Cobotics enhances manufacturing by enabling collaborative robots to work safely alongside human operators, improving precision and flexibility on the production line. Autonomous Guided Vehicles (AGVs) optimize factory logistics through automated material transport, reducing manual labor and increasing efficiency in warehouse workflows. Explore how cobotics and AGVs transform modern manufacturing environments.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between cobotics and autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes by leveraging the unique strengths of human-robot collaboration versus fully automated transport. Cobotics enhance flexibility and precision in tasks requiring human interaction and complex manipulation, while AGVs improve material handling efficiency through autonomous navigation and delivery within facilities. Selecting the appropriate technology directly impacts productivity, safety standards, and cost-effectiveness in manufacturing operations. Precise deployment of cobotics and AGVs drives innovation and competitiveness in the Industry 4.0 landscape.
Comparison Table
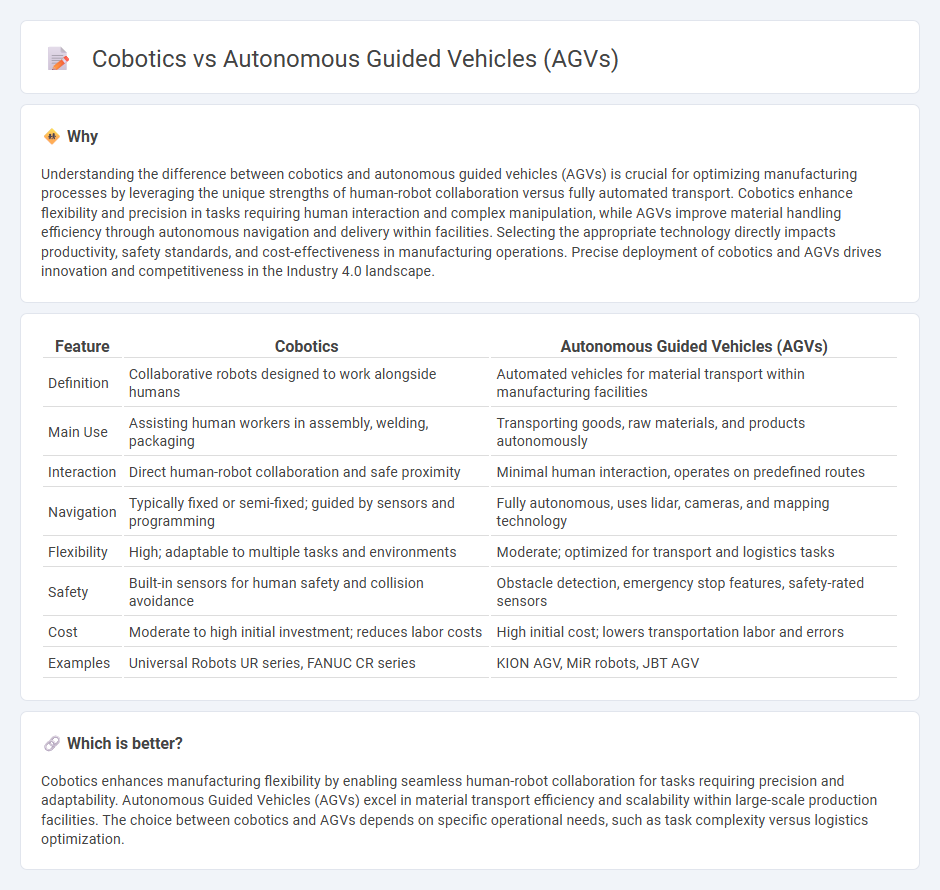
| Feature | Cobotics | Autonomous Guided Vehicles (AGVs) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaborative robots designed to work alongside humans | Automated vehicles for material transport within manufacturing facilities |
| Main Use | Assisting human workers in assembly, welding, packaging | Transporting goods, raw materials, and products autonomously |
| Interaction | Direct human-robot collaboration and safe proximity | Minimal human interaction, operates on predefined routes |
| Navigation | Typically fixed or semi-fixed; guided by sensors and programming | Fully autonomous, uses lidar, cameras, and mapping technology |
| Flexibility | High; adaptable to multiple tasks and environments | Moderate; optimized for transport and logistics tasks |
| Safety | Built-in sensors for human safety and collision avoidance | Obstacle detection, emergency stop features, safety-rated sensors |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment; reduces labor costs | High initial cost; lowers transportation labor and errors |
| Examples | Universal Robots UR series, FANUC CR series | KION AGV, MiR robots, JBT AGV |
Which is better?
Cobotics enhances manufacturing flexibility by enabling seamless human-robot collaboration for tasks requiring precision and adaptability. Autonomous Guided Vehicles (AGVs) excel in material transport efficiency and scalability within large-scale production facilities. The choice between cobotics and AGVs depends on specific operational needs, such as task complexity versus logistics optimization.
Connection
Cobotics and autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) are connected through their role in enhancing automation and efficiency in manufacturing environments. Cobots collaborate with human workers for tasks requiring precision and adaptability, while AGVs autonomously transport materials and products across factory floors. Integration of cobotics with AGVs enables synchronized workflow, reducing downtime and increasing productivity in smart manufacturing systems.
Key Terms
Navigation
Autonomous Guided Vehicles (AGVs) leverage predefined paths using sensors and mapping technologies like LiDAR and vision systems for precise navigation in industrial environments. Cobotics emphasizes collaborative robots designed to interact safely with human workers, often utilizing advanced sensors and adaptive navigation algorithms to maneuver dynamically in shared spaces. Explore how AGVs and cobotics revolutionize navigation strategies in automation by learning more about their distinct technological innovations.
Human-robot collaboration
Autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) navigate industrial environments independently to transport materials, reducing human labor in repetitive and hazardous tasks. Cobotics, on the other hand, emphasizes human-robot collaboration where robots assist workers by enhancing precision and safety without replacing human roles entirely. Explore how integrating AGVs and cobotics can optimize productivity and workplace synergy in modern manufacturing.
Flexibility
Autonomous Guided Vehicles (AGVs) offer consistent, pre-programmed paths suited for repetitive tasks, ensuring operational efficiency but limited adaptability. Cobotics involves collaborative robots designed to work alongside humans, providing enhanced flexibility through real-time responsiveness and customizable interactions for diverse applications. Explore how integrating AGVs and cobotics can optimize your production flexibility and efficiency.
Source and External Links
What Are Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)? - Spectra by MHI - AGVs are autonomous, driverless vehicles that transport goods in warehouses, factories, and hospitals, helping address labor shortages by automating repetitive material handling tasks.
Fundamentals of Automated Guided Vehicles - AGVs are self-guided robotic vehicles designed to autonomously move materials in industrial environments, typically following fixed routes using guidance systems like magnetic strips or optical lines, while AGV systems manage multiple vehicles within a facility.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGV) | Meaning, Types & Use - AGVs operate in controlled environments, following predefined paths using technologies such as magnetic tape, wires, or laser navigation, and are equipped with sensors for obstacle detection and safety.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com