The digital thread integrates data flow from design to production, enabling seamless traceability and real-time feedback across manufacturing processes. Industrial IoT (IIoT) uses connected sensors and devices to optimize operations, enhance predictive maintenance, and reduce downtime on the factory floor. Explore how these technologies transform smart manufacturing for increased efficiency and innovation.
Why it is important
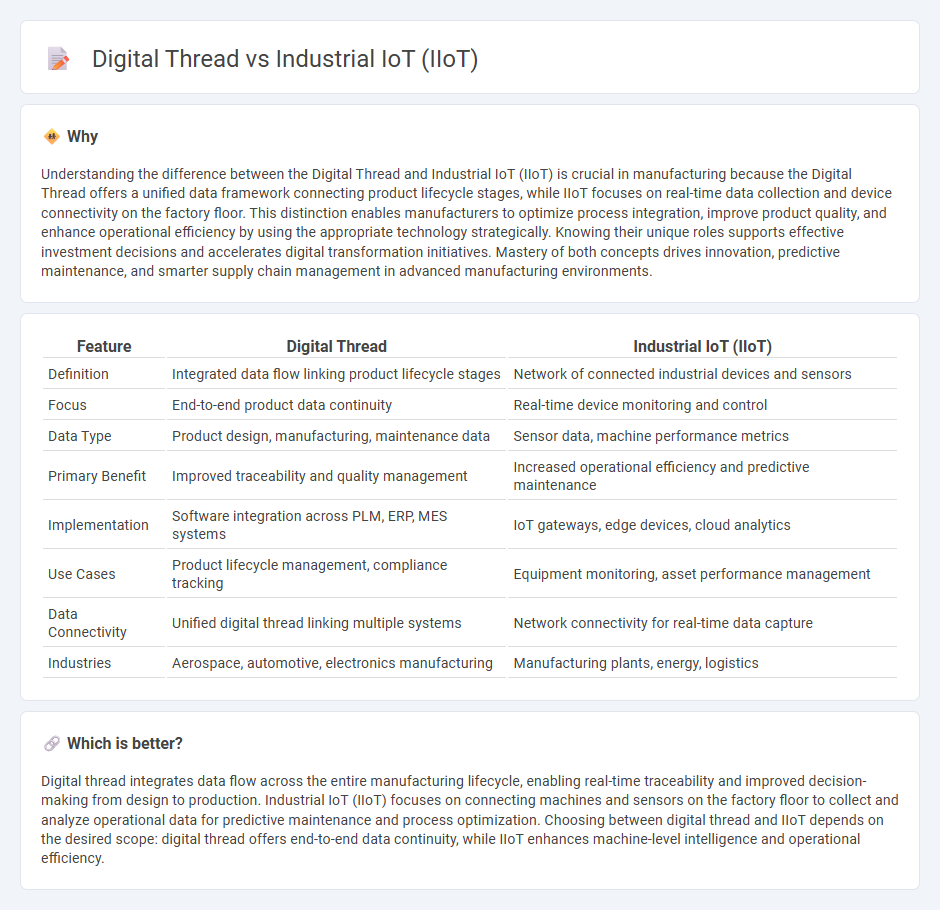
Understanding the difference between the Digital Thread and Industrial IoT (IIoT) is crucial in manufacturing because the Digital Thread offers a unified data framework connecting product lifecycle stages, while IIoT focuses on real-time data collection and device connectivity on the factory floor. This distinction enables manufacturers to optimize process integration, improve product quality, and enhance operational efficiency by using the appropriate technology strategically. Knowing their unique roles supports effective investment decisions and accelerates digital transformation initiatives. Mastery of both concepts drives innovation, predictive maintenance, and smarter supply chain management in advanced manufacturing environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Thread | Industrial IoT (IIoT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrated data flow linking product lifecycle stages | Network of connected industrial devices and sensors |
| Focus | End-to-end product data continuity | Real-time device monitoring and control |
| Data Type | Product design, manufacturing, maintenance data | Sensor data, machine performance metrics |
| Primary Benefit | Improved traceability and quality management | Increased operational efficiency and predictive maintenance |
| Implementation | Software integration across PLM, ERP, MES systems | IoT gateways, edge devices, cloud analytics |
| Use Cases | Product lifecycle management, compliance tracking | Equipment monitoring, asset performance management |
| Data Connectivity | Unified digital thread linking multiple systems | Network connectivity for real-time data capture |
| Industries | Aerospace, automotive, electronics manufacturing | Manufacturing plants, energy, logistics |
Which is better?
Digital thread integrates data flow across the entire manufacturing lifecycle, enabling real-time traceability and improved decision-making from design to production. Industrial IoT (IIoT) focuses on connecting machines and sensors on the factory floor to collect and analyze operational data for predictive maintenance and process optimization. Choosing between digital thread and IIoT depends on the desired scope: digital thread offers end-to-end data continuity, while IIoT enhances machine-level intelligence and operational efficiency.
Connection
Digital thread integrates data flow across the entire manufacturing lifecycle, enabling real-time visibility and traceability of products from design to production. Industrial IoT (IIoT) supplies the sensor data and connectivity necessary for the digital thread to capture machine status, equipment performance, and environmental conditions on the factory floor. Together, they enhance predictive maintenance, optimize asset utilization, and accelerate decision-making through seamless data integration in smart manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Connectivity
Industrial IoT (IIoT) emphasizes connectivity through a network of sensors, devices, and machines that collect and exchange real-time data to enhance operational efficiency and predictive maintenance in manufacturing environments. The digital thread integrates this data across the entire product lifecycle, providing a seamless flow of information from design to production and beyond, enabling improved traceability and decision-making. Explore how these technologies connect and collaborate to transform smart manufacturing processes.
Data Integration
Industrial IoT (IIoT) emphasizes real-time data collection from sensors and machinery to enhance operational efficiency, while the Digital Thread integrates data across the entire product lifecycle, from design to manufacturing and maintenance. IIoT enables seamless connectivity and analysis of equipment data, whereas the Digital Thread ensures traceability and contextual understanding by linking diverse data sources into a coherent framework. Explore how these complementary data integration frameworks drive smarter manufacturing processes and innovation.
Lifecycle Traceability
Industrial IoT (IIoT) leverages interconnected sensors and devices to collect real-time operational data, enhancing asset monitoring throughout the product lifecycle. The digital thread provides a comprehensive, unified view by integrating data across design, manufacturing, and service phases, enabling precise lifecycle traceability from conception to end-of-life. Explore how combining IIoT and digital thread technologies optimizes traceability and improves manufacturing efficiency.
Source and External Links
Industrial IoT | Digital Transformation - AWS - Industrial IoT (IIoT) integrates machines, cloud computing, analytics, and people to enhance industrial process performance and productivity, enabling predictive maintenance, asset monitoring, and process optimization across various industries such as manufacturing and energy.
Industrial IoT: Understanding the Basics - IIoT is a specialized branch of IoT focused on connecting rugged and sophisticated devices in industrial settings for real-time data acquisition, predictive maintenance, and process visibility, driving efficiency and quality improvements in manufacturing and supply chains.
What is IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things)? | Definition from TechTarget - IIoT uses smart sensors and networked devices to capture and analyze real-time data, enhancing industrial processes with applications like predictive maintenance, energy management, and supply chain traceability for greater efficiency and reliability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com