The industrial metaverse integrates virtual environments with real-world manufacturing processes, enhancing collaboration, simulation, and digital twin technologies for optimized production. Augmented reality overlays digital information onto physical equipment, enabling maintenance, training, and real-time data visualization on factory floors. Explore how these cutting-edge technologies transform manufacturing efficiency and innovation.
Why it is important
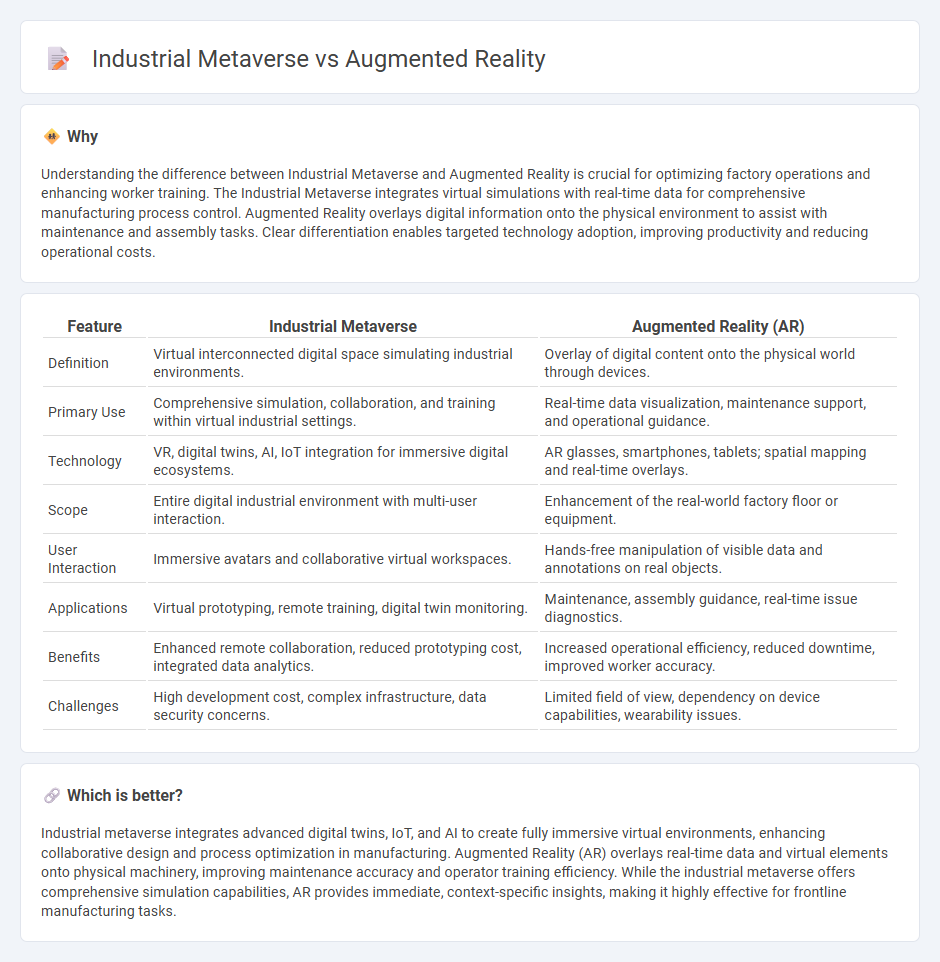
Understanding the difference between Industrial Metaverse and Augmented Reality is crucial for optimizing factory operations and enhancing worker training. The Industrial Metaverse integrates virtual simulations with real-time data for comprehensive manufacturing process control. Augmented Reality overlays digital information onto the physical environment to assist with maintenance and assembly tasks. Clear differentiation enables targeted technology adoption, improving productivity and reducing operational costs.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Industrial Metaverse | Augmented Reality (AR) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual interconnected digital space simulating industrial environments. | Overlay of digital content onto the physical world through devices. |
| Primary Use | Comprehensive simulation, collaboration, and training within virtual industrial settings. | Real-time data visualization, maintenance support, and operational guidance. |
| Technology | VR, digital twins, AI, IoT integration for immersive digital ecosystems. | AR glasses, smartphones, tablets; spatial mapping and real-time overlays. |
| Scope | Entire digital industrial environment with multi-user interaction. | Enhancement of the real-world factory floor or equipment. |
| User Interaction | Immersive avatars and collaborative virtual workspaces. | Hands-free manipulation of visible data and annotations on real objects. |
| Applications | Virtual prototyping, remote training, digital twin monitoring. | Maintenance, assembly guidance, real-time issue diagnostics. |
| Benefits | Enhanced remote collaboration, reduced prototyping cost, integrated data analytics. | Increased operational efficiency, reduced downtime, improved worker accuracy. |
| Challenges | High development cost, complex infrastructure, data security concerns. | Limited field of view, dependency on device capabilities, wearability issues. |
Which is better?
Industrial metaverse integrates advanced digital twins, IoT, and AI to create fully immersive virtual environments, enhancing collaborative design and process optimization in manufacturing. Augmented Reality (AR) overlays real-time data and virtual elements onto physical machinery, improving maintenance accuracy and operator training efficiency. While the industrial metaverse offers comprehensive simulation capabilities, AR provides immediate, context-specific insights, making it highly effective for frontline manufacturing tasks.
Connection
The industrial metaverse integrates augmented reality (AR) to create immersive, real-time digital twins of manufacturing environments, enabling enhanced visualization and interactive monitoring of production processes. AR overlays critical data and instructions on physical machinery, facilitating remote collaboration and reducing downtime through predictive maintenance and instant troubleshooting. This synergy accelerates innovation, improves operational efficiency, and supports smart factory implementations within Industry 4.0 frameworks.
Key Terms
Digital Twin
Digital Twin technology serves as a critical link between Augmented Reality (AR) and the Industrial Metaverse by enabling real-time, high-fidelity simulations of physical assets and processes within virtual environments. AR overlays live digital content onto the physical world, enhancing user interaction with digital twins by providing contextual data visualization and remote operation capabilities, crucial for manufacturing and maintenance sectors. Discover how Digital Twin integration transforms operational efficiency and innovation through immersive industrial applications.
Spatial Computing
Augmented Reality (AR) leverages spatial computing to overlay digital information onto the physical world, enhancing real-time interaction and visualization in industrial environments. The industrial metaverse expands this concept by creating immersive, interconnected virtual spaces that simulate entire manufacturing processes and supply chains, enabling remote collaboration and digital twins. Discover how spatial computing drives innovation at the intersection of AR and the industrial metaverse for smarter, more efficient operations.
Real-time Data Visualization
Real-time data visualization in augmented reality (AR) enables overlaying dynamic, context-specific information directly onto physical environments, enhancing situational awareness and decision-making on industrial floors. In contrast, the industrial metaverse integrates real-time data within immersive 3D virtual spaces, allowing collaborative simulation, training, and design review that transcend physical limitations. Explore how these technologies transform operational efficiency by visiting our detailed analysis.
Source and External Links
What is Augmented Reality? | IBM - Augmented reality (AR) integrates digital information and virtual objects in real time into the user's physical environment, enhancing rather than replacing reality.
Augmented reality - Wikipedia - AR overlays computer-generated graphics and sometimes other sensory stimuli onto the real world, perceived as immersive aspects of one's actual surroundings.
Augmented reality | Definition, Examples, & Facts - Britannica - AR combines or "augments" real-world visuals (like video or photographs) with computer-generated data and overlays, used in fields ranging from entertainment to navigation and retail.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com