Lights out factories operate fully automated production with minimal human intervention, enhancing efficiency and reducing labor costs in manufacturing processes. Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) integrate automated machinery and computer control to adapt quickly to changes in product design and volume, offering versatility in production. Discover how these advanced manufacturing strategies can transform your industrial operations.
Why it is important
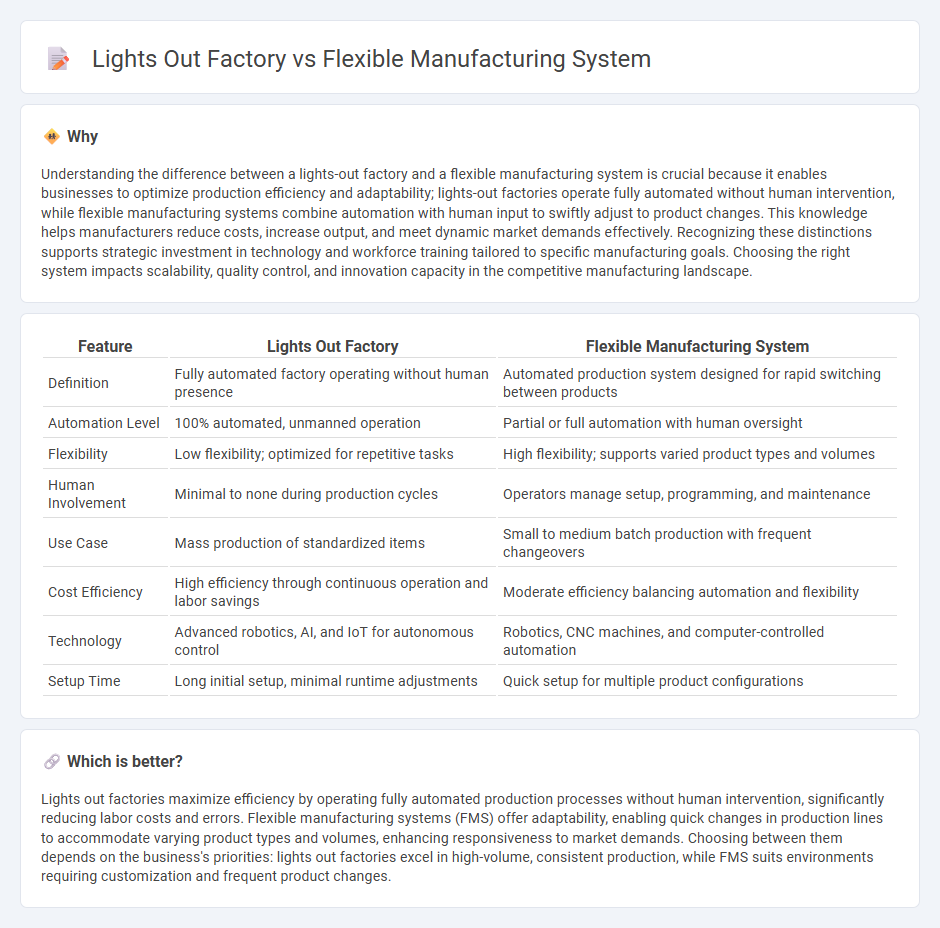
Understanding the difference between a lights-out factory and a flexible manufacturing system is crucial because it enables businesses to optimize production efficiency and adaptability; lights-out factories operate fully automated without human intervention, while flexible manufacturing systems combine automation with human input to swiftly adjust to product changes. This knowledge helps manufacturers reduce costs, increase output, and meet dynamic market demands effectively. Recognizing these distinctions supports strategic investment in technology and workforce training tailored to specific manufacturing goals. Choosing the right system impacts scalability, quality control, and innovation capacity in the competitive manufacturing landscape.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Lights Out Factory | Flexible Manufacturing System |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated factory operating without human presence | Automated production system designed for rapid switching between products |
| Automation Level | 100% automated, unmanned operation | Partial or full automation with human oversight |
| Flexibility | Low flexibility; optimized for repetitive tasks | High flexibility; supports varied product types and volumes |
| Human Involvement | Minimal to none during production cycles | Operators manage setup, programming, and maintenance |
| Use Case | Mass production of standardized items | Small to medium batch production with frequent changeovers |
| Cost Efficiency | High efficiency through continuous operation and labor savings | Moderate efficiency balancing automation and flexibility |
| Technology | Advanced robotics, AI, and IoT for autonomous control | Robotics, CNC machines, and computer-controlled automation |
| Setup Time | Long initial setup, minimal runtime adjustments | Quick setup for multiple product configurations |
Which is better?
Lights out factories maximize efficiency by operating fully automated production processes without human intervention, significantly reducing labor costs and errors. Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) offer adaptability, enabling quick changes in production lines to accommodate varying product types and volumes, enhancing responsiveness to market demands. Choosing between them depends on the business's priorities: lights out factories excel in high-volume, consistent production, while FMS suits environments requiring customization and frequent product changes.
Connection
Lights-out factories rely on automated systems to operate without human intervention, integrating seamlessly with flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) that allow rapid adjustments in production processes. The combination enhances efficiency by enabling continuous, adaptive manufacturing runs optimized by real-time data and robotic automation. This synergy reduces downtime, increases output quality, and supports mass customization in dynamic production environments.
Key Terms
Flexible Manufacturing System:
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) integrate automated machines and computer-controlled processes to adapt quickly to varying production requirements, increasing efficiency and reducing downtime. Unlike lights out factories, which operate fully autonomously without on-site human intervention, FMS combines flexibility with human oversight to manage complex manufacturing tasks. Explore how Flexible Manufacturing Systems drive innovation and optimize production workflows.
Automation
Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) integrate robotic automation with computer-controlled machinery to adapt swiftly to varying product designs, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime compared to traditional methods. Lights-out factories operate with full automation in unmanned environments, utilizing AI-driven robots and IoT sensors for continuous, 24/7 production with minimal human intervention. Discover how advanced automation technologies are revolutionizing manufacturing by exploring in-depth comparisons between FMS and lights-out factory models.
CNC Machines
Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) enable CNC machines to switch between different part programs quickly, optimizing production efficiency and reducing downtime for small to medium batch runs. Lights out factories operate CNC machines autonomously without human intervention, maximizing productivity through continuous, overnight operation and minimizing labor costs. Explore how integrating FMS with lights out strategies can transform CNC machining processes for your manufacturing needs.
Source and External Links
Flexible manufacturing system - Wikipedia - A flexible manufacturing system (FMS) is a manufacturing system designed to react to changes through routing flexibility (ability to change product types and operation sequences) and machine flexibility (ability to use multiple machines for the same task), typically involving automated CNC machines, material handling system, and a central control computer to optimize production of small product sets with advantages like reduced costs, improved productivity, and adaptability.
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) - Autodesk - FMS is a computer-controlled production setup offering routing flexibility (adapting sequence of operations) and machine flexibility (using different machines for same operations), with types including dedicated, sequential, engineered, random, and modular systems tailored to varying industry needs like aerospace and automotive.
Flexible Manufacturing Systems: Types, Examples, & Advantages - FMS enables adaptability to changes in product requirements, reducing production time and resource use by automating operations like machining, assembly, and inspection, thereby supporting production of customized or varied products with less human intervention.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com