Lights-out manufacturing leverages fully automated systems operating without human intervention, maximizing productivity and reducing labor costs, while lean manufacturing emphasizes minimizing waste and optimizing workflows to improve efficiency and quality. Both methodologies drive operational excellence but focus on different aspects: automation intensity versus process improvement. Discover how integrating these strategies can revolutionize your production line.
Why it is important
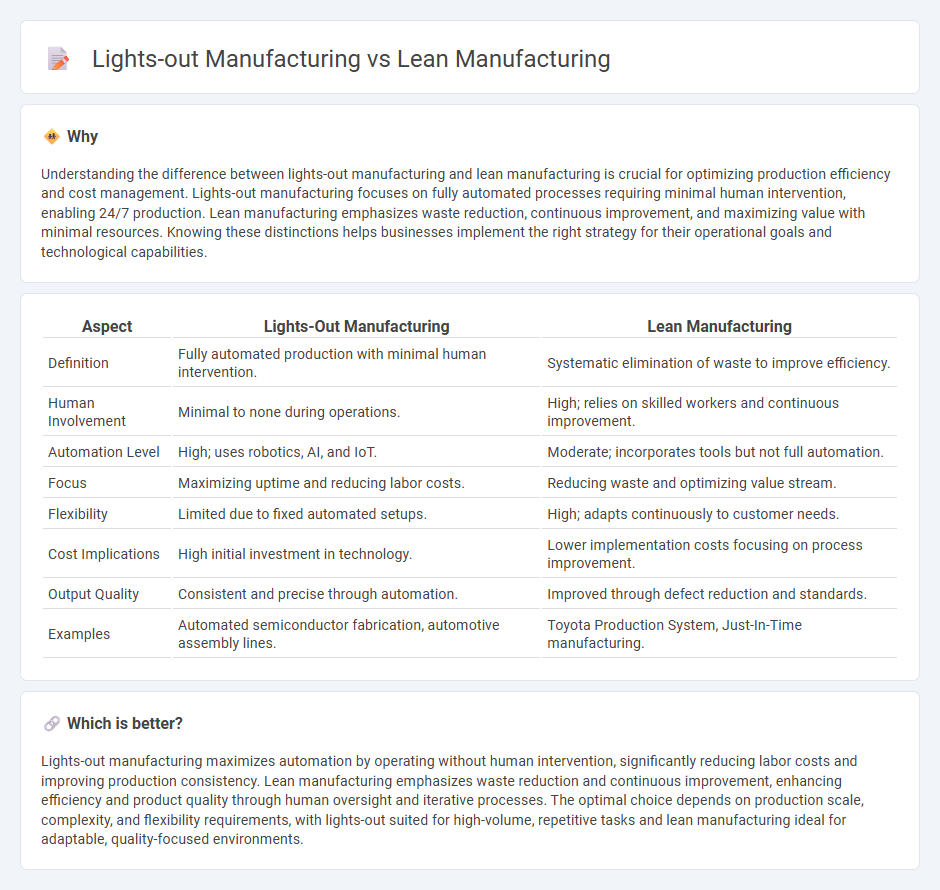
Understanding the difference between lights-out manufacturing and lean manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and cost management. Lights-out manufacturing focuses on fully automated processes requiring minimal human intervention, enabling 24/7 production. Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction, continuous improvement, and maximizing value with minimal resources. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses implement the right strategy for their operational goals and technological capabilities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Lights-Out Manufacturing | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated production with minimal human intervention. | Systematic elimination of waste to improve efficiency. |
| Human Involvement | Minimal to none during operations. | High; relies on skilled workers and continuous improvement. |
| Automation Level | High; uses robotics, AI, and IoT. | Moderate; incorporates tools but not full automation. |
| Focus | Maximizing uptime and reducing labor costs. | Reducing waste and optimizing value stream. |
| Flexibility | Limited due to fixed automated setups. | High; adapts continuously to customer needs. |
| Cost Implications | High initial investment in technology. | Lower implementation costs focusing on process improvement. |
| Output Quality | Consistent and precise through automation. | Improved through defect reduction and standards. |
| Examples | Automated semiconductor fabrication, automotive assembly lines. | Toyota Production System, Just-In-Time manufacturing. |
Which is better?
Lights-out manufacturing maximizes automation by operating without human intervention, significantly reducing labor costs and improving production consistency. Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction and continuous improvement, enhancing efficiency and product quality through human oversight and iterative processes. The optimal choice depends on production scale, complexity, and flexibility requirements, with lights-out suited for high-volume, repetitive tasks and lean manufacturing ideal for adaptable, quality-focused environments.
Connection
Lights-out manufacturing leverages automated processes and robotics to operate production facilities without human intervention, significantly reducing labor costs and increasing efficiency. Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste elimination, continuous improvement, and streamlined workflows to optimize productivity and quality. Integrating lights-out manufacturing with lean principles enhances operational efficiency by minimizing downtime, reducing defects, and maximizing resource utilization.
Key Terms
**Lean Manufacturing:**
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction, continuous improvement, and just-in-time production to enhance efficiency and product quality. It relies on human involvement and process optimization to minimize defects, inventory, and lead times in manufacturing operations. Explore detailed strategies and benefits of lean manufacturing to transform your production system.
Waste Reduction
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction by eliminating non-value-added activities through continuous improvement and employee involvement, targeting defects, overproduction, and excess inventory. Lights-out manufacturing reduces waste by automating production processes to operate without human intervention, minimizing downtime, and improving energy efficiency. Discover how integrating both approaches can maximize waste reduction and operational productivity.
Continuous Improvement (Kaizen)
Lean manufacturing emphasizes continuous improvement (Kaizen) by systematically eliminating waste and optimizing processes to enhance efficiency and quality. Lights-out manufacturing leverages automation to run production with minimal human intervention, enabling continuous operation and real-time process adjustments based on data analytics. Explore the key differences and benefits of integrating Kaizen principles within these manufacturing strategies for transformative productivity gains.
Source and External Links
Lean manufacturing - Wikipedia - Lean manufacturing is a production method focused on reducing waste and shortening production times through continuous improvement and just-in-time inventory management, originating from the Toyota Production System.
What is Lean Manufacturing? | Definition from TechTarget - Lean manufacturing is a methodology that minimizes waste in manufacturing systems while maximizing productivity, built on principles like Kaizen and widely adopted by companies across various industries.
What is Lean Manufacturing and the 5 Principles Used? - TWI - Lean manufacturing streamlines processes by following five core principles--value, value stream, flow, pull, and perfection--to eliminate waste and deliver what customers want.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com