Condition-based monitoring utilizes real-time data from sensors and IoT devices to predict equipment failures and schedule maintenance proactively, enhancing operational efficiency. Corrective maintenance addresses repairs only after equipment breakdowns occur, often leading to unplanned downtime and higher costs. Explore how these approaches impact manufacturing productivity and cost management.
Why it is important
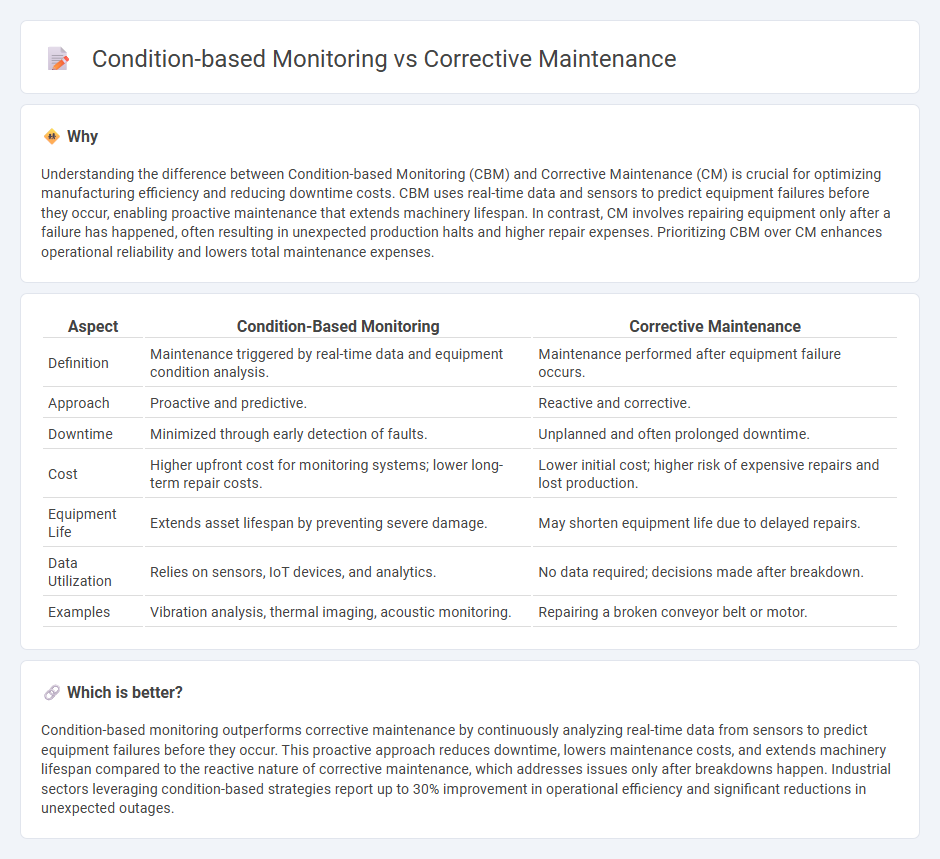
Understanding the difference between Condition-based Monitoring (CBM) and Corrective Maintenance (CM) is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and reducing downtime costs. CBM uses real-time data and sensors to predict equipment failures before they occur, enabling proactive maintenance that extends machinery lifespan. In contrast, CM involves repairing equipment only after a failure has happened, often resulting in unexpected production halts and higher repair expenses. Prioritizing CBM over CM enhances operational reliability and lowers total maintenance expenses.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Condition-Based Monitoring | Corrective Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintenance triggered by real-time data and equipment condition analysis. | Maintenance performed after equipment failure occurs. |
| Approach | Proactive and predictive. | Reactive and corrective. |
| Downtime | Minimized through early detection of faults. | Unplanned and often prolonged downtime. |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost for monitoring systems; lower long-term repair costs. | Lower initial cost; higher risk of expensive repairs and lost production. |
| Equipment Life | Extends asset lifespan by preventing severe damage. | May shorten equipment life due to delayed repairs. |
| Data Utilization | Relies on sensors, IoT devices, and analytics. | No data required; decisions made after breakdown. |
| Examples | Vibration analysis, thermal imaging, acoustic monitoring. | Repairing a broken conveyor belt or motor. |
Which is better?
Condition-based monitoring outperforms corrective maintenance by continuously analyzing real-time data from sensors to predict equipment failures before they occur. This proactive approach reduces downtime, lowers maintenance costs, and extends machinery lifespan compared to the reactive nature of corrective maintenance, which addresses issues only after breakdowns happen. Industrial sectors leveraging condition-based strategies report up to 30% improvement in operational efficiency and significant reductions in unexpected outages.
Connection
Condition-based monitoring enhances manufacturing efficiency by continuously tracking equipment performance using sensors and real-time data analytics. This data-driven approach enables timely identification of deviations and potential failures, directly informing corrective maintenance actions to address specific issues before catastrophic breakdowns occur. Integrating condition-based monitoring with corrective maintenance reduces downtime, extends machinery lifespan, and optimizes resource allocation within manufacturing facilities.
Key Terms
Breakdown
Breakdown in corrective maintenance occurs after equipment failure, leading to unplanned downtime and repair costs. Condition-based monitoring uses real-time data to detect early signs of wear or failure, preventing breakdowns through timely interventions. Discover how condition-based monitoring enhances operational efficiency by minimizing unexpected breakdowns.
Real-time sensors
Corrective maintenance relies on repairing equipment after failure, often leading to unexpected downtime and higher costs. Condition-based monitoring uses real-time sensors to continuously track equipment health, enabling predictive interventions that reduce failures and optimize performance. Discover how integrating sensor technology can transform maintenance strategies and improve operational efficiency.
Failure prediction
Corrective maintenance addresses equipment failures only after they occur, leading to unexpected downtime and higher repair costs, while condition-based monitoring leverages real-time data and sensor analytics to predict failures before they happen, optimizing operational efficiency and reducing maintenance expenses. Failure prediction techniques in condition-based monitoring utilize vibration analysis, thermography, and machine learning algorithms to detect early signs of wear and potential breakdowns. Explore advanced predictive maintenance strategies and tools to enhance reliability and minimize disruptions.
Source and External Links
What is Corrective Maintenance? Examples, Best Practices - Corrective maintenance is performed to return malfunctioning hardware or equipment to proper working order, often reactively after a failure, but sometimes proactively if issues are detected early.
Corrective maintenance - Corrective maintenance involves identifying, isolating, and rectifying a fault to restore equipment or systems to operational condition, and can be immediate or deferred depending on urgency.
What is Corrective Maintenance? Guide and Best Practices - Corrective maintenance repairs or restores equipment after a failure or defect is identified, differing from preventive maintenance by addressing issues as they arise rather than preventing them.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com