Cobots, or collaborative robots, enhance manufacturing by working safely alongside human operators, improving flexibility and precision in assembly tasks compared to traditional assembly lines. Unlike fixed automation, cobots adapt quickly to changes, reducing downtime and increasing productivity with real-time data integration. Explore how cobots revolutionize manufacturing efficiency and workforce collaboration.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between cobots and traditional assembly lines is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and reducing labor costs. Cobots enhance flexibility by collaborating safely with human workers, enabling customized production runs and faster changeovers. Traditional assembly lines are best suited for high-volume, repetitive tasks but lack adaptability. Choosing the right approach impacts overall productivity, safety, and return on investment in manufacturing operations.
Comparison Table
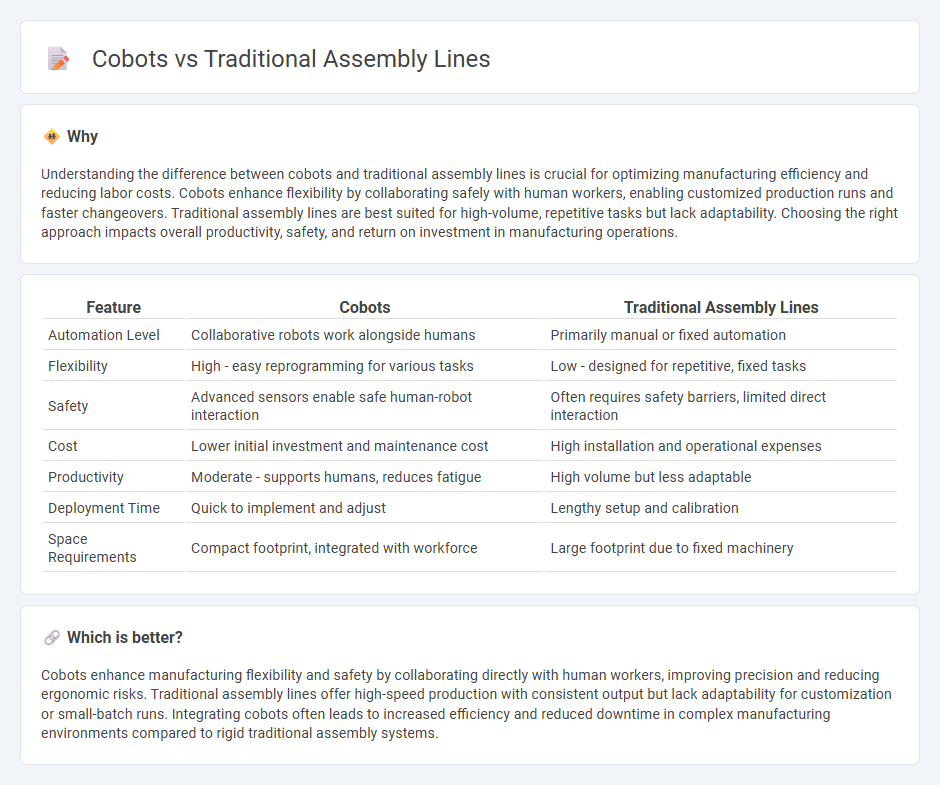
| Feature | Cobots | Traditional Assembly Lines |
|---|---|---|
| Automation Level | Collaborative robots work alongside humans | Primarily manual or fixed automation |
| Flexibility | High - easy reprogramming for various tasks | Low - designed for repetitive, fixed tasks |
| Safety | Advanced sensors enable safe human-robot interaction | Often requires safety barriers, limited direct interaction |
| Cost | Lower initial investment and maintenance cost | High installation and operational expenses |
| Productivity | Moderate - supports humans, reduces fatigue | High volume but less adaptable |
| Deployment Time | Quick to implement and adjust | Lengthy setup and calibration |
| Space Requirements | Compact footprint, integrated with workforce | Large footprint due to fixed machinery |
Which is better?
Cobots enhance manufacturing flexibility and safety by collaborating directly with human workers, improving precision and reducing ergonomic risks. Traditional assembly lines offer high-speed production with consistent output but lack adaptability for customization or small-batch runs. Integrating cobots often leads to increased efficiency and reduced downtime in complex manufacturing environments compared to rigid traditional assembly systems.
Connection
Cobots enhance traditional assembly lines by integrating advanced automation with human collaboration, increasing precision and efficiency in manufacturing processes. These collaborative robots work alongside human operators, handling repetitive tasks while allowing workers to focus on complex problem-solving and quality control. The synergy between cobots and conventional assembly systems drives higher productivity, reduces error rates, and accelerates production cycles.
Key Terms
Human Labor
Traditional assembly lines rely heavily on human labor performing repetitive tasks, often leading to worker fatigue and increased risk of errors or injury. Cobots, or collaborative robots, work alongside humans, enhancing productivity by automating strenuous or monotonous tasks while enabling workers to engage in more complex and creative activities. Discover how integrating cobots can revolutionize workforce efficiency and safety in your manufacturing process.
Automation
Traditional assembly lines rely heavily on human labor for repetitive tasks, often leading to slower production rates and higher error margins. Cobots, or collaborative robots, enhance automation by working alongside humans to increase precision, flexibility, and efficiency in manufacturing processes. Discover how integrating cobots can transform your assembly line and boost productivity.
Collaborative Robots
Collaborative robots (cobots) are transforming traditional assembly lines by enhancing flexibility, precision, and safety in manufacturing processes. Unlike conventional automated systems, cobots work alongside human operators, adapting seamlessly to complex tasks and reducing the risk of workplace injuries. Explore the advantages and integration strategies of cobots to revolutionize your assembly line performance.
Source and External Links
The Different Types of Assembly Lines in Manufacturing - Classic assembly lines use sequential steps performed by different workers to build identical products, exemplified by early car manufacturing methods.
Assembly line - In traditional assembly lines, products move through multiple stations, each responsible for a specific part of assembly, allowing simultaneous work on several units and improving overall throughput.
Manufacturing Assembly Line: Understanding the Set-up - Traditional assembly lines are characterized by a linear series of workstations where each worker or group performs a defined task in sequence to construct the final product.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com