Dark factories utilize automation and robotics to operate with minimal human intervention, aiming to reduce labor costs and increase efficiency. Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction, continuous improvement, and maximizing value through streamlined processes and employee involvement. Discover more about how these distinct approaches shape the future of manufacturing efficiency.
Why it is important
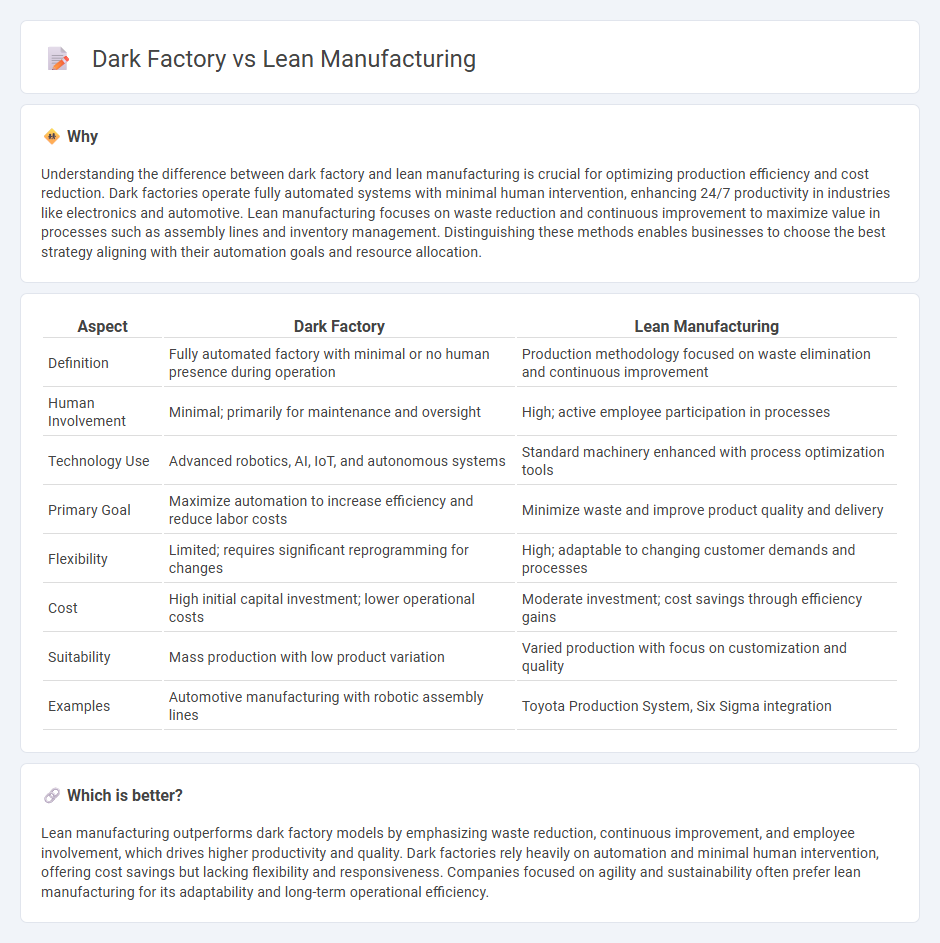
Understanding the difference between dark factory and lean manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and cost reduction. Dark factories operate fully automated systems with minimal human intervention, enhancing 24/7 productivity in industries like electronics and automotive. Lean manufacturing focuses on waste reduction and continuous improvement to maximize value in processes such as assembly lines and inventory management. Distinguishing these methods enables businesses to choose the best strategy aligning with their automation goals and resource allocation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Factory | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated factory with minimal or no human presence during operation | Production methodology focused on waste elimination and continuous improvement |
| Human Involvement | Minimal; primarily for maintenance and oversight | High; active employee participation in processes |
| Technology Use | Advanced robotics, AI, IoT, and autonomous systems | Standard machinery enhanced with process optimization tools |
| Primary Goal | Maximize automation to increase efficiency and reduce labor costs | Minimize waste and improve product quality and delivery |
| Flexibility | Limited; requires significant reprogramming for changes | High; adaptable to changing customer demands and processes |
| Cost | High initial capital investment; lower operational costs | Moderate investment; cost savings through efficiency gains |
| Suitability | Mass production with low product variation | Varied production with focus on customization and quality |
| Examples | Automotive manufacturing with robotic assembly lines | Toyota Production System, Six Sigma integration |
Which is better?
Lean manufacturing outperforms dark factory models by emphasizing waste reduction, continuous improvement, and employee involvement, which drives higher productivity and quality. Dark factories rely heavily on automation and minimal human intervention, offering cost savings but lacking flexibility and responsiveness. Companies focused on agility and sustainability often prefer lean manufacturing for its adaptability and long-term operational efficiency.
Connection
Dark factories utilize automation and robotics to operate with minimal human intervention, aligning closely with lean manufacturing principles that focus on waste reduction and efficiency improvement. By integrating advanced sensors, machine learning, and real-time data analytics, dark factories optimize production flow and minimize downtime, enhancing lean manufacturing's goal of continuous process improvement. This synergy leads to higher productivity, lower operational costs, and improved product quality in modern manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Lean Manufacturing:
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction, continuous improvement, and efficient resource utilization to enhance productivity and quality in production processes. It relies heavily on human skills, standardized workflows, and just-in-time inventory management to minimize costs and improve customer value. Explore the principles and benefits of lean manufacturing to optimize your industrial operations.
Waste Reduction
Lean manufacturing emphasizes systematic waste reduction by identifying and eliminating non-value-added activities, improving process efficiency through techniques like Just-In-Time (JIT) and Kaizen. In contrast, a dark factory leverages automation and robotics to minimize human error and downtime, inherently reducing waste in production cycles. Explore how integrating these approaches can revolutionize your waste reduction strategy.
Continuous Improvement
Lean manufacturing emphasizes continuous improvement by systematically eliminating waste and enhancing processes to boost efficiency and quality. Dark factories leverage automation and robotics to maintain consistent operations without human intervention, allowing ongoing production and iterative improvements through data-driven insights. Explore how integrating continuous improvement strategies in both systems can revolutionize manufacturing performance.
Source and External Links
Understanding a New Manufacturing System - Lean manufacturing is a system that emphasizes worker participation, continuous improvement, and minimal inventory to quickly identify and correct quality issues, contrasting with traditional mass production by prioritizing flexibility and quality control over large stockpiles.
Lean manufacturing - Lean manufacturing aims to reduce waste and inefficiency in production by focusing on just-in-time delivery, continuous improvement, and eliminating non-value-added activities, originally developed through the Toyota Production System.
What is Lean Manufacturing? - Lean manufacturing is a methodology designed to minimize waste and maximize productivity by ensuring every step adds value for the customer, with principles such as Kaizen (continuous improvement) widely applied across industries beyond manufacturing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com