Microfactories focus on compact, modular production units designed for customization and rapid deployment, enabling localized manufacturing with reduced lead times and lower capital investment. Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) integrate automated machinery and computer-controlled processes to efficiently produce varied products on shared equipment, maximizing throughput and minimizing downtime. Discover how these innovative manufacturing approaches can transform your production strategy.
Why it is important
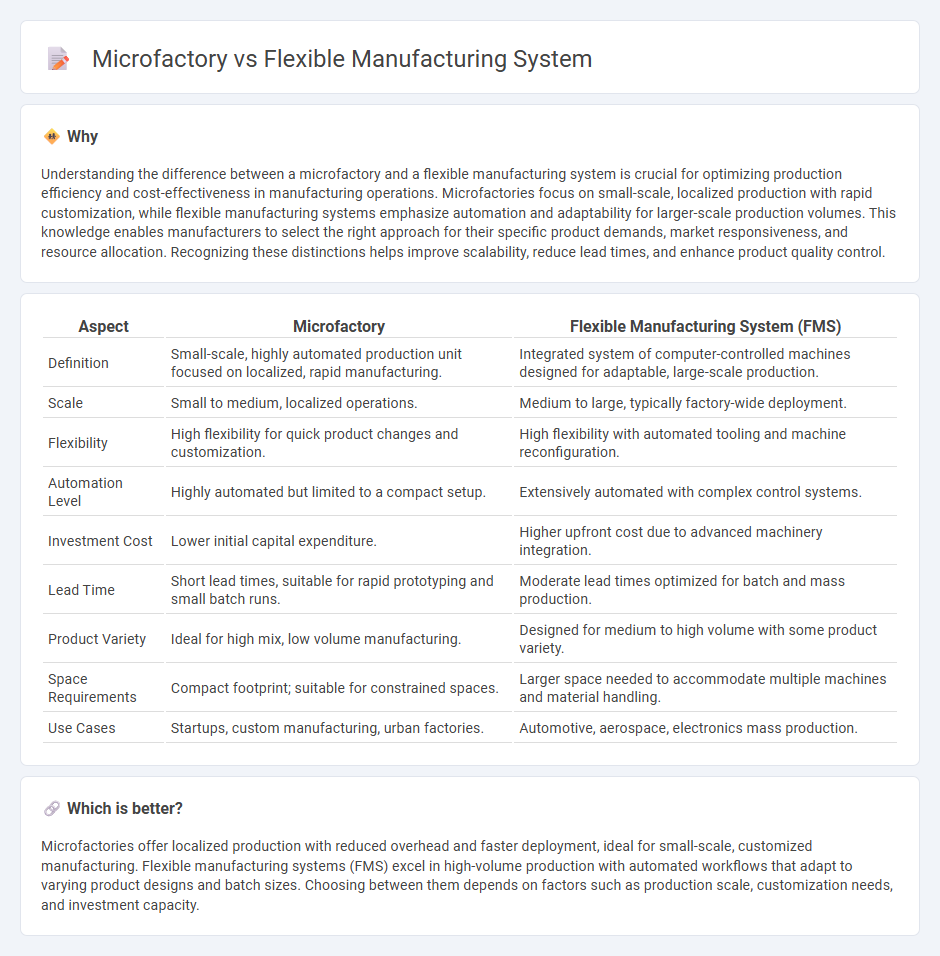
Understanding the difference between a microfactory and a flexible manufacturing system is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and cost-effectiveness in manufacturing operations. Microfactories focus on small-scale, localized production with rapid customization, while flexible manufacturing systems emphasize automation and adaptability for larger-scale production volumes. This knowledge enables manufacturers to select the right approach for their specific product demands, market responsiveness, and resource allocation. Recognizing these distinctions helps improve scalability, reduce lead times, and enhance product quality control.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microfactory | Flexible Manufacturing System (FMS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small-scale, highly automated production unit focused on localized, rapid manufacturing. | Integrated system of computer-controlled machines designed for adaptable, large-scale production. |
| Scale | Small to medium, localized operations. | Medium to large, typically factory-wide deployment. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility for quick product changes and customization. | High flexibility with automated tooling and machine reconfiguration. |
| Automation Level | Highly automated but limited to a compact setup. | Extensively automated with complex control systems. |
| Investment Cost | Lower initial capital expenditure. | Higher upfront cost due to advanced machinery integration. |
| Lead Time | Short lead times, suitable for rapid prototyping and small batch runs. | Moderate lead times optimized for batch and mass production. |
| Product Variety | Ideal for high mix, low volume manufacturing. | Designed for medium to high volume with some product variety. |
| Space Requirements | Compact footprint; suitable for constrained spaces. | Larger space needed to accommodate multiple machines and material handling. |
| Use Cases | Startups, custom manufacturing, urban factories. | Automotive, aerospace, electronics mass production. |
Which is better?
Microfactories offer localized production with reduced overhead and faster deployment, ideal for small-scale, customized manufacturing. Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) excel in high-volume production with automated workflows that adapt to varying product designs and batch sizes. Choosing between them depends on factors such as production scale, customization needs, and investment capacity.
Connection
Microfactories utilize flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) to enhance adaptability and efficiency in small-scale production environments. Flexible manufacturing systems integrate automated machinery and computerized controls, enabling microfactories to quickly switch between product types and customize outputs. This synergy reduces lead times and operational costs while maintaining high quality in manufacturing processes.
Key Terms
**Flexible Manufacturing System:**
Flexible Manufacturing System (FMS) integrates computer-controlled machines, automated material handling, and centralized control to enable rapid adaptation to changing product designs and volumes, optimizing efficiency and reducing downtime in production lines. This system excels in batch production environments where diverse product types require frequent changeovers, enhancing scalability and operational flexibility. Discover more about how FMS can revolutionize your manufacturing processes with advanced automation and precision.
Automation
Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) integrate automated machinery and robotics to enable efficient production of varied product types with minimal manual intervention, optimizing customization and batch size flexibility. Microfactories emphasize compact, highly automated environments designed for rapid deployment, localized manufacturing, and reduced material waste through AI-driven process control and smart robotics. Explore further to understand how automation innovations drive efficiency in these advanced manufacturing models.
CNC Machines
Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) integrate CNC machines with automated material handling and computer-controlled operations to optimize production flexibility and efficiency for medium to large-scale manufacturing. Microfactories emphasize compact, highly specialized setups often using CNC machines tailored for small-batch or customized production, allowing rapid reconfiguration and reduced footprint. Explore detailed comparisons on CNC applications within FMS and microfactories to understand their impact on manufacturing agility and productivity.
Source and External Links
Flexible manufacturing system - A flexible manufacturing system (FMS) is a manufacturing system with the ability to adapt to changes such as new product types or operation orders, consisting mainly of automated CNC machines, material handling systems, and a central control computer, providing advantages like reduced costs, improved quality, and faster production rates.
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) | What is ... - FMS is a computer-controlled production setup designed to adapt at any time to changes like product details or production sequence through routing flexibility and machine flexibility, with various types such as dedicated, sequential, engineered, random, and modular FMS to serve different manufacturing needs.
How Flexible Manufacturing System (FMS) is Changing ... - An FMS integrates computer-controlled scheduling, material handling, and synchronized operations using automation like AGVs and conveyors, enabling real-time adaptation, rerouting, and quality maintenance, resulting in a responsive and self-learning manufacturing ecosystem.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com