Microfactories focus on compact, flexible production units designed for rapid customization and local manufacturing, leveraging advanced automation and digital integration. Lean manufacturing plants emphasize eliminating waste, streamlining processes, and optimizing efficiency across large-scale operations through continuous improvement and just-in-time production methods. Explore the benefits and challenges of microfactories versus lean manufacturing plants to enhance your production strategy.
Why it is important
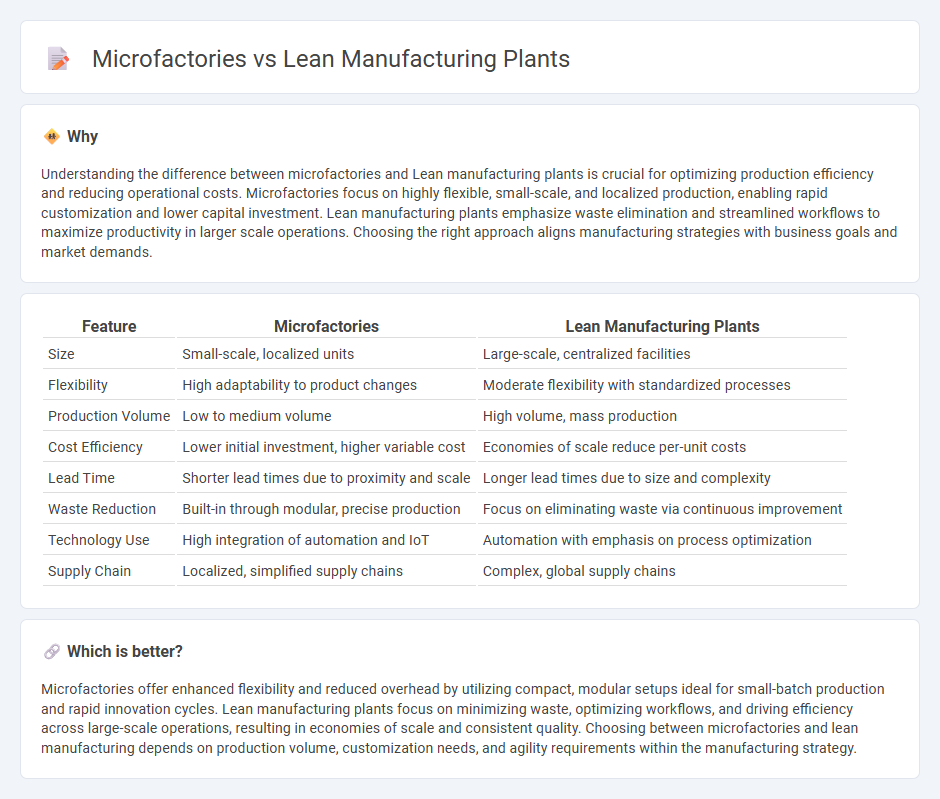
Understanding the difference between microfactories and Lean manufacturing plants is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and reducing operational costs. Microfactories focus on highly flexible, small-scale, and localized production, enabling rapid customization and lower capital investment. Lean manufacturing plants emphasize waste elimination and streamlined workflows to maximize productivity in larger scale operations. Choosing the right approach aligns manufacturing strategies with business goals and market demands.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Microfactories | Lean Manufacturing Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Small-scale, localized units | Large-scale, centralized facilities |
| Flexibility | High adaptability to product changes | Moderate flexibility with standardized processes |
| Production Volume | Low to medium volume | High volume, mass production |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower initial investment, higher variable cost | Economies of scale reduce per-unit costs |
| Lead Time | Shorter lead times due to proximity and scale | Longer lead times due to size and complexity |
| Waste Reduction | Built-in through modular, precise production | Focus on eliminating waste via continuous improvement |
| Technology Use | High integration of automation and IoT | Automation with emphasis on process optimization |
| Supply Chain | Localized, simplified supply chains | Complex, global supply chains |
Which is better?
Microfactories offer enhanced flexibility and reduced overhead by utilizing compact, modular setups ideal for small-batch production and rapid innovation cycles. Lean manufacturing plants focus on minimizing waste, optimizing workflows, and driving efficiency across large-scale operations, resulting in economies of scale and consistent quality. Choosing between microfactories and lean manufacturing depends on production volume, customization needs, and agility requirements within the manufacturing strategy.
Connection
Microfactories and Lean manufacturing plants both focus on maximizing efficiency and minimizing waste through streamlined workflows and just-in-time production. Microfactories leverage modular, compact setups ideal for rapid customization and scalability, aligning with Lean principles of reducing excess inventory and enabling continuous improvement. The integration of smart technologies in both enhances real-time data monitoring, fostering precision and agility in manufacturing processes.
Key Terms
Scale of Production
Lean manufacturing plants optimize large-scale production by minimizing waste and improving efficiency across extensive assembly lines, making them ideal for high-volume output. Microfactories concentrate on small-batch, highly customizable production with compact setups that enable rapid response to market changes and local demand. Discover how these production models impact scalability and operational agility in modern manufacturing.
Flexibility
Lean manufacturing plants emphasize waste reduction and efficiency through standardized processes, often resulting in rigid production lines with limited ability to adapt quickly. Microfactories prioritize flexibility with modular equipment and scalable layouts, enabling rapid customization and agile responses to market demands. Explore the benefits of integrating microfactory flexibility into lean manufacturing principles for optimized production agility.
Automation
Lean manufacturing plants emphasize minimizing waste and optimizing production efficiency through streamlined processes and just-in-time inventory, often incorporating automation to enhance repeatability and reduce errors. Microfactories utilize advanced automation technologies, such as robotics and IoT, to enable flexible, scalable, and localized production with quicker changeovers and reduced footprint. Explore how automation drives innovation and operational excellence in both lean manufacturing plants and microfactories.
Source and External Links
The Ultimate Guide To Lean Plant Layout (with Designs) - Lean manufacturing plants use layouts focused on value streams with connected processes, reducing material handling, work-in-process inventory, and lead times by grouping machines by product families rather than traditional departmental silos.
Understanding a New Manufacturing System - Lean manufacturing plants maintain a continuous, tightly controlled yet decentralized flow of parts and materials, emphasizing flexibility, quick setup, reduced floor space, and the use of kanban to adapt efficiently to demand changes.
9 Companies That Use Lean Manufacturing - Leading companies like Ford and General Electric apply lean principles such as Just-In-Time inventory, 5S, Kaizen, and visual management in their manufacturing plants to reduce waste, improve efficiency, and enhance product quality.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com