Zero Defect Manufacturing focuses on producing flawless products by minimizing defects through stringent quality control and process optimization, ensuring high reliability and customer satisfaction. Additive Manufacturing builds objects layer-by-layer using digital models, enabling complex designs, material efficiency, and faster prototyping compared to traditional subtractive methods. Explore further to understand the unique advantages and applications of these innovative manufacturing approaches.
Why it is important
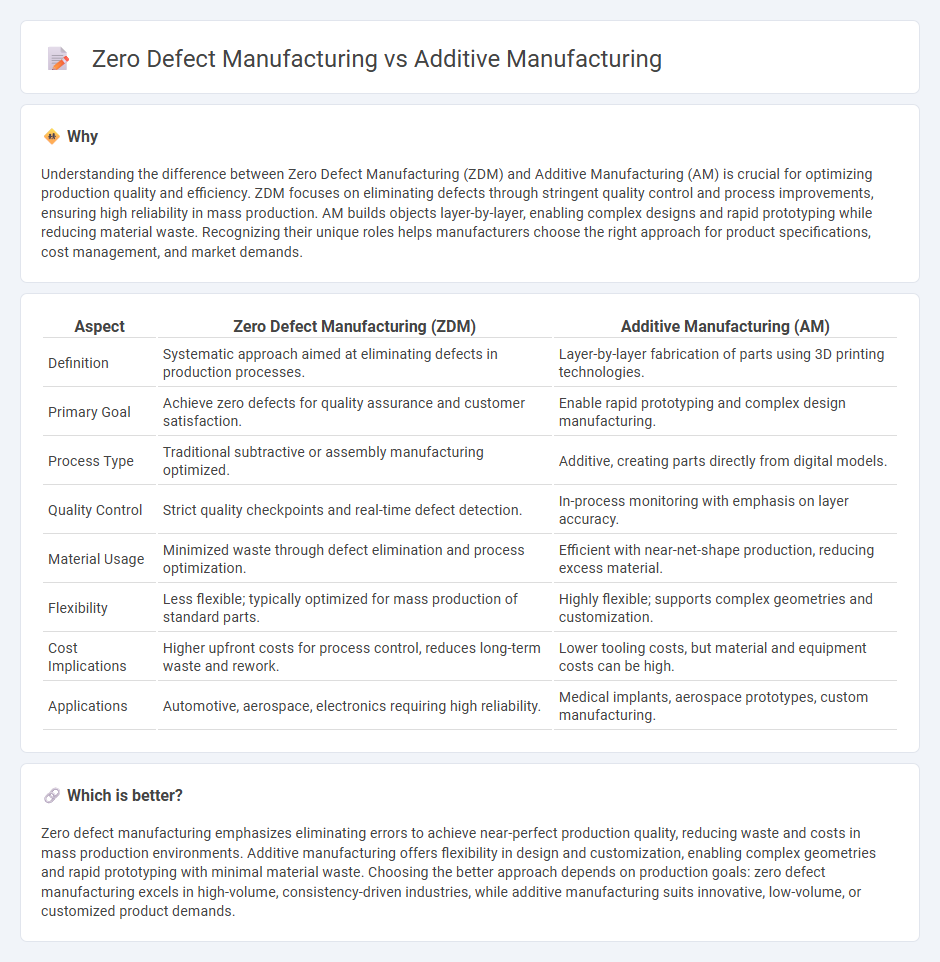
Understanding the difference between Zero Defect Manufacturing (ZDM) and Additive Manufacturing (AM) is crucial for optimizing production quality and efficiency. ZDM focuses on eliminating defects through stringent quality control and process improvements, ensuring high reliability in mass production. AM builds objects layer-by-layer, enabling complex designs and rapid prototyping while reducing material waste. Recognizing their unique roles helps manufacturers choose the right approach for product specifications, cost management, and market demands.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero Defect Manufacturing (ZDM) | Additive Manufacturing (AM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic approach aimed at eliminating defects in production processes. | Layer-by-layer fabrication of parts using 3D printing technologies. |
| Primary Goal | Achieve zero defects for quality assurance and customer satisfaction. | Enable rapid prototyping and complex design manufacturing. |
| Process Type | Traditional subtractive or assembly manufacturing optimized. | Additive, creating parts directly from digital models. |
| Quality Control | Strict quality checkpoints and real-time defect detection. | In-process monitoring with emphasis on layer accuracy. |
| Material Usage | Minimized waste through defect elimination and process optimization. | Efficient with near-net-shape production, reducing excess material. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; typically optimized for mass production of standard parts. | Highly flexible; supports complex geometries and customization. |
| Cost Implications | Higher upfront costs for process control, reduces long-term waste and rework. | Lower tooling costs, but material and equipment costs can be high. |
| Applications | Automotive, aerospace, electronics requiring high reliability. | Medical implants, aerospace prototypes, custom manufacturing. |
Which is better?
Zero defect manufacturing emphasizes eliminating errors to achieve near-perfect production quality, reducing waste and costs in mass production environments. Additive manufacturing offers flexibility in design and customization, enabling complex geometries and rapid prototyping with minimal material waste. Choosing the better approach depends on production goals: zero defect manufacturing excels in high-volume, consistency-driven industries, while additive manufacturing suits innovative, low-volume, or customized product demands.
Connection
Zero Defect Manufacturing (ZDM) and Additive Manufacturing (AM) are connected through their shared emphasis on precision and quality control to minimize defects and reduce waste. AM enables the production of complex components with high accuracy, supporting ZDM's goal of achieving near-perfect products by allowing iterative design adjustments and real-time defect detection. This synergy enhances manufacturing efficiency and product reliability across various industries.
Key Terms
Layer-by-layer fabrication
Additive Manufacturing (AM) achieves complex, layer-by-layer fabrication by precisely depositing material, enabling customization and reducing waste compared to traditional methods. Zero Defect Manufacturing (ZDM) emphasizes eliminating defects at each production stage, ensuring consistent quality and reliability through real-time monitoring and control of fabrication layers. Explore how integrating AM and ZDM can revolutionize precision and efficiency in advanced manufacturing processes.
Real-time quality monitoring
Additive Manufacturing leverages layer-by-layer fabrication techniques, enabling intricate designs but often faces challenges in maintaining consistent quality without defects. Zero Defect Manufacturing emphasizes stringent real-time quality monitoring systems using sensors and AI-driven analytics to detect and correct anomalies during production, ensuring flawless outputs. Explore advanced real-time quality monitoring technologies to fully understand how these approaches optimize manufacturing precision.
Process automation
Additive Manufacturing enhances process automation by enabling layer-by-layer fabrication with minimal human intervention, optimizing both design flexibility and production speed. Zero Defect Manufacturing focuses on process automation through real-time monitoring and advanced control systems to eliminate defects and ensure consistent product quality. Explore how integrating these approaches transforms manufacturing precision and efficiency.
Source and External Links
Additive manufacturing, explained | MIT Sloan - Additive manufacturing is the process of creating an object by building it one layer at a time, typically using 3D printing, allowing direct digital-to-physical production with diverse materials like polymers, metals, and biomaterials.
Additive manufacturing | NIST - Additive manufacturing uses digital designs to fabricate 3D products layer-by-layer, enabling complex shapes with less material waste and is applied in areas such as aerospace and customized biomedical implants.
What Is Additive Manufacturing? | 3D Printing Simulation Software - Additive manufacturing builds 3D objects from digital CAD models by layering materials via 3D printer technologies like powder bed fusion, material extrusion, and photopolymerization, supporting prototyping and production parts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com