Adaptive machining employs real-time data and sensor feedback to dynamically adjust cutting parameters, enhancing precision and reducing waste in manufacturing processes. Digital twin technology creates a virtual replica of physical assets, enabling simulation and predictive maintenance to optimize production efficiency and minimize downtime. Explore how these advanced technologies are transforming modern manufacturing workflows.
Why it is important
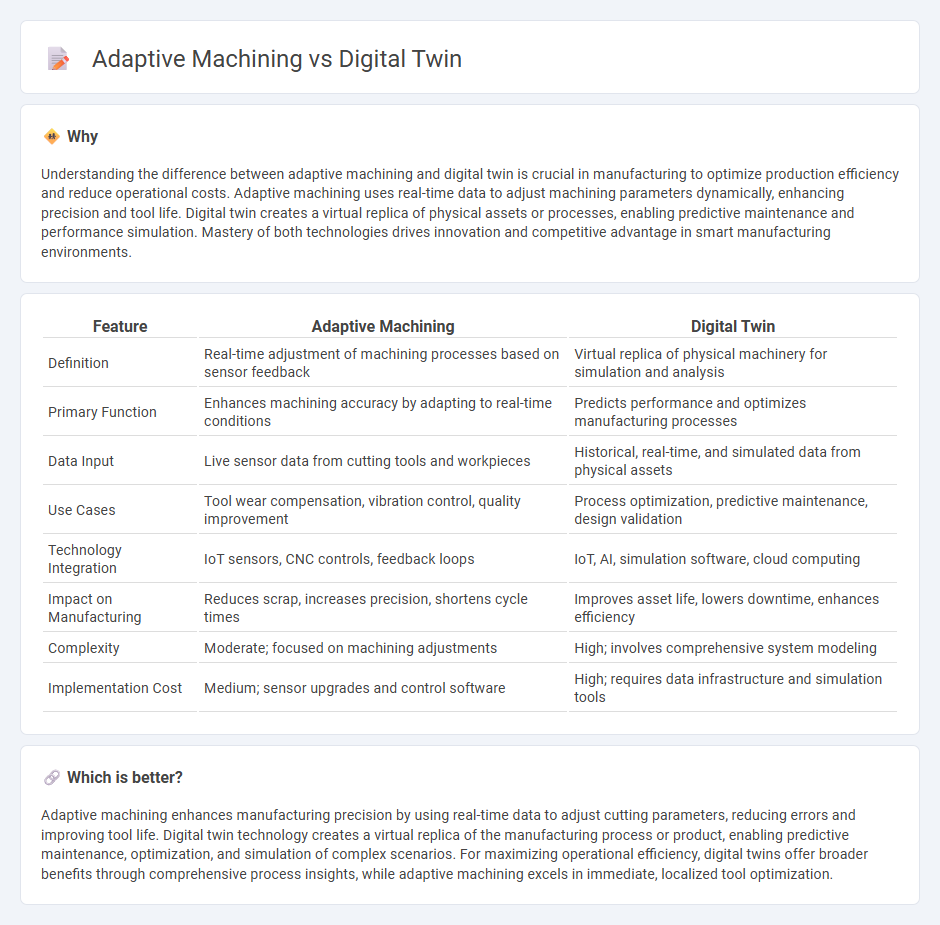
Understanding the difference between adaptive machining and digital twin is crucial in manufacturing to optimize production efficiency and reduce operational costs. Adaptive machining uses real-time data to adjust machining parameters dynamically, enhancing precision and tool life. Digital twin creates a virtual replica of physical assets or processes, enabling predictive maintenance and performance simulation. Mastery of both technologies drives innovation and competitive advantage in smart manufacturing environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Adaptive Machining | Digital Twin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time adjustment of machining processes based on sensor feedback | Virtual replica of physical machinery for simulation and analysis |
| Primary Function | Enhances machining accuracy by adapting to real-time conditions | Predicts performance and optimizes manufacturing processes |
| Data Input | Live sensor data from cutting tools and workpieces | Historical, real-time, and simulated data from physical assets |
| Use Cases | Tool wear compensation, vibration control, quality improvement | Process optimization, predictive maintenance, design validation |
| Technology Integration | IoT sensors, CNC controls, feedback loops | IoT, AI, simulation software, cloud computing |
| Impact on Manufacturing | Reduces scrap, increases precision, shortens cycle times | Improves asset life, lowers downtime, enhances efficiency |
| Complexity | Moderate; focused on machining adjustments | High; involves comprehensive system modeling |
| Implementation Cost | Medium; sensor upgrades and control software | High; requires data infrastructure and simulation tools |
Which is better?
Adaptive machining enhances manufacturing precision by using real-time data to adjust cutting parameters, reducing errors and improving tool life. Digital twin technology creates a virtual replica of the manufacturing process or product, enabling predictive maintenance, optimization, and simulation of complex scenarios. For maximizing operational efficiency, digital twins offer broader benefits through comprehensive process insights, while adaptive machining excels in immediate, localized tool optimization.
Connection
Adaptive machining enhances manufacturing precision by continuously adjusting machine parameters based on real-time sensor data. Digital twin technology creates a virtual replica of the physical machining process, enabling simulations and predictive analytics. Integrating digital twins with adaptive machining allows manufacturers to optimize performance, reduce downtime, and improve product quality through data-driven decision-making.
Key Terms
Real-time simulation
Digital twin technology enables real-time simulation by creating a virtual replica of a physical machine, allowing continuous monitoring and predictive analysis to optimize performance and prevent failures. Adaptive machining leverages real-time data from sensors to adjust cutting parameters dynamically, improving precision and tool life during the manufacturing process. Explore the detailed differences and applications of digital twins and adaptive machining in manufacturing for enhanced operational efficiency.
Sensor feedback
Digital twins integrate real-time sensor feedback to create virtual replicas of physical systems, enabling precise monitoring and predictive maintenance. Adaptive machining uses sensor inputs to adjust machining parameters dynamically, optimizing tool performance and minimizing defects during manufacturing. Explore how sensor feedback revolutionizes industrial processes by enhancing accuracy and efficiency.
Process optimization
Digital twin technology simulates manufacturing processes in real-time, enabling precise monitoring and predictive maintenance to optimize production efficiency. Adaptive machining adjusts cutting parameters dynamically based on sensor feedback to improve tool life and part quality. Explore in-depth how these innovations drive process optimization in modern manufacturing.
Source and External Links
Definition of a Digital Twin - A digital twin is an integrated data-driven virtual representation of real-world entities and processes, synchronized in real time, used to accelerate understanding, decision-making, and improvement of those entities or processes.
What Is a Digital Twin? - A digital twin is a virtual model of a physical object or system that uses real-time data from sensors to simulate, analyze, and optimize its physical counterpart throughout its lifecycle.
Digital twin - A digital twin is a digital model of a real-world physical product, system, or process that replicates behavior using adaptive models updated with real-time data to predict failures and optimize performance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com