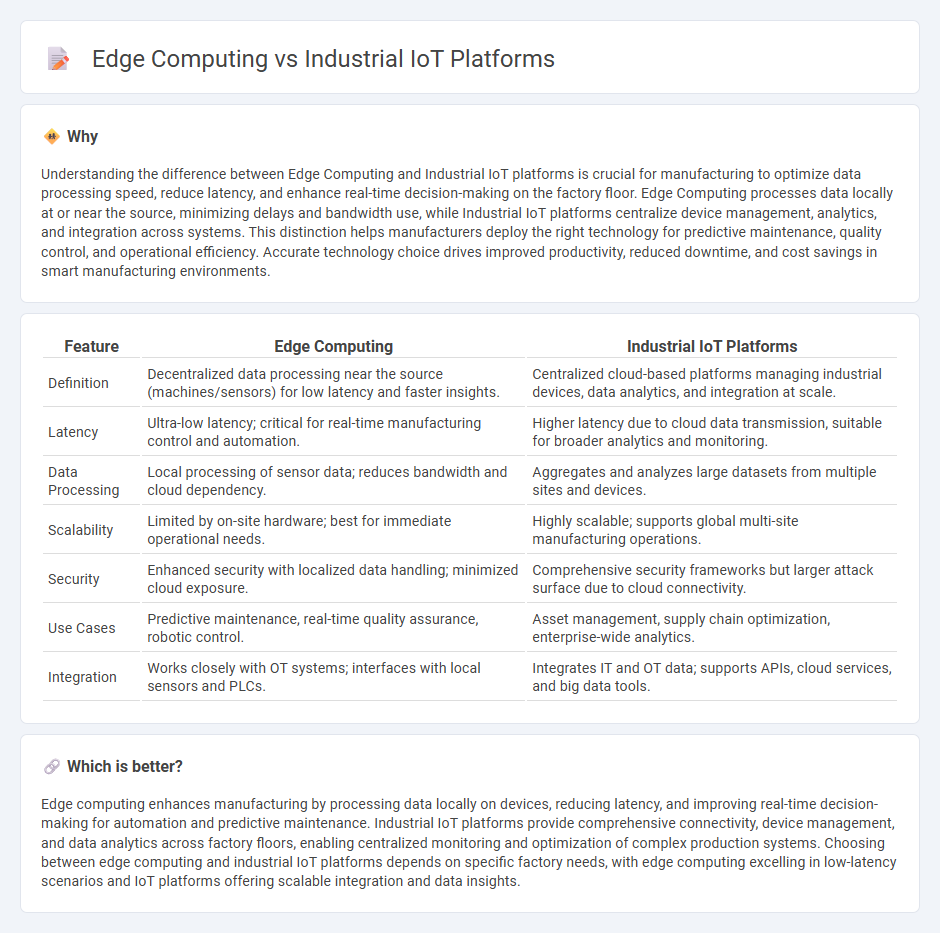
Understanding the difference between Edge Computing and Industrial IoT platforms is crucial for manufacturing to optimize data processing speed, reduce latency, and enhance real-time decision-making on the factory floor. Edge Computing processes data locally at or near the source, minimizing delays and bandwidth use, while Industrial IoT platforms centralize device management, analytics, and integration across systems. This distinction helps manufacturers deploy the right technology for predictive maintenance, quality control, and operational efficiency. Accurate technology choice drives improved productivity, reduced downtime, and cost savings in smart manufacturing environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Edge Computing | Industrial IoT Platforms |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decentralized data processing near the source (machines/sensors) for low latency and faster insights. | Centralized cloud-based platforms managing industrial devices, data analytics, and integration at scale. |
| Latency | Ultra-low latency; critical for real-time manufacturing control and automation. | Higher latency due to cloud data transmission, suitable for broader analytics and monitoring. |
| Data Processing | Local processing of sensor data; reduces bandwidth and cloud dependency. | Aggregates and analyzes large datasets from multiple sites and devices. |
| Scalability | Limited by on-site hardware; best for immediate operational needs. | Highly scalable; supports global multi-site manufacturing operations. |
| Security | Enhanced security with localized data handling; minimized cloud exposure. | Comprehensive security frameworks but larger attack surface due to cloud connectivity. |
| Use Cases | Predictive maintenance, real-time quality assurance, robotic control. | Asset management, supply chain optimization, enterprise-wide analytics. |
| Integration | Works closely with OT systems; interfaces with local sensors and PLCs. | Integrates IT and OT data; supports APIs, cloud services, and big data tools. |
Which is better?
Edge computing enhances manufacturing by processing data locally on devices, reducing latency, and improving real-time decision-making for automation and predictive maintenance. Industrial IoT platforms provide comprehensive connectivity, device management, and data analytics across factory floors, enabling centralized monitoring and optimization of complex production systems. Choosing between edge computing and industrial IoT platforms depends on specific factory needs, with edge computing excelling in low-latency scenarios and IoT platforms offering scalable integration and data insights.
Connection
Edge computing enhances Industrial IoT platforms by processing data locally on manufacturing equipment, reducing latency and enabling real-time analytics for predictive maintenance and quality control. Industrial IoT platforms aggregate and analyze data from connected sensors and machines, leveraging edge computing to optimize production workflows and minimize downtime. This integration supports scalable, secure, and efficient smart manufacturing environments by enabling faster decision-making and improved asset management.
Key Terms
Data acquisition
Industrial IoT platforms centralize data acquisition by aggregating sensor inputs from multiple devices into cloud environments for real-time analytics, enabling comprehensive monitoring and predictive maintenance across industrial operations. Edge computing processes data locally on devices or nearby servers, reducing latency and bandwidth usage by handling critical analytics directly at the source before sending summarized insights to centralized systems. Explore the nuances of these technologies to optimize data acquisition strategies in modern industrial environments.
Real-time processing
Industrial IoT platforms enable centralized data management and analytics, supporting large-scale device connectivity but often facing latency challenges in real-time processing. Edge computing processes data closer to the source, significantly reducing latency for time-sensitive applications like predictive maintenance and automated control systems in manufacturing. Explore the advantages and use cases of both technologies to optimize real-time industrial operations.
Cloud integration
Industrial IoT platforms leverage cloud integration to enable centralized data storage, analytics, and remote management of connected devices, optimizing operational efficiency and scalability. Edge computing complements this by processing data locally near the source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage while enhancing real-time decision-making in industrial environments. Discover how combining Industrial IoT platforms with Edge computing and cloud integration drives smarter, more resilient industrial systems.
Source and External Links
Azure Industrial IoT - IoT for Industry 4.0 | Microsoft Azure - Azure Industrial IoT enables building open, interoperable solutions that integrate new or legacy industrial machines, connect the supply chain, and provide security and scalability for Industry 4.0 applications using edge and cloud services.
The Best Industrial IoT Software of 2025 | SafetyCulture - Leading industrial IoT platforms like Davra and Particle provide comprehensive cloud and edge solutions with features such as predictive analytics, asset and equipment monitoring, and secure data storage for sectors like manufacturing and transportation.
Best Global Industrial IoT Platforms Reviews 2025 - Gartner - Industrial IoT platforms offer integrated middleware that connects OT assets and other industrial data sources to enable intelligent applications, remote operations, sustainability management, and IT/OT convergence through edge-to-cloud architectures.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com