Adaptive machining employs real-time data and advanced sensors to dynamically adjust manufacturing processes, enhancing precision and reducing waste. Lean manufacturing focuses on systematically eliminating inefficiencies, optimizing workflow, and minimizing inventory to improve overall productivity. Explore how integrating adaptive machining with lean principles can revolutionize production efficiency and quality.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between adaptive machining and lean manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and minimizing waste. Adaptive machining uses real-time data to adjust processes dynamically, enhancing precision and reducing errors. Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating non-value-added activities to improve overall workflow and cost-effectiveness. Differentiating these approaches allows manufacturers to strategically implement the right methods for quality improvement and resource management.
Comparison Table
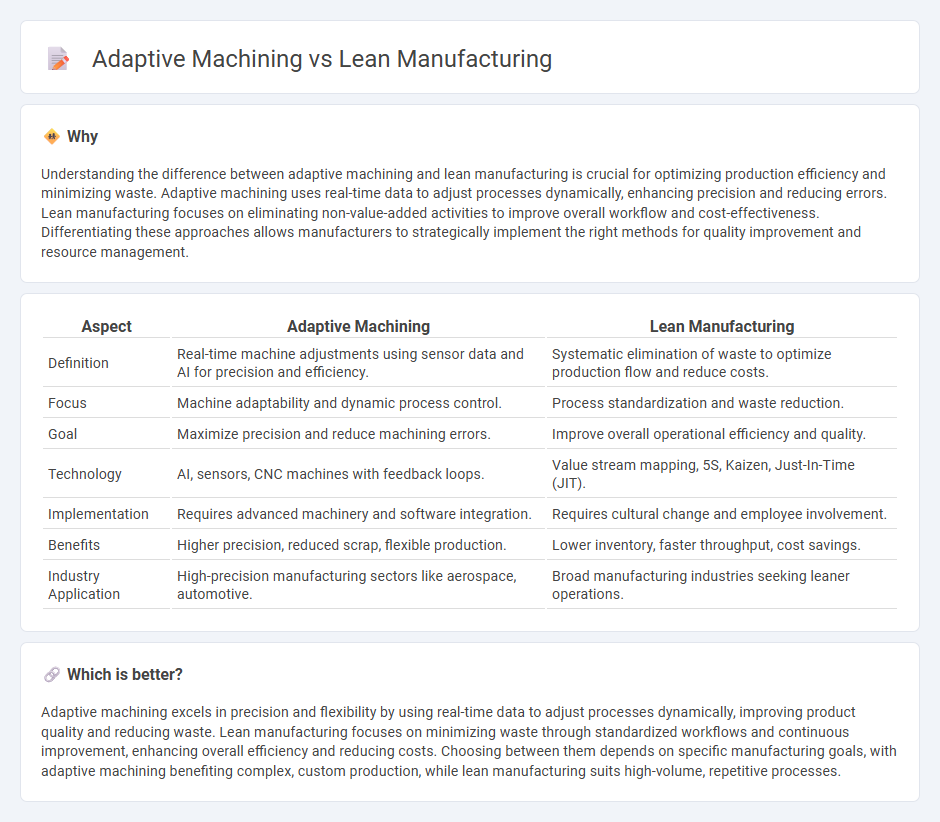
| Aspect | Adaptive Machining | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time machine adjustments using sensor data and AI for precision and efficiency. | Systematic elimination of waste to optimize production flow and reduce costs. |
| Focus | Machine adaptability and dynamic process control. | Process standardization and waste reduction. |
| Goal | Maximize precision and reduce machining errors. | Improve overall operational efficiency and quality. |
| Technology | AI, sensors, CNC machines with feedback loops. | Value stream mapping, 5S, Kaizen, Just-In-Time (JIT). |
| Implementation | Requires advanced machinery and software integration. | Requires cultural change and employee involvement. |
| Benefits | Higher precision, reduced scrap, flexible production. | Lower inventory, faster throughput, cost savings. |
| Industry Application | High-precision manufacturing sectors like aerospace, automotive. | Broad manufacturing industries seeking leaner operations. |
Which is better?
Adaptive machining excels in precision and flexibility by using real-time data to adjust processes dynamically, improving product quality and reducing waste. Lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste through standardized workflows and continuous improvement, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing costs. Choosing between them depends on specific manufacturing goals, with adaptive machining benefiting complex, custom production, while lean manufacturing suits high-volume, repetitive processes.
Connection
Adaptive machining enhances Lean manufacturing by dynamically adjusting processes to reduce waste and improve efficiency in real-time. This synergy minimizes downtime and material usage while maximizing production speed and quality. Integrating adaptive machining with Lean principles drives continuous improvement and cost savings in manufacturing operations.
Key Terms
Waste Reduction (Lean manufacturing)
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction by eliminating non-value-added activities through continuous improvement techniques like 5S, Kaizen, and Just-In-Time production, effectively minimizing overproduction, waiting times, and defects. Adaptive machining focuses on waste reduction by dynamically adjusting cutting parameters in real-time, enhancing tool life and material efficiency while reducing scrap rates. Explore how integrating lean manufacturing principles with adaptive machining technologies can further optimize waste reduction and operational efficiency.
Flexibility (Adaptive machining)
Adaptive machining offers unparalleled flexibility by dynamically adjusting machining parameters in real-time to accommodate variations in material properties and design specifications, unlike lean manufacturing which emphasizes waste reduction through standardized processes. This real-time adaptability minimizes downtime and maximizes efficiency, crucial for custom and small-batch production environments. Discover how adaptive machining can revolutionize your manufacturing approach for greater flexibility and responsiveness.
Continuous Improvement (Lean/Adaptive overlap)
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction through standardized processes and continuous improvement cycles like Kaizen, enhancing operational efficiency. Adaptive machining integrates real-time data and flexible adjustments to optimize production, promoting agility alongside Lean principles. Explore how combining Lean manufacturing with Adaptive machining fosters a resilient, continuously improving production environment.
Source and External Links
Lean manufacturing - Lean manufacturing is a method focused on reducing production and response times, eliminating non-value-adding activities, and minimizing the seven wastes identified by Toyota to improve efficiency and customer value.
Understanding a New Manufacturing System - Lean manufacturing emphasizes worker participation, multitasking, continuous improvement, and prioritizes quality control with minimal inventory, contrasting with traditional Fordist methods.
What is Lean Manufacturing? | Definition from TechTarget - Lean manufacturing is a methodology to minimize waste and maximize productivity, based on Toyota Production System principles and including practices like Kaizen for continuous improvement.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com