Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time feedback and data analytics to continuously optimize production processes, reducing waste and enhancing product quality. Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating non-value-added activities by streamlining workflows and minimizing inventory to achieve efficient resource utilization. Explore detailed comparisons of closed-loop and lean manufacturing principles to identify the best fit for your operational goals.
Why it is important
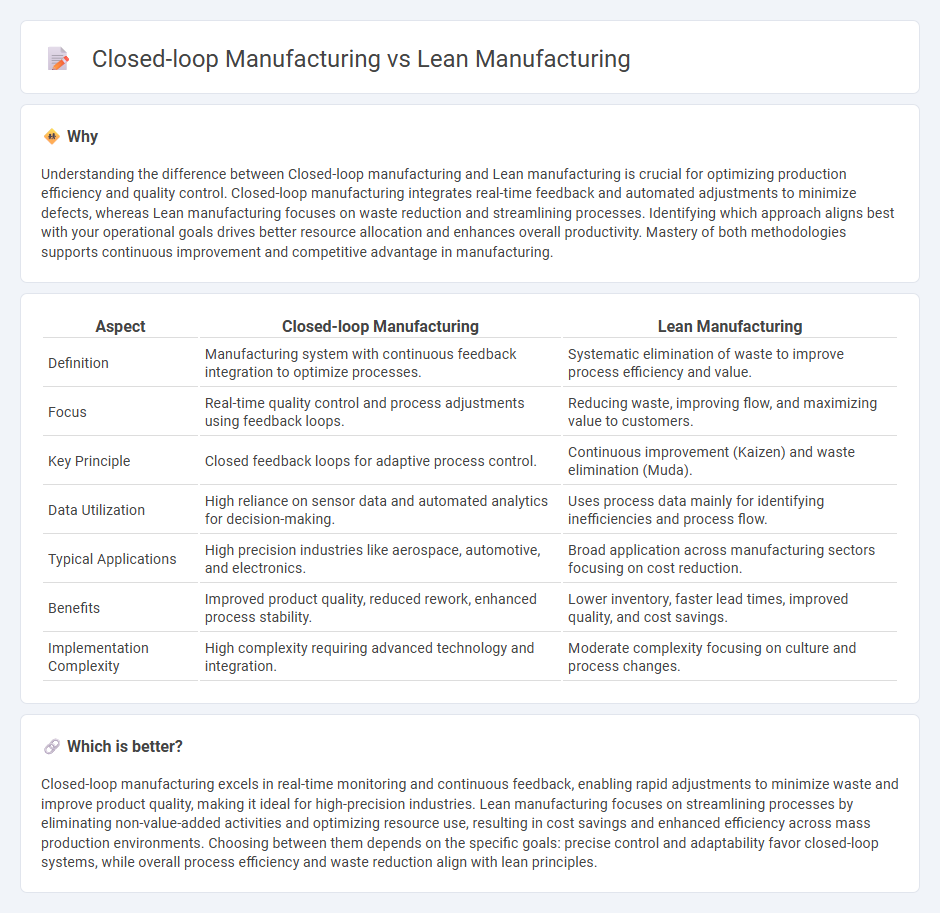
Understanding the difference between Closed-loop manufacturing and Lean manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and quality control. Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time feedback and automated adjustments to minimize defects, whereas Lean manufacturing focuses on waste reduction and streamlining processes. Identifying which approach aligns best with your operational goals drives better resource allocation and enhances overall productivity. Mastery of both methodologies supports continuous improvement and competitive advantage in manufacturing.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Closed-loop Manufacturing | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturing system with continuous feedback integration to optimize processes. | Systematic elimination of waste to improve process efficiency and value. |
| Focus | Real-time quality control and process adjustments using feedback loops. | Reducing waste, improving flow, and maximizing value to customers. |
| Key Principle | Closed feedback loops for adaptive process control. | Continuous improvement (Kaizen) and waste elimination (Muda). |
| Data Utilization | High reliance on sensor data and automated analytics for decision-making. | Uses process data mainly for identifying inefficiencies and process flow. |
| Typical Applications | High precision industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics. | Broad application across manufacturing sectors focusing on cost reduction. |
| Benefits | Improved product quality, reduced rework, enhanced process stability. | Lower inventory, faster lead times, improved quality, and cost savings. |
| Implementation Complexity | High complexity requiring advanced technology and integration. | Moderate complexity focusing on culture and process changes. |
Which is better?
Closed-loop manufacturing excels in real-time monitoring and continuous feedback, enabling rapid adjustments to minimize waste and improve product quality, making it ideal for high-precision industries. Lean manufacturing focuses on streamlining processes by eliminating non-value-added activities and optimizing resource use, resulting in cost savings and enhanced efficiency across mass production environments. Choosing between them depends on the specific goals: precise control and adaptability favor closed-loop systems, while overall process efficiency and waste reduction align with lean principles.
Connection
Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time data feedback into production processes, enabling continuous improvement and waste reduction, which aligns closely with Lean manufacturing principles focused on maximizing efficiency and minimizing waste. Both methodologies emphasize the elimination of inefficiencies by using data-driven insights to optimize workflows and reduce resource consumption. This synergy enhances overall manufacturing agility, product quality, and cost-effectiveness.
Key Terms
Waste Reduction (Lean)
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction by eliminating non-value-added activities through techniques like Just-In-Time (JIT) production, 5S, and continuous improvement (Kaizen), resulting in lower inventory costs and increased efficiency. Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time feedback and data analytics to monitor and reduce waste throughout the entire production cycle, enhancing resource reuse and minimizing environmental impact. Explore detailed strategies and comparative benefits of both approaches to optimize waste reduction in your manufacturing processes.
Real-time Feedback (Closed-loop)
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction and continuous improvement through standardized processes, while closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time feedback systems to dynamically adjust production based on immediate data inputs from sensors and machinery. Closed-loop manufacturing enhances responsiveness and quality control by continuously monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) such as cycle time, defect rates, and machine utilization, enabling prompt corrective actions. Explore how real-time feedback in closed-loop manufacturing transforms operational efficiency and product quality.
Continuous Improvement
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction and process efficiency through tools like Kaizen and value stream mapping to foster continuous improvement. Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time feedback systems, enabling dynamic adjustments and quality control throughout production cycles for sustained enhancement. Explore how these methodologies drive operational excellence and continuous improvement in manufacturing.
Source and External Links
Lean manufacturing - Wikipedia - Lean manufacturing is a method aimed at reducing production and supplier response times by eliminating waste and improving efficiency, closely related to just-in-time manufacturing and originally developed as the Toyota Production System focusing on seven types of waste.
Lean Manufacturing: Understanding a New Manufacturing System - Lean manufacturing emphasizes multi-skilled teams, worker participation, quality control, minimal inventory, and continuous improvement to achieve efficient and flexible production.
What is Lean Manufacturing? | Definition from TechTarget - Lean manufacturing is a methodology focused on minimizing waste and maximizing productivity based on principles like continuous improvement and is widely adopted across various industries beyond manufacturing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com