Factory as a Service (FaaS) streamlines production by providing on-demand access to manufacturing facilities, reducing capital investment and enabling flexible scalability. Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, builds components layer by layer directly from digital models, allowing for complex geometries and rapid prototyping. Discover how these innovative manufacturing solutions transform production efficiency and customization.
Why it is important
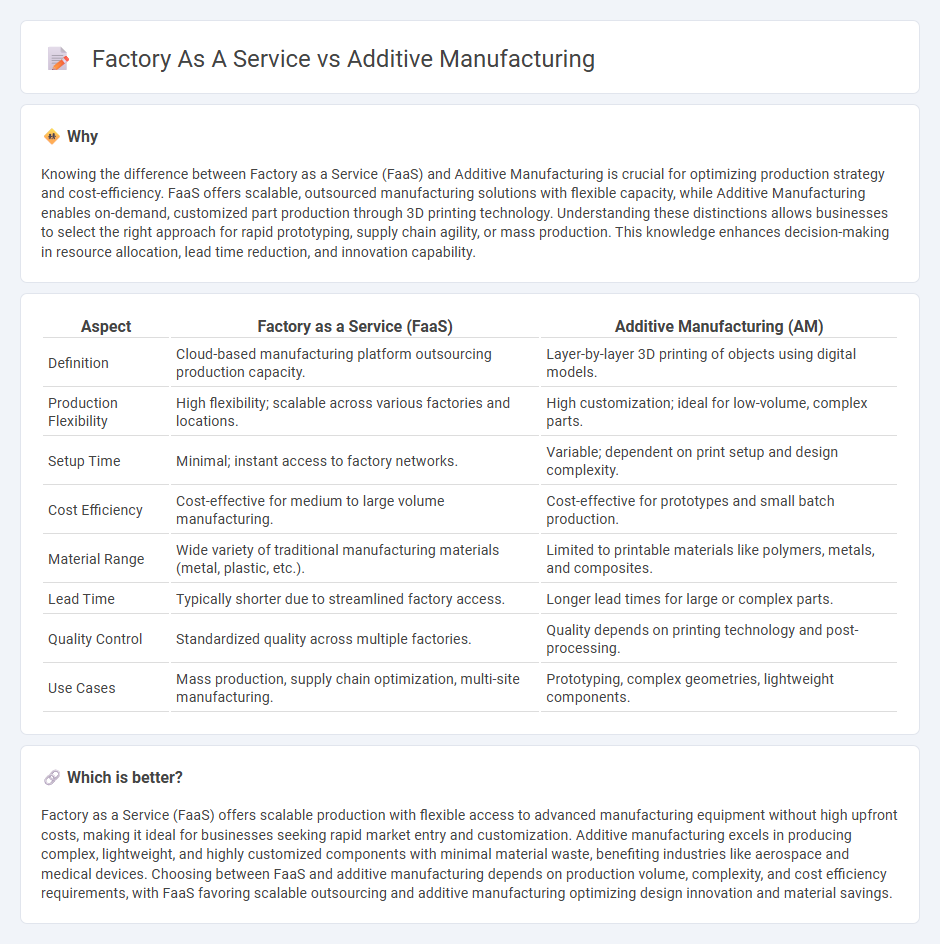
Knowing the difference between Factory as a Service (FaaS) and Additive Manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production strategy and cost-efficiency. FaaS offers scalable, outsourced manufacturing solutions with flexible capacity, while Additive Manufacturing enables on-demand, customized part production through 3D printing technology. Understanding these distinctions allows businesses to select the right approach for rapid prototyping, supply chain agility, or mass production. This knowledge enhances decision-making in resource allocation, lead time reduction, and innovation capability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Factory as a Service (FaaS) | Additive Manufacturing (AM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cloud-based manufacturing platform outsourcing production capacity. | Layer-by-layer 3D printing of objects using digital models. |
| Production Flexibility | High flexibility; scalable across various factories and locations. | High customization; ideal for low-volume, complex parts. |
| Setup Time | Minimal; instant access to factory networks. | Variable; dependent on print setup and design complexity. |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for medium to large volume manufacturing. | Cost-effective for prototypes and small batch production. |
| Material Range | Wide variety of traditional manufacturing materials (metal, plastic, etc.). | Limited to printable materials like polymers, metals, and composites. |
| Lead Time | Typically shorter due to streamlined factory access. | Longer lead times for large or complex parts. |
| Quality Control | Standardized quality across multiple factories. | Quality depends on printing technology and post-processing. |
| Use Cases | Mass production, supply chain optimization, multi-site manufacturing. | Prototyping, complex geometries, lightweight components. |
Which is better?
Factory as a Service (FaaS) offers scalable production with flexible access to advanced manufacturing equipment without high upfront costs, making it ideal for businesses seeking rapid market entry and customization. Additive manufacturing excels in producing complex, lightweight, and highly customized components with minimal material waste, benefiting industries like aerospace and medical devices. Choosing between FaaS and additive manufacturing depends on production volume, complexity, and cost efficiency requirements, with FaaS favoring scalable outsourcing and additive manufacturing optimizing design innovation and material savings.
Connection
Factory as a Service (FaaS) integrates additive manufacturing by offering on-demand, scalable production capabilities without the need for significant capital investment in traditional factories. Additive manufacturing enables rapid prototyping and custom part production within FaaS environments, enhancing flexibility and reducing lead times. Together, they optimize manufacturing workflows by leveraging digital platforms for seamless resource allocation and real-time monitoring.
Key Terms
Additive Manufacturing:
Additive manufacturing leverages layer-by-layer 3D printing technology to create complex, customized parts with reduced material waste and faster prototyping compared to traditional factory production. Unlike Factory as a Service, which optimizes entire manufacturing facilities for scalable production, additive manufacturing excels in flexibility and on-demand manufacturing for low to medium volume runs. Explore how additive manufacturing can transform your production processes with greater efficiency and innovation.
3D Printing
Additive manufacturing leverages 3D printing technology to create complex, customized parts layer by layer, reducing waste and enabling rapid prototyping compared to traditional factory setups. Factory as a Service (FaaS) integrates 3D printing into scalable, on-demand production platforms, offering flexible manufacturing without the need for capital-intensive facilities. Explore how these advancements transform industrial production by unlocking efficiency and innovation through 3D printing solutions.
Layer-by-Layer Fabrication
Additive manufacturing employs layer-by-layer fabrication to create complex geometries with minimal material waste, enabling rapid prototyping and customization. Factory as a Service (FaaS) integrates additive manufacturing within a scalable, on-demand production ecosystem, facilitating flexible supply chains and reduced capital investment. Explore how these technologies transform manufacturing efficiency and innovation potentials.
Source and External Links
Additive manufacturing, explained - Additive manufacturing is the process of creating objects layer by layer, typically using 3D printing, which builds physical items directly from digital designs without traditional subtractive methods like cutting away material.
Additive manufacturing | NIST - Additive manufacturing (AM) uses digital designs to fabricate products layer by layer, enabling complex structures with less waste, and is applied across industries including aerospace and biomedical implants.
What Is Additive Manufacturing? | 3D Printing Simulation ... - Additive manufacturing builds three-dimensional objects from digital CAD models by layering materials through various technologies like powder bed fusion and material extrusion, supporting industrial applications and faster innovation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com