Hyperautomation integrates advanced technologies like AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation to streamline manufacturing workflows, enhancing efficiency and reducing human error. Lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste and optimizing processes through continuous improvement and just-in-time production, boosting operational agility and cost savings. Explore how combining hyperautomation and lean manufacturing can revolutionize your production strategy.
Why it is important
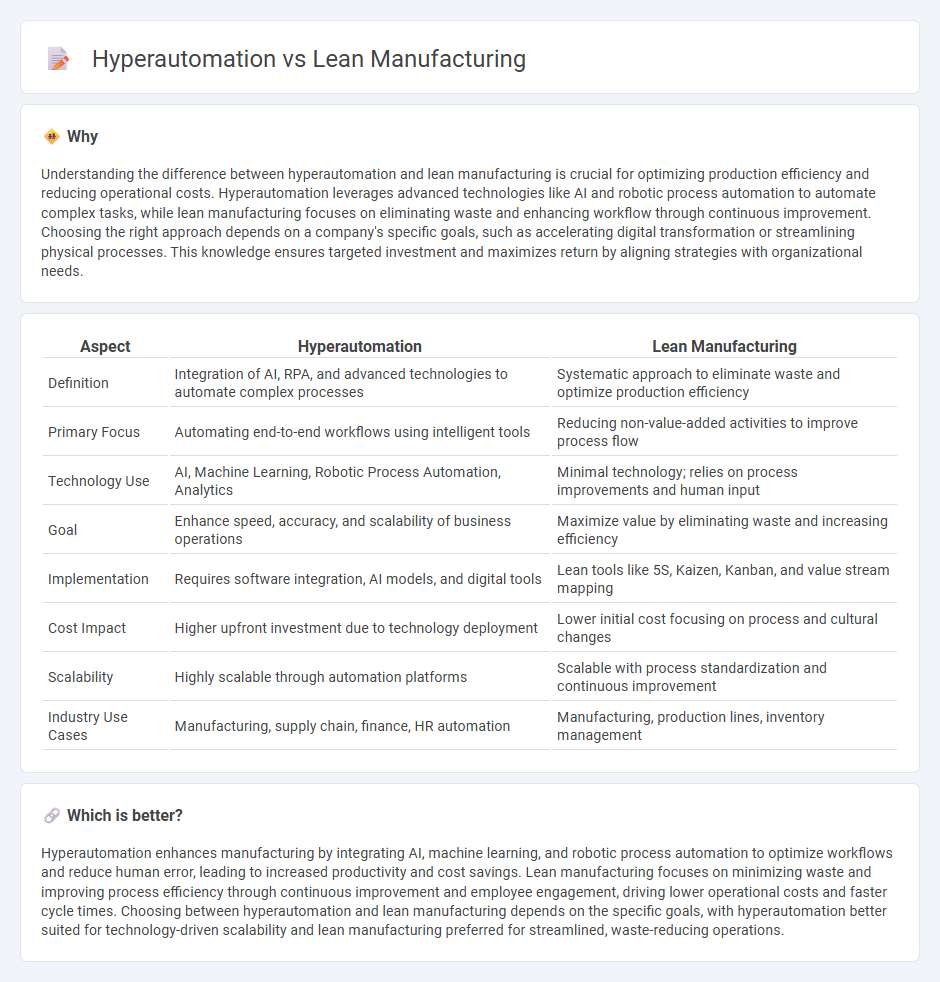
Understanding the difference between hyperautomation and lean manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and reducing operational costs. Hyperautomation leverages advanced technologies like AI and robotic process automation to automate complex tasks, while lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste and enhancing workflow through continuous improvement. Choosing the right approach depends on a company's specific goals, such as accelerating digital transformation or streamlining physical processes. This knowledge ensures targeted investment and maximizes return by aligning strategies with organizational needs.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Hyperautomation | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of AI, RPA, and advanced technologies to automate complex processes | Systematic approach to eliminate waste and optimize production efficiency |
| Primary Focus | Automating end-to-end workflows using intelligent tools | Reducing non-value-added activities to improve process flow |
| Technology Use | AI, Machine Learning, Robotic Process Automation, Analytics | Minimal technology; relies on process improvements and human input |
| Goal | Enhance speed, accuracy, and scalability of business operations | Maximize value by eliminating waste and increasing efficiency |
| Implementation | Requires software integration, AI models, and digital tools | Lean tools like 5S, Kaizen, Kanban, and value stream mapping |
| Cost Impact | Higher upfront investment due to technology deployment | Lower initial cost focusing on process and cultural changes |
| Scalability | Highly scalable through automation platforms | Scalable with process standardization and continuous improvement |
| Industry Use Cases | Manufacturing, supply chain, finance, HR automation | Manufacturing, production lines, inventory management |
Which is better?
Hyperautomation enhances manufacturing by integrating AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation to optimize workflows and reduce human error, leading to increased productivity and cost savings. Lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste and improving process efficiency through continuous improvement and employee engagement, driving lower operational costs and faster cycle times. Choosing between hyperautomation and lean manufacturing depends on the specific goals, with hyperautomation better suited for technology-driven scalability and lean manufacturing preferred for streamlined, waste-reducing operations.
Connection
Hyperautomation integrates advanced technologies like AI, RPA, and IoT to streamline manufacturing processes, while lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste and improving efficiency. Together, they enhance operational performance by automating repetitive tasks, reducing errors, and optimizing workflow in production lines. The synergy of hyperautomation and lean principles drives higher productivity, cost savings, and continuous improvement in manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Source and External Links
Lean manufacturing - Wikipedia - Lean manufacturing is a method focused on reducing production and supplier response times by eliminating non-value-adding activities and wastes, largely based on the Toyota Production System and the just-in-time manufacturing approach.
What is Lean Manufacturing? | Definition from TechTarget - Lean manufacturing is a methodology that minimizes waste while maximizing productivity, based on principles like continuous improvement and widely used beyond manufacturing in industries such as healthcare and software development.
What is Lean Manufacturing and the 5 Principles Used? - TWI - Lean manufacturing emphasizes maximizing productivity and minimizing waste by following five core principles: value, value stream, flow, pull, and perfection, aiming to do more with less while delivering exactly what customers want.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com