Microfactories focus on compact, flexible production units designed to optimize space and reduce lead times, often utilizing advanced automation and digital technologies. Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into cells, grouping machines and operators to enhance workflow efficiency and minimize material handling. Explore the advantages and applications of microfactories versus cellular manufacturing for modern production strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between microfactory and cellular manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and scalability. Microfactories focus on small, highly automated facilities designed for localized production and rapid customization. Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into cells for producing families of similar products, enhancing workflow and reducing waste. Selecting the appropriate model depends on product complexity, volume, and flexibility requirements in manufacturing operations.
Comparison Table
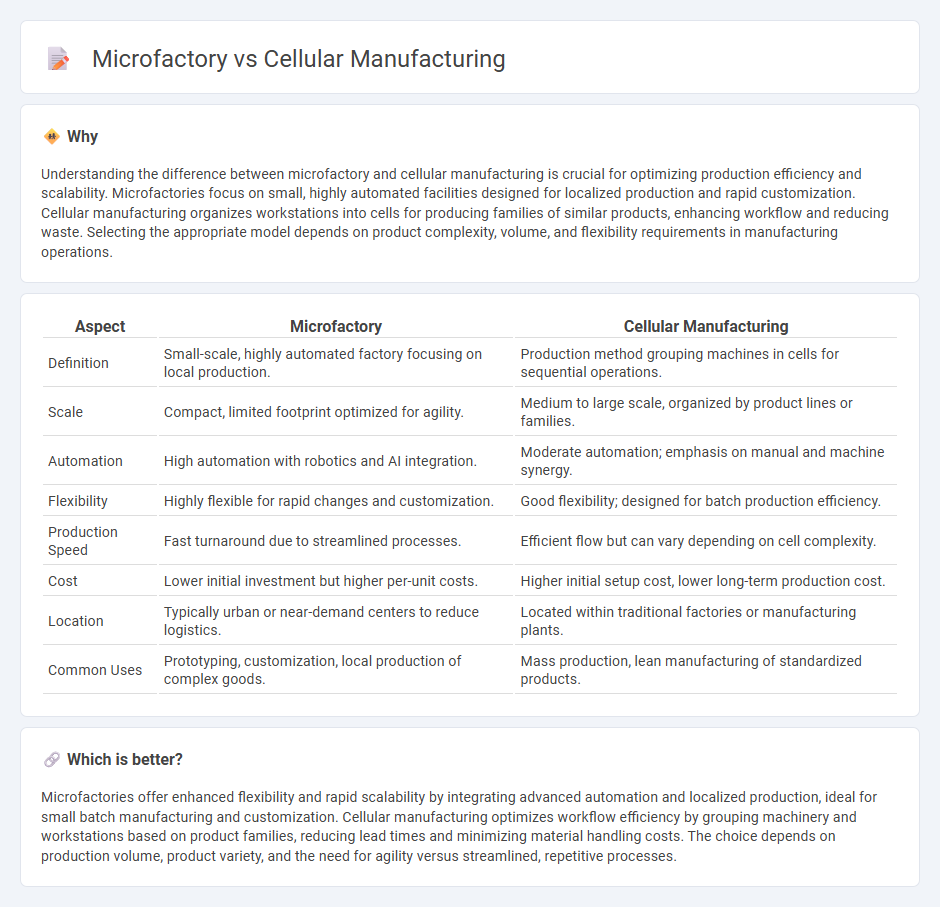
| Aspect | Microfactory | Cellular Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small-scale, highly automated factory focusing on local production. | Production method grouping machines in cells for sequential operations. |
| Scale | Compact, limited footprint optimized for agility. | Medium to large scale, organized by product lines or families. |
| Automation | High automation with robotics and AI integration. | Moderate automation; emphasis on manual and machine synergy. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible for rapid changes and customization. | Good flexibility; designed for batch production efficiency. |
| Production Speed | Fast turnaround due to streamlined processes. | Efficient flow but can vary depending on cell complexity. |
| Cost | Lower initial investment but higher per-unit costs. | Higher initial setup cost, lower long-term production cost. |
| Location | Typically urban or near-demand centers to reduce logistics. | Located within traditional factories or manufacturing plants. |
| Common Uses | Prototyping, customization, local production of complex goods. | Mass production, lean manufacturing of standardized products. |
Which is better?
Microfactories offer enhanced flexibility and rapid scalability by integrating advanced automation and localized production, ideal for small batch manufacturing and customization. Cellular manufacturing optimizes workflow efficiency by grouping machinery and workstations based on product families, reducing lead times and minimizing material handling costs. The choice depends on production volume, product variety, and the need for agility versus streamlined, repetitive processes.
Connection
Microfactories utilize cellular manufacturing principles by organizing production into small, flexible units that optimize workflow and decrease lead times. Cellular manufacturing enhances microfactory efficiency through specialized work cells that reduce waste and improve quality control. Together, these approaches streamline manufacturing processes, increase adaptability, and lower operational costs.
Key Terms
Cellular Manufacturing:
Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into small, self-contained units called cells, enhancing efficiency by minimizing movement and reducing production time for specific product families. It emphasizes workflow optimization, lean production, and flexibility to quickly adapt to changes in demand or product design. Discover how cellular manufacturing transforms production processes and improves operational performance in detail.
Work Cells
Work cells in cellular manufacturing consist of small, organized groups of machines and operators designed for efficient, continuous production of specific product families, minimizing waste and lead time. Microfactories incorporate work cells but extend flexibility through modular, reconfigurable layouts and advanced automation to adapt quickly to varying product demands and smaller batch sizes. Explore the benefits and applications of these innovative production strategies to enhance manufacturing efficiency and responsiveness.
Flow Efficiency
Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into compact, self-contained units to streamline production flow and minimize waste, enhancing flow efficiency through reduced transportation and waiting times. Microfactories leverage advanced automation and modular design to create highly flexible production environments, allowing rapid scaling and adaptation while maintaining smooth material and information flow. Explore the differences in flow efficiency between cellular manufacturing and microfactories to optimize your production strategy.
Source and External Links
Cellular Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide - Deskera - Cellular manufacturing is a production system that combines multiple processes into a single manufacturing cell, designed through assessing the production environment, creating process flow charts, assigning resources, and continuously monitoring for efficiency.
Cellular manufacturing - Wikipedia - Cellular manufacturing arranges multiple machines into production cells designed to complete specific tasks, enabling faster production, flexibility, waste reduction, and improved communication, often using a U-shaped layout for efficiency.
What Is Cellular Manufacturing? - MRPeasy - Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations and equipment into self-sufficient production cells where workers are cross-trained, improving communication, reducing lead times, minimizing wastes and space requirements, and used in industries like automotive and electronics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com