Machine vision inspection uses high-resolution cameras and advanced image processing algorithms to detect surface defects, measure dimensions, and ensure product quality with precision and speed. Infrared inspection captures thermal data to identify hidden faults such as overheating components, electrical issues, or material inconsistencies that are invisible to the naked eye or standard vision systems. Discover how integrating both technologies can enhance manufacturing quality control and operational efficiency.
Why it is important
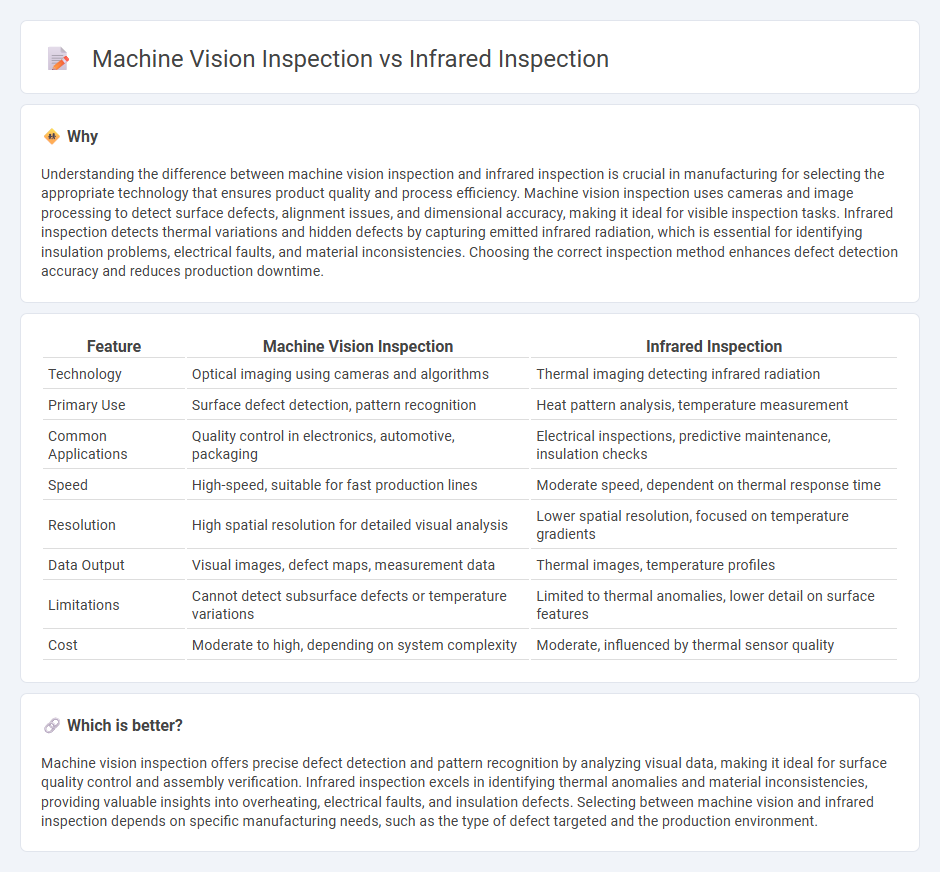
Understanding the difference between machine vision inspection and infrared inspection is crucial in manufacturing for selecting the appropriate technology that ensures product quality and process efficiency. Machine vision inspection uses cameras and image processing to detect surface defects, alignment issues, and dimensional accuracy, making it ideal for visible inspection tasks. Infrared inspection detects thermal variations and hidden defects by capturing emitted infrared radiation, which is essential for identifying insulation problems, electrical faults, and material inconsistencies. Choosing the correct inspection method enhances defect detection accuracy and reduces production downtime.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Machine Vision Inspection | Infrared Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Optical imaging using cameras and algorithms | Thermal imaging detecting infrared radiation |
| Primary Use | Surface defect detection, pattern recognition | Heat pattern analysis, temperature measurement |
| Common Applications | Quality control in electronics, automotive, packaging | Electrical inspections, predictive maintenance, insulation checks |
| Speed | High-speed, suitable for fast production lines | Moderate speed, dependent on thermal response time |
| Resolution | High spatial resolution for detailed visual analysis | Lower spatial resolution, focused on temperature gradients |
| Data Output | Visual images, defect maps, measurement data | Thermal images, temperature profiles |
| Limitations | Cannot detect subsurface defects or temperature variations | Limited to thermal anomalies, lower detail on surface features |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on system complexity | Moderate, influenced by thermal sensor quality |
Which is better?
Machine vision inspection offers precise defect detection and pattern recognition by analyzing visual data, making it ideal for surface quality control and assembly verification. Infrared inspection excels in identifying thermal anomalies and material inconsistencies, providing valuable insights into overheating, electrical faults, and insulation defects. Selecting between machine vision and infrared inspection depends on specific manufacturing needs, such as the type of defect targeted and the production environment.
Connection
Machine vision inspection and infrared inspection are interconnected technologies in manufacturing that enhance quality control by detecting surface defects and thermal anomalies, respectively. Machine vision uses high-resolution cameras and image processing algorithms to identify dimensional inaccuracies and surface flaws, while infrared inspection captures thermal patterns to spot overheating issues and material inconsistencies. Combining these methods provides comprehensive defect detection, improving production efficiency and reducing error rates.
Key Terms
Thermal Imaging
Infrared inspection utilizes thermal imaging to detect temperature variations and identify defects invisible to the naked eye or standard cameras, making it ideal for electrical systems, building diagnostics, and manufacturing processes. Machine vision inspection uses visible spectrum cameras and advanced algorithms to analyze surface features, shape, color, and texture for quality control and automation. Explore how integrating thermal imaging with machine vision enhances defect detection accuracy and operational efficiency.
Optical Sensors
Infrared inspection utilizes thermal imaging cameras to detect temperature variations, enabling identification of heat signatures and potential faults in materials or electronics that are invisible to the naked eye. Machine vision inspection employs optical sensors such as CCD or CMOS cameras for high-resolution imaging to assess surface defects, alignment, and dimensional accuracy in real-time production environments. Learn more about how optical sensor technologies enhance inspection accuracy and efficiency in industrial applications.
Defect Detection
Infrared inspection excels in detecting thermal anomalies and hidden defects such as insulation failures or overheating components by capturing heat signatures that are invisible to the naked eye. Machine vision inspection leverages high-resolution imaging and advanced algorithms to identify surface defects, shape irregularities, and assembly errors with precise visual data. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which technique best suits your defect detection needs.
Source and External Links
Infrared Inspection Windows | Prevent Downtime - IRISS infrared inspection windows enable safe, clear viewing of energized electrical equipment using patented polymer optics, enhancing safety and maintenance efficiency with a durable, moisture-resistant design and lifetime warranty.
Infrared Thermography Overview for Home Inspectors - Infrared thermography utilizes specialized cameras and devices to detect and visualize heat patterns, allowing inspectors to identify temperature anomalies and heat flow in buildings and systems.
Thermal Imaging (Infrared) Inspections - Thermal imaging inspections use infrared cameras to reveal hidden home issues such as insulation gaps, water leaks, and electrical faults, providing valuable insights beyond standard visual inspections.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com