Lights out factories operate fully automated production lines with minimal human intervention, enhancing efficiency and reducing labor costs. Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into small, self-contained units to streamline workflow and improve flexibility in production. Discover how these innovative manufacturing approaches can transform your production processes.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between lights out factory and cellular manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and reducing labor costs. Lights out factories operate fully automated systems with minimal human intervention, enabling 24/7 production and enhanced consistency. Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations in a sequence to improve workflow and reduce setup time, increasing flexibility and product quality. Identifying the appropriate manufacturing strategy can significantly impact operational scalability and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
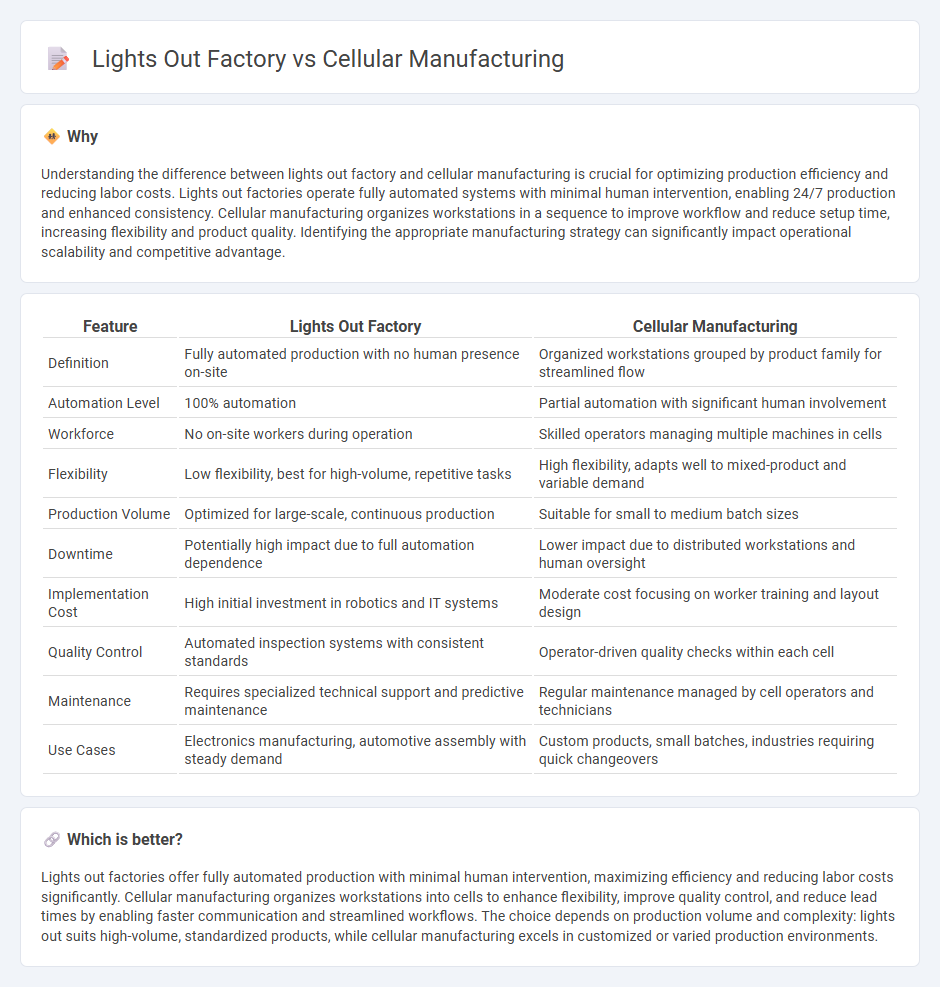
| Feature | Lights Out Factory | Cellular Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated production with no human presence on-site | Organized workstations grouped by product family for streamlined flow |
| Automation Level | 100% automation | Partial automation with significant human involvement |
| Workforce | No on-site workers during operation | Skilled operators managing multiple machines in cells |
| Flexibility | Low flexibility, best for high-volume, repetitive tasks | High flexibility, adapts well to mixed-product and variable demand |
| Production Volume | Optimized for large-scale, continuous production | Suitable for small to medium batch sizes |
| Downtime | Potentially high impact due to full automation dependence | Lower impact due to distributed workstations and human oversight |
| Implementation Cost | High initial investment in robotics and IT systems | Moderate cost focusing on worker training and layout design |
| Quality Control | Automated inspection systems with consistent standards | Operator-driven quality checks within each cell |
| Maintenance | Requires specialized technical support and predictive maintenance | Regular maintenance managed by cell operators and technicians |
| Use Cases | Electronics manufacturing, automotive assembly with steady demand | Custom products, small batches, industries requiring quick changeovers |
Which is better?
Lights out factories offer fully automated production with minimal human intervention, maximizing efficiency and reducing labor costs significantly. Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into cells to enhance flexibility, improve quality control, and reduce lead times by enabling faster communication and streamlined workflows. The choice depends on production volume and complexity: lights out suits high-volume, standardized products, while cellular manufacturing excels in customized or varied production environments.
Connection
Lights out factories utilize cellular manufacturing to enable fully automated production with minimal human intervention, optimizing workflow and reducing downtime. The modular layout of cellular manufacturing supports continuous, autonomous operations essential for lights out processes, enhancing productivity and efficiency. Integrating these systems allows seamless adaptation to demand fluctuations while maintaining high-quality output in manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
**Cellular Manufacturing:**
Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into small, self-contained units called cells, each dedicated to producing a specific product family, enhancing efficiency and reducing waste through streamlined workflows. This system relies heavily on skilled workers performing multiple tasks within the cell to maintain flexibility and quick responses to production changes. Explore how cellular manufacturing drives lean operations and improves productivity by learning more about its principles and benefits.
Work Cells
Work cells in cellular manufacturing are designed to group related machines and operators into compact units to optimize workflow and reduce material handling, emphasizing human intervention and flexibility. Lights out factories rely on fully automated, unmanned work cells where machines operate continuously without human presence, maximizing efficiency through robotics and advanced control systems. Explore the key differences between these approaches to enhance production strategy insights.
Group Technology
Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into cells to enhance efficiency and reduce waste by grouping similar processes based on Group Technology principles. Lights out factories employ full automation and robotics to enable continuous, unmanned production, which can complement cellular manufacturing by integrating automated cells for higher productivity. Explore how combining Group Technology with lights out automation can revolutionize manufacturing workflows.
Source and External Links
Cellular manufacturing - Wikipedia - Cellular manufacturing is a lean production system using multiple machines arranged into cells, each performing a specific task, aimed at maximizing flow, flexibility, reducing waste, and improving productivity by grouping processes to create specific outputs efficiently.
Cellular Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide - Deskera - This method combines production line processes into a single manufacturing cell, optimizing layout, resources, and workflow through designing production cells, assigning resources, and monitoring performance for efficiency.
What Is Cellular Manufacturing? - MRPeasy - Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into self-sufficient cells with cross-trained workers, improving communication, reducing lead times, waste, and space needs by optimizing continuous product flow in various cellular layouts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com