Smart dust consists of tiny, wireless microelectromechanical sensors that enable real-time data collection at a granular level in manufacturing environments, offering unprecedented precision in monitoring processes and equipment. IoT sensors, while larger, provide broad connectivity and integration capabilities across manufacturing systems, enhancing automation and operational efficiency through networked data exchange. Explore how smart dust and IoT sensors transform manufacturing with cutting-edge technology and innovation.
Why it is important
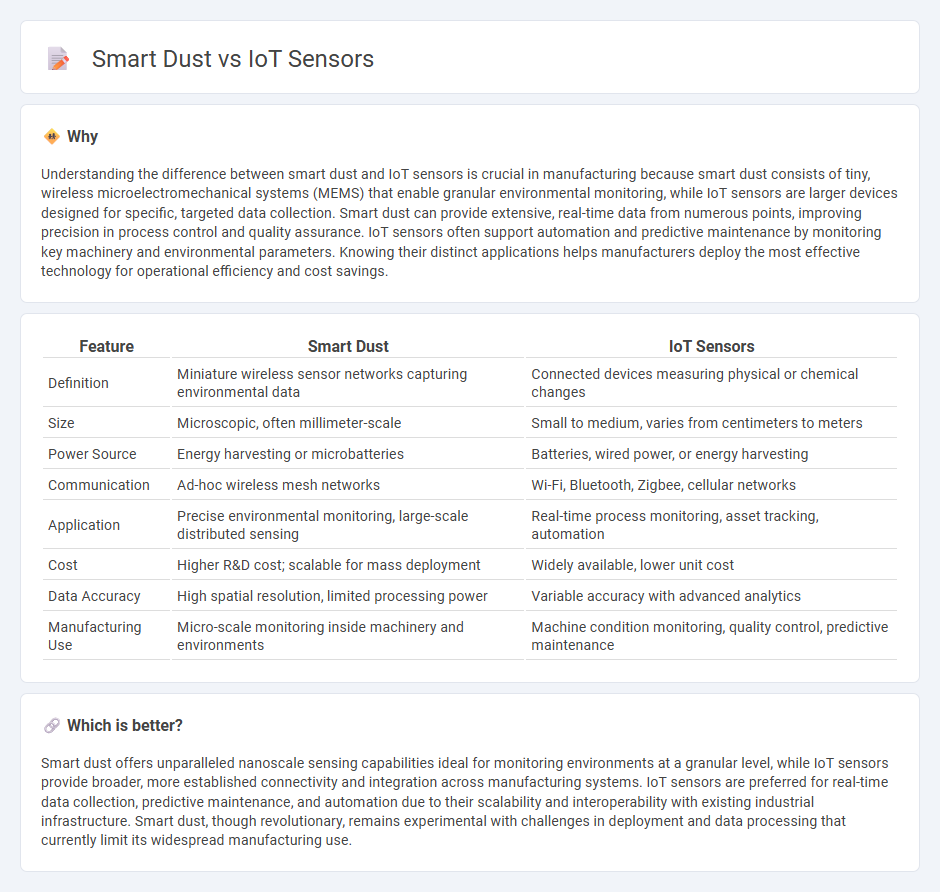
Understanding the difference between smart dust and IoT sensors is crucial in manufacturing because smart dust consists of tiny, wireless microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) that enable granular environmental monitoring, while IoT sensors are larger devices designed for specific, targeted data collection. Smart dust can provide extensive, real-time data from numerous points, improving precision in process control and quality assurance. IoT sensors often support automation and predictive maintenance by monitoring key machinery and environmental parameters. Knowing their distinct applications helps manufacturers deploy the most effective technology for operational efficiency and cost savings.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Smart Dust | IoT Sensors |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Miniature wireless sensor networks capturing environmental data | Connected devices measuring physical or chemical changes |
| Size | Microscopic, often millimeter-scale | Small to medium, varies from centimeters to meters |
| Power Source | Energy harvesting or microbatteries | Batteries, wired power, or energy harvesting |
| Communication | Ad-hoc wireless mesh networks | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, cellular networks |
| Application | Precise environmental monitoring, large-scale distributed sensing | Real-time process monitoring, asset tracking, automation |
| Cost | Higher R&D cost; scalable for mass deployment | Widely available, lower unit cost |
| Data Accuracy | High spatial resolution, limited processing power | Variable accuracy with advanced analytics |
| Manufacturing Use | Micro-scale monitoring inside machinery and environments | Machine condition monitoring, quality control, predictive maintenance |
Which is better?
Smart dust offers unparalleled nanoscale sensing capabilities ideal for monitoring environments at a granular level, while IoT sensors provide broader, more established connectivity and integration across manufacturing systems. IoT sensors are preferred for real-time data collection, predictive maintenance, and automation due to their scalability and interoperability with existing industrial infrastructure. Smart dust, though revolutionary, remains experimental with challenges in deployment and data processing that currently limit its widespread manufacturing use.
Connection
Smart dust consists of tiny, wireless microelectromechanical sensors that collect real-time data in manufacturing environments, enhancing precision and efficiency. IoT sensors integrate with smart dust technology by transmitting collected data to centralized systems for analysis and automated decision-making. Together, they enable advanced monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimized production workflows in smart factories.
Key Terms
Data Collection
IoT sensors collect data through interconnected devices, enabling real-time monitoring and analysis across various industries such as agriculture, healthcare, and manufacturing. Smart dust consists of tiny, wireless microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) capable of sensing environmental variables at a granular level, offering unprecedented spatial resolution in data collection. Explore the distinctive advantages and applications of both technologies to understand their impact on data-driven decision-making.
Miniaturization
IoT sensors and smart dust represent advancements in miniaturization, with smart dust pushing boundaries by integrating microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) for ultra-small, wireless sensing capabilities. IoT sensors vary in size depending on application but generally remain larger, focusing on connectivity and data transmission efficiency. Discover how miniaturization drives innovation in environmental monitoring and healthcare by exploring smart dust technologies in depth.
Wireless Communication
IoT sensors primarily rely on established wireless communication protocols such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and Zigbee, enabling robust data transmission over moderate distances with reliable power consumption. Smart dust, composed of ultra-miniature sensor nodes, utilizes low-power, short-range wireless communication often based on novel protocols optimized for ultra-low energy usage and dense network deployment. Explore the advancements in wireless communication technologies driving the future of IoT and smart dust for detailed insights.
Source and External Links
Top 10 IoT Sensor Types, Use Cases, and Examples - Simbase - IoT sensors are devices that collect environmental data like temperature, humidity, motion, light, and gas, transmitting it via the Internet to create smart, interconnected systems used across industries such as agriculture, healthcare, and smart cities.
16 Types of IoT Sensors | Built In - IoT sensors, integrated into devices like thermostats and cars, capture data such as air quality, electric current, and biomedical signals, sending it in real time to the cloud for remote monitoring and analysis.
16 Types of sensors used in IoT - Freeeway - IoT sensors are electronic chipsets that detect environmental conditions through physical contact, radiation, or magnetic fields, classified as passive or active sensors, and often combined with AI and cloud computing for data-driven actions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com