Dark factories operate with minimal to no human presence, utilizing fully automated systems and robotics to achieve continuous production and reduce labor costs. Flexible manufacturing systems adapt quickly to changes in product design and volume through programmable machines and modular setups, enhancing responsiveness and customization. Explore the distinctions and benefits of dark factories versus flexible manufacturing to optimize your production strategy.
Why it is important
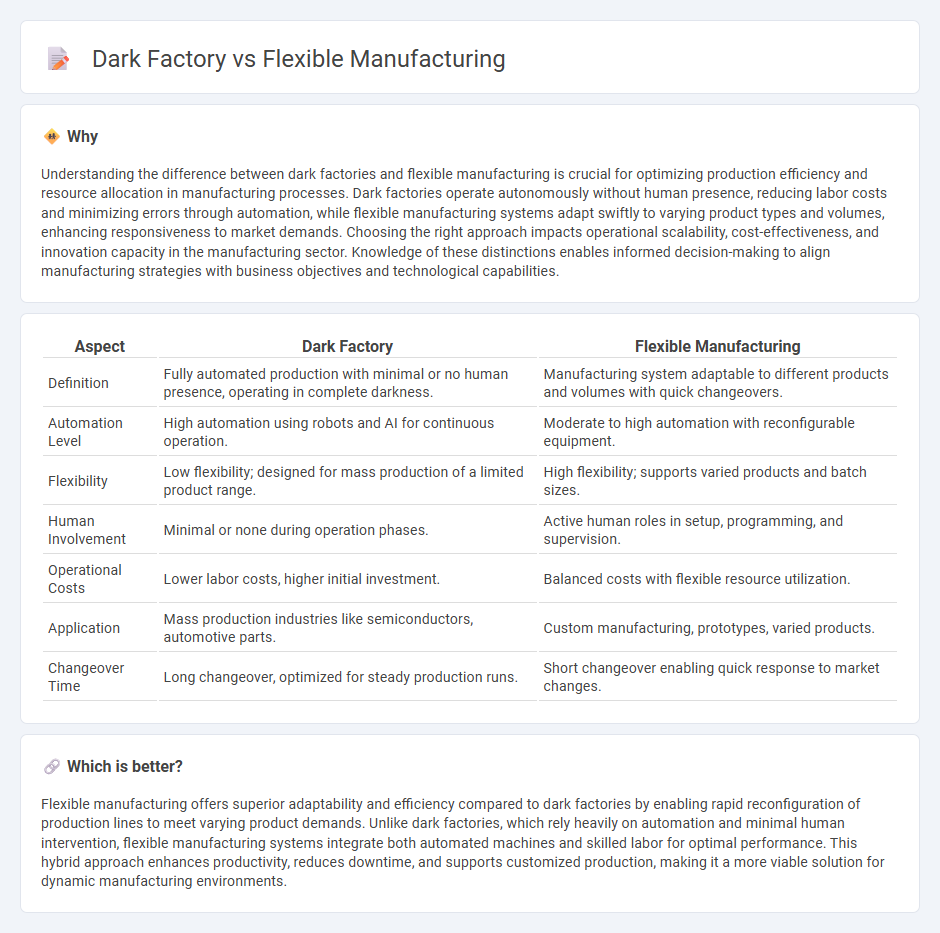
Understanding the difference between dark factories and flexible manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and resource allocation in manufacturing processes. Dark factories operate autonomously without human presence, reducing labor costs and minimizing errors through automation, while flexible manufacturing systems adapt swiftly to varying product types and volumes, enhancing responsiveness to market demands. Choosing the right approach impacts operational scalability, cost-effectiveness, and innovation capacity in the manufacturing sector. Knowledge of these distinctions enables informed decision-making to align manufacturing strategies with business objectives and technological capabilities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Factory | Flexible Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated production with minimal or no human presence, operating in complete darkness. | Manufacturing system adaptable to different products and volumes with quick changeovers. |
| Automation Level | High automation using robots and AI for continuous operation. | Moderate to high automation with reconfigurable equipment. |
| Flexibility | Low flexibility; designed for mass production of a limited product range. | High flexibility; supports varied products and batch sizes. |
| Human Involvement | Minimal or none during operation phases. | Active human roles in setup, programming, and supervision. |
| Operational Costs | Lower labor costs, higher initial investment. | Balanced costs with flexible resource utilization. |
| Application | Mass production industries like semiconductors, automotive parts. | Custom manufacturing, prototypes, varied products. |
| Changeover Time | Long changeover, optimized for steady production runs. | Short changeover enabling quick response to market changes. |
Which is better?
Flexible manufacturing offers superior adaptability and efficiency compared to dark factories by enabling rapid reconfiguration of production lines to meet varying product demands. Unlike dark factories, which rely heavily on automation and minimal human intervention, flexible manufacturing systems integrate both automated machines and skilled labor for optimal performance. This hybrid approach enhances productivity, reduces downtime, and supports customized production, making it a more viable solution for dynamic manufacturing environments.
Connection
Dark factories utilize automated systems and robotics to operate with minimal human intervention, enhancing efficiency and reducing labor costs. Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) enable quick adaptation to product changes through programmable machinery, supporting diverse production runs. The integration of dark factories with flexible manufacturing principles creates highly adaptable, autonomous production environments that optimize throughput and minimize downtime.
Key Terms
**Flexible Manufacturing:**
Flexible manufacturing systems use adaptable machines and robots to efficiently produce a variety of products with minimal downtime, optimizing operational flexibility and cost-effectiveness. These systems integrate automation, real-time data monitoring, and quick changeovers to respond swiftly to market demands and customization needs. Explore more about how flexible manufacturing transforms production agility and reduces lead times.
Reconfigurability
Flexible manufacturing emphasizes reconfigurability by allowing quick adjustments to production lines to accommodate different products and volumes, optimizing operational efficiency. Dark factories enhance reconfigurability through advanced automation and robotics, enabling continuous, lights-out production with minimal human intervention. Explore the latest innovations in reconfigurable manufacturing systems for a deeper understanding.
CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
Flexible manufacturing systems leverage CNC technology to enable rapid adaptation and customization of production processes, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime. Dark factories utilize CNC machines in fully automated environments with minimal human intervention, often operating 24/7 to maximize productivity and consistency. Explore how CNC integration transforms manufacturing by comparing flexible systems and dark factory benefits in detail.
Source and External Links
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) - Autodesk - A flexible manufacturing system is a computer-controlled production setup designed to quickly adapt to changes such as product details, variations in order sequences, or production volumes by enabling routing and machine flexibility.
Flexible manufacturing system - Wikipedia - Flexible manufacturing systems allow manufacturers to efficiently respond to changes by offering routing flexibility (changing operations order or product types) and machine flexibility (using different machines for the same operation), all managed by automated work machines, material handling, and a central control computer.
What is Flexible Manufacturing - Big Sky Engineering, Inc. - Flexible manufacturing enables companies to quickly adapt their production operations for different parts or products without major retooling, leading to faster turnaround, greater flexibility in order sizes, and optimized manufacturing processes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com