Decentralized manufacturing distributes production processes across multiple locations to enhance flexibility, reduce transportation costs, and improve local responsiveness, while just-in-time manufacturing focuses on minimizing inventory and delivering materials precisely when needed to reduce waste and increase efficiency. Companies leveraging decentralized manufacturing benefit from risk mitigation and localized customization, whereas just-in-time manufacturing excels in streamlining operations and lowering inventory overhead. Explore the key differences and applications of these manufacturing approaches to optimize your production strategy.
Why it is important
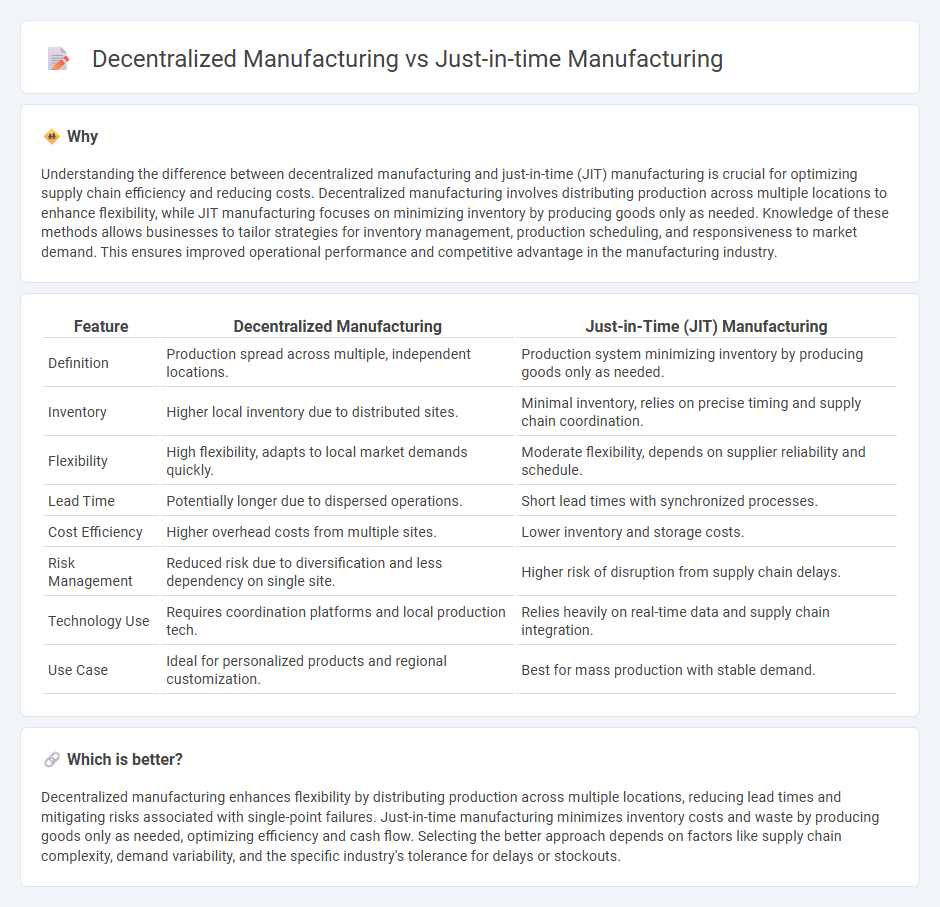
Understanding the difference between decentralized manufacturing and just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing costs. Decentralized manufacturing involves distributing production across multiple locations to enhance flexibility, while JIT manufacturing focuses on minimizing inventory by producing goods only as needed. Knowledge of these methods allows businesses to tailor strategies for inventory management, production scheduling, and responsiveness to market demand. This ensures improved operational performance and competitive advantage in the manufacturing industry.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Manufacturing | Just-in-Time (JIT) Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Production spread across multiple, independent locations. | Production system minimizing inventory by producing goods only as needed. |
| Inventory | Higher local inventory due to distributed sites. | Minimal inventory, relies on precise timing and supply chain coordination. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, adapts to local market demands quickly. | Moderate flexibility, depends on supplier reliability and schedule. |
| Lead Time | Potentially longer due to dispersed operations. | Short lead times with synchronized processes. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher overhead costs from multiple sites. | Lower inventory and storage costs. |
| Risk Management | Reduced risk due to diversification and less dependency on single site. | Higher risk of disruption from supply chain delays. |
| Technology Use | Requires coordination platforms and local production tech. | Relies heavily on real-time data and supply chain integration. |
| Use Case | Ideal for personalized products and regional customization. | Best for mass production with stable demand. |
Which is better?
Decentralized manufacturing enhances flexibility by distributing production across multiple locations, reducing lead times and mitigating risks associated with single-point failures. Just-in-time manufacturing minimizes inventory costs and waste by producing goods only as needed, optimizing efficiency and cash flow. Selecting the better approach depends on factors like supply chain complexity, demand variability, and the specific industry's tolerance for delays or stockouts.
Connection
Decentralized manufacturing enhances just-in-time manufacturing by distributing production closer to end-users, reducing lead times and inventory costs. This integration allows companies to respond rapidly to market demands and customize products more efficiently. Leveraging advanced technologies such as IoT and AI ensures seamless coordination across decentralized sites, optimizing supply chain flexibility and minimizing waste.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Just-in-time manufacturing minimizes inventory by receiving materials only as needed, reducing storage costs and waste while requiring precise demand forecasting and supplier reliability. Decentralized manufacturing distributes production across multiple locations, allowing for localized inventory that enhances flexibility and responsiveness but may lead to higher overall inventory levels. Explore the advantages and challenges of these inventory management strategies to optimize your manufacturing process.
Production Scheduling
Just-in-time manufacturing optimizes production scheduling by minimizing inventory levels and producing goods only as needed, reducing waste and increasing efficiency. Decentralized manufacturing distributes production across multiple locations, allowing more flexible schedules tailored to regional demand but requiring complex coordination to avoid delays. Explore how these production scheduling strategies impact operational costs and responsiveness in different industries.
Autonomy
Just-in-time manufacturing emphasizes minimizing inventory through synchronized production schedules, relying on centralized control to maintain efficiency and reduce waste. Decentralized manufacturing fosters autonomy by distributing decision-making and production processes across multiple locations, enhancing responsiveness and adaptability to local demands. Explore how autonomy impacts operational agility and competitive advantage in manufacturing systems.
Source and External Links
Just In Time Manufacturing: Definition, Benefits, and Origin - Just-in-Time manufacturing is a strategy to increase efficiency and reduce waste by producing goods only as needed, leading to lower inventory costs, better supplier relationships, improved product quality, and flexibility to adapt to market changes.
What is just-in-time manufacturing (JIT manufacturing)? - TechTarget - JIT manufacturing is a production model where items are created to meet demand precisely, minimizing overproduction and inventory to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and speed product delivery.
What is Just-in-Time Manufacturing (JIT)? - Planview - JIT is a workflow methodology aimed at reducing production flow times and response times from suppliers, emphasizing disciplined inventory limits, visual communication, and lean manufacturing practices to improve productivity and reduce costs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com