Machine vision systems use cameras and advanced image processing to inspect, guide, and analyze manufacturing processes with high precision and speed. Industrial sensors detect physical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and proximity to ensure equipment safety and operational efficiency. Explore the differences and applications of machine vision versus industrial sensors to optimize your manufacturing solutions.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between machine vision and industrial sensors is crucial because machine vision systems capture and analyze visual data for quality control, object recognition, and precise measurements, while industrial sensors detect physical conditions like temperature, pressure, or proximity. Machine vision enhances automation by providing detailed inspection capabilities, whereas industrial sensors offer real-time monitoring of environmental or operational parameters. Choosing the correct technology optimizes manufacturing efficiency, reduces errors, and improves overall product quality. This knowledge enables tailored integration into production lines, maximizing ROI and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
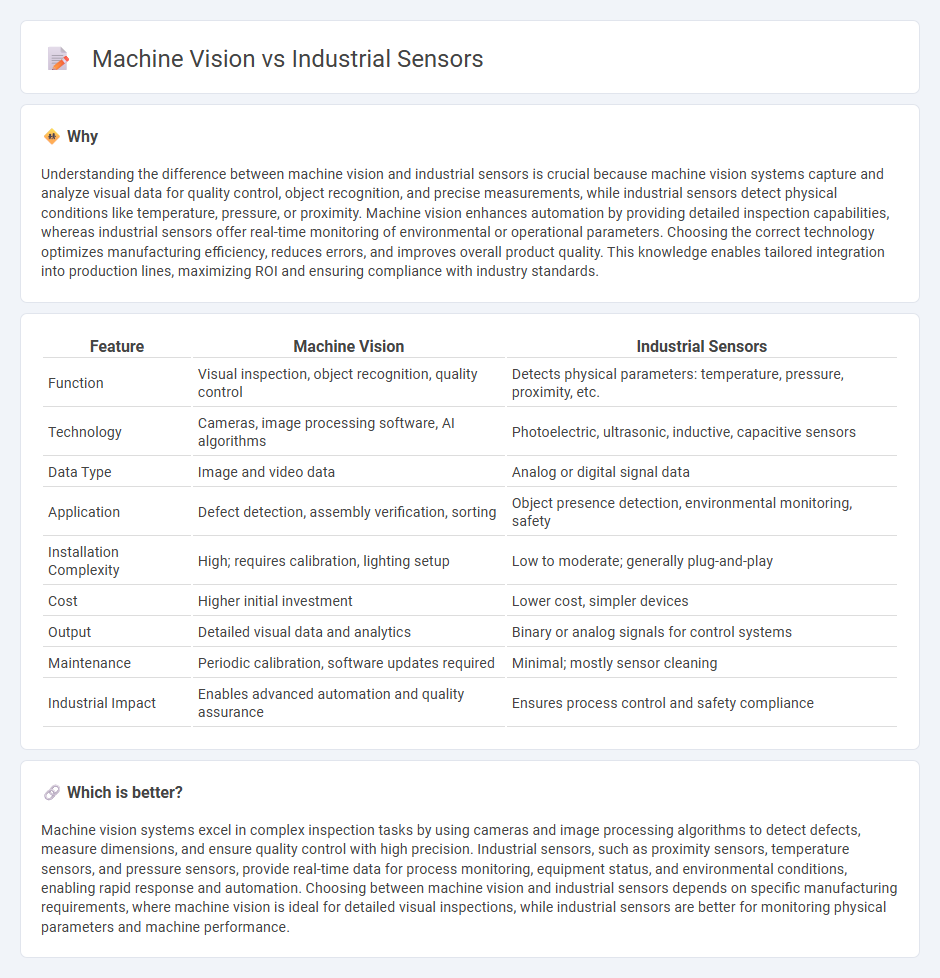
Comparison Table
| Feature | Machine Vision | Industrial Sensors |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Visual inspection, object recognition, quality control | Detects physical parameters: temperature, pressure, proximity, etc. |
| Technology | Cameras, image processing software, AI algorithms | Photoelectric, ultrasonic, inductive, capacitive sensors |
| Data Type | Image and video data | Analog or digital signal data |
| Application | Defect detection, assembly verification, sorting | Object presence detection, environmental monitoring, safety |
| Installation Complexity | High; requires calibration, lighting setup | Low to moderate; generally plug-and-play |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower cost, simpler devices |
| Output | Detailed visual data and analytics | Binary or analog signals for control systems |
| Maintenance | Periodic calibration, software updates required | Minimal; mostly sensor cleaning |
| Industrial Impact | Enables advanced automation and quality assurance | Ensures process control and safety compliance |
Which is better?
Machine vision systems excel in complex inspection tasks by using cameras and image processing algorithms to detect defects, measure dimensions, and ensure quality control with high precision. Industrial sensors, such as proximity sensors, temperature sensors, and pressure sensors, provide real-time data for process monitoring, equipment status, and environmental conditions, enabling rapid response and automation. Choosing between machine vision and industrial sensors depends on specific manufacturing requirements, where machine vision is ideal for detailed visual inspections, while industrial sensors are better for monitoring physical parameters and machine performance.
Connection
Machine vision systems and industrial sensors are interconnected through data acquisition and real-time monitoring, enabling precise quality control and automation in manufacturing processes. Industrial sensors capture physical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and proximity, while machine vision systems analyze visual data to detect defects and guide robotic operations. Integrating these technologies enhances operational efficiency, reduces downtime, and improves product consistency in smart factories.
Key Terms
Data Acquisition
Industrial sensors provide precise point measurements of physical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and vibration, delivering real-time data essential for monitoring and control. Machine vision systems capture detailed images to analyze patterns, defects, and object positioning, enabling complex visual inspections and dimensional measurements. Explore how each technology enhances data acquisition in industrial automation to optimize performance and quality.
Defect Detection
Industrial sensors such as proximity sensors, pressure sensors, and temperature sensors provide real-time data essential for monitoring manufacturing conditions, while machine vision systems utilize cameras and AI algorithms to detect surface defects and quality inconsistencies with high precision. Machine vision excels in identifying visual anomalies like scratches, dents, and misalignments that traditional sensors might overlook, enhancing defect detection accuracy and reducing false positives. Discover more about how combining industrial sensors and machine vision can optimize defect detection processes in your production line.
Automation
Industrial sensors provide precise data on temperature, pressure, and proximity essential for automation control systems, enabling real-time monitoring and feedback loops. Machine vision systems use advanced cameras and image processing algorithms to detect defects, guide robotic arms, and perform quality inspections with high accuracy. Explore how integrating both technologies revolutionizes automation efficiency and accuracy.
Source and External Links
Types of Industrial Manufacturing Sensors | KEYENCE America - Describes the key roles of temperature, pressure, proximity, flow, and level sensors in monitoring and controlling manufacturing processes to ensure efficiency and quality.
Types of Industrial Sensors - Automation - Renke - Highlights the evolution of smart sensors for industrial automation, emphasizing their role in collecting, analyzing, and transmitting data for intelligent manufacturing and Industry 4.0 applications.
Types of Industrial Sensors: Manufacturing, Automation, IoT, & More - Categorizes industrial sensors by function--such as position, pressure, temperature, vibration, motion, flow, and level--and their specific uses in diverse industrial environments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com