Decentralized manufacturing distributes production across multiple locations, enhancing responsiveness and reducing supply chain risks by localizing operations. Flexible manufacturing employs adaptable systems and machinery to switch quickly between product types, increasing efficiency and meeting variable market demands. Explore further to understand how these approaches transform modern production strategies.
Why it is important
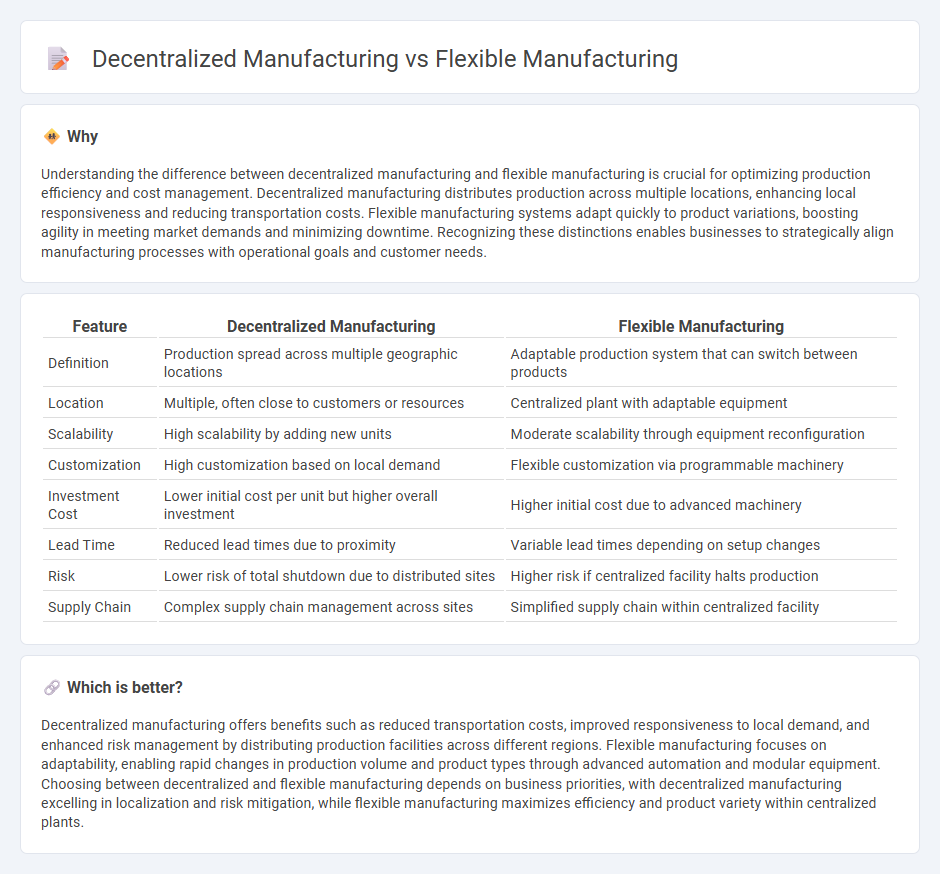
Understanding the difference between decentralized manufacturing and flexible manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and cost management. Decentralized manufacturing distributes production across multiple locations, enhancing local responsiveness and reducing transportation costs. Flexible manufacturing systems adapt quickly to product variations, boosting agility in meeting market demands and minimizing downtime. Recognizing these distinctions enables businesses to strategically align manufacturing processes with operational goals and customer needs.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Manufacturing | Flexible Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Production spread across multiple geographic locations | Adaptable production system that can switch between products |
| Location | Multiple, often close to customers or resources | Centralized plant with adaptable equipment |
| Scalability | High scalability by adding new units | Moderate scalability through equipment reconfiguration |
| Customization | High customization based on local demand | Flexible customization via programmable machinery |
| Investment Cost | Lower initial cost per unit but higher overall investment | Higher initial cost due to advanced machinery |
| Lead Time | Reduced lead times due to proximity | Variable lead times depending on setup changes |
| Risk | Lower risk of total shutdown due to distributed sites | Higher risk if centralized facility halts production |
| Supply Chain | Complex supply chain management across sites | Simplified supply chain within centralized facility |
Which is better?
Decentralized manufacturing offers benefits such as reduced transportation costs, improved responsiveness to local demand, and enhanced risk management by distributing production facilities across different regions. Flexible manufacturing focuses on adaptability, enabling rapid changes in production volume and product types through advanced automation and modular equipment. Choosing between decentralized and flexible manufacturing depends on business priorities, with decentralized manufacturing excelling in localization and risk mitigation, while flexible manufacturing maximizes efficiency and product variety within centralized plants.
Connection
Decentralized manufacturing distributes production processes across multiple locations, enhancing responsiveness and reducing supply chain risks. Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) enable quick adaptation to product changes and volume fluctuations, supporting diverse customer demands. Together, decentralized manufacturing leverages flexible manufacturing technologies to increase efficiency, scalability, and customization in production networks.
Key Terms
**Flexible Manufacturing:**
Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) enable rapid production adjustments by utilizing computer-controlled machines and automation to handle diverse products within a single facility, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime. These systems are particularly advantageous for industries requiring customization and quick response to market changes, such as automotive and electronics manufacturing. Explore more to understand how flexible manufacturing drives innovation and operational agility in modern production environments.
Automation
Flexible manufacturing employs advanced automation systems to adapt production lines quickly for various products, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime. Decentralized manufacturing relies on multiple automated facilities distributed geographically, enabling localized production and faster response to market demands. Explore how automation transforms both manufacturing strategies to optimize productivity and innovation.
Reconfigurability
Flexible manufacturing systems enable rapid adaptation to changes in product design or volume through modular equipment and programmable controls, enhancing reconfigurability by allowing quick setup changes and scalability. Decentralized manufacturing disperses production capabilities across multiple locations, improving reconfigurability by enabling localized customization and reduced dependency on single facilities. Explore further to understand how reconfigurability drives efficiency and responsiveness in diverse manufacturing environments.
Source and External Links
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) - Autodesk - A flexible manufacturing system (FMS) is a computer-controlled production setup designed to adapt to product changes with routing flexibility (changing production sequence) and machine flexibility (using different machines for the same product), including types like dedicated, sequential, engineered, random, and modular FMS to fit various manufacturing needs.
Flexible manufacturing system - Wikipedia - FMS is a manufacturing system that reacts to changes through routing and machine flexibility, involving automated CNC machines, material handling systems, and central control computers, offering advantages such as reduced costs, higher productivity, improved quality, and shorter lead times.
What is Flexible Manufacturing - Big Sky Engineering, Inc. - Flexible manufacturing enables companies to rapidly adapt production to different parts or markets with minimal retooling, enhancing production flexibility, faster turnaround, and efficiency while lowering costs by optimizing processes and workforce.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com