Flexible manufacturing systems enable rapid adaptation to product variations and customization through automated equipment and robotic integration, optimizing production efficiency for small to medium batch sizes. Mass production focuses on high-volume output by utilizing dedicated assembly lines and standardized processes, achieving economies of scale and cost reduction for uniform products. Explore how these manufacturing approaches impact industry competitiveness and operational agility.
Why it is important
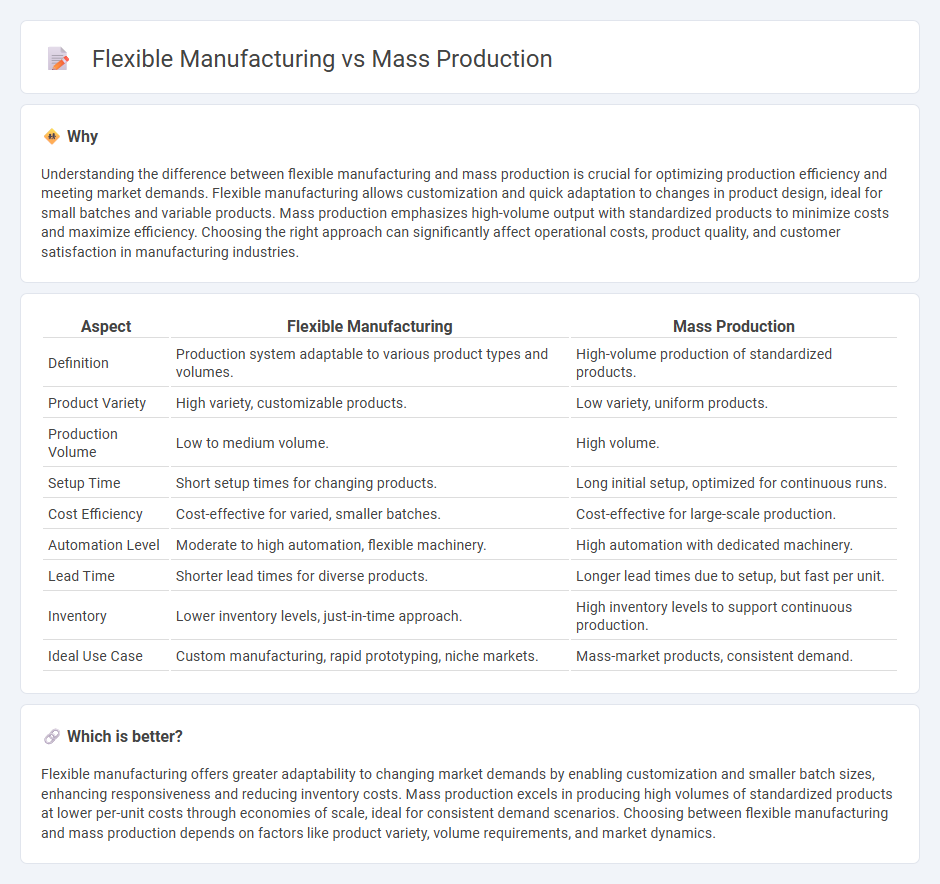
Understanding the difference between flexible manufacturing and mass production is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and meeting market demands. Flexible manufacturing allows customization and quick adaptation to changes in product design, ideal for small batches and variable products. Mass production emphasizes high-volume output with standardized products to minimize costs and maximize efficiency. Choosing the right approach can significantly affect operational costs, product quality, and customer satisfaction in manufacturing industries.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Flexible Manufacturing | Mass Production |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Production system adaptable to various product types and volumes. | High-volume production of standardized products. |
| Product Variety | High variety, customizable products. | Low variety, uniform products. |
| Production Volume | Low to medium volume. | High volume. |
| Setup Time | Short setup times for changing products. | Long initial setup, optimized for continuous runs. |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for varied, smaller batches. | Cost-effective for large-scale production. |
| Automation Level | Moderate to high automation, flexible machinery. | High automation with dedicated machinery. |
| Lead Time | Shorter lead times for diverse products. | Longer lead times due to setup, but fast per unit. |
| Inventory | Lower inventory levels, just-in-time approach. | High inventory levels to support continuous production. |
| Ideal Use Case | Custom manufacturing, rapid prototyping, niche markets. | Mass-market products, consistent demand. |
Which is better?
Flexible manufacturing offers greater adaptability to changing market demands by enabling customization and smaller batch sizes, enhancing responsiveness and reducing inventory costs. Mass production excels in producing high volumes of standardized products at lower per-unit costs through economies of scale, ideal for consistent demand scenarios. Choosing between flexible manufacturing and mass production depends on factors like product variety, volume requirements, and market dynamics.
Connection
Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) enhance mass production by integrating automation and adaptable machinery, allowing for rapid changes in product designs and volumes without significant downtime. This connection optimizes resource use and minimizes waste, enabling manufacturers to meet diverse market demands efficiently while maintaining the high output rates characteristic of mass production. The synergy between flexible manufacturing and mass production results in increased productivity, reduced lead times, and improved competitiveness in global markets.
Key Terms
Scalability
Mass production excels in scalability by enabling high-volume output with consistent product quality through standardized processes and automation. Flexible manufacturing, however, provides scalable solutions by allowing rapid adjustments to production lines and customization without significant downtime. Explore how these approaches impact your scalability objectives and operational efficiency.
Customization
Mass production emphasizes standardized products with limited customization to achieve economies of scale and reduce costs. Flexible manufacturing systems enable high customization by allowing quick adjustments in production processes to meet diverse customer demands. Explore how flexible manufacturing transforms product personalization and market responsiveness.
Automation
Mass production leverages automated assembly lines to achieve high-volume, consistent output with minimal human intervention, optimizing efficiency and reducing unit costs. Flexible manufacturing systems use automation to quickly adapt production lines for different products, enhancing responsiveness to market changes and customization needs. Explore how automation technologies transform manufacturing strategies by balancing scale and agility.
Source and External Links
What Is Mass Production? A Comprehensive Guide - MRPeasy - Mass production is a manufacturing process designed to produce large quantities of standardized products using specialization, mechanization, and economies of scale for high efficiency and consistency, typically involving steps like design, procurement, planning, and division of labor.
Mass production - Wikipedia - Mass production is the high-volume production of standardized products through assembly line techniques, involving capital- and energy-intensive automation to decrease per-unit costs and increase supply rapidly.
Mass Production - Overview, How It Works, Advantages - Mass production uses automation and assembly lines to manufacture large quantities of the same standardized product over prolonged periods, focusing on labor division and advanced technology to lower costs and enhance efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com