Factory as a Service (FaaS) offers on-demand access to manufacturing facilities, enabling companies to scale production without heavy capital expenditure or long-term commitments. Distributed manufacturing decentralizes production by utilizing multiple small-scale factories closer to end-users, reducing logistics costs and lead times while increasing flexibility. Explore how these innovative manufacturing models can revolutionize your production strategy.
Why it is important
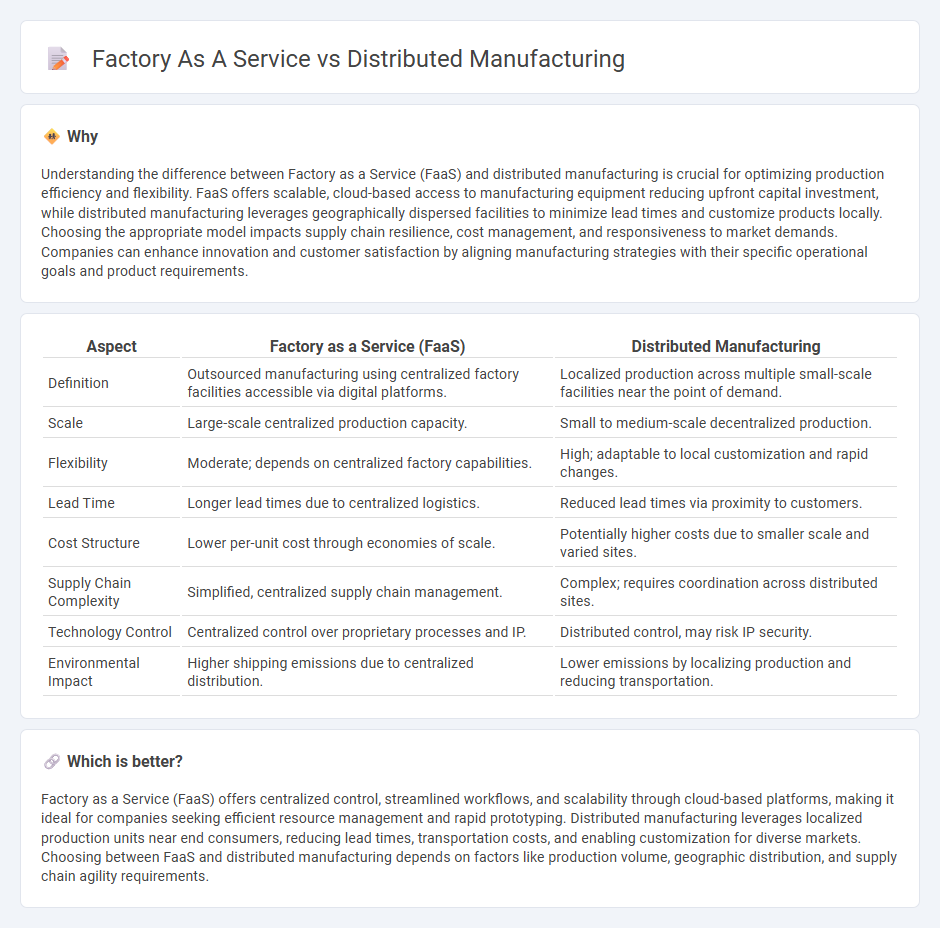
Understanding the difference between Factory as a Service (FaaS) and distributed manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and flexibility. FaaS offers scalable, cloud-based access to manufacturing equipment reducing upfront capital investment, while distributed manufacturing leverages geographically dispersed facilities to minimize lead times and customize products locally. Choosing the appropriate model impacts supply chain resilience, cost management, and responsiveness to market demands. Companies can enhance innovation and customer satisfaction by aligning manufacturing strategies with their specific operational goals and product requirements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Factory as a Service (FaaS) | Distributed Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Outsourced manufacturing using centralized factory facilities accessible via digital platforms. | Localized production across multiple small-scale facilities near the point of demand. |
| Scale | Large-scale centralized production capacity. | Small to medium-scale decentralized production. |
| Flexibility | Moderate; depends on centralized factory capabilities. | High; adaptable to local customization and rapid changes. |
| Lead Time | Longer lead times due to centralized logistics. | Reduced lead times via proximity to customers. |
| Cost Structure | Lower per-unit cost through economies of scale. | Potentially higher costs due to smaller scale and varied sites. |
| Supply Chain Complexity | Simplified, centralized supply chain management. | Complex; requires coordination across distributed sites. |
| Technology Control | Centralized control over proprietary processes and IP. | Distributed control, may risk IP security. |
| Environmental Impact | Higher shipping emissions due to centralized distribution. | Lower emissions by localizing production and reducing transportation. |
Which is better?
Factory as a Service (FaaS) offers centralized control, streamlined workflows, and scalability through cloud-based platforms, making it ideal for companies seeking efficient resource management and rapid prototyping. Distributed manufacturing leverages localized production units near end consumers, reducing lead times, transportation costs, and enabling customization for diverse markets. Choosing between FaaS and distributed manufacturing depends on factors like production volume, geographic distribution, and supply chain agility requirements.
Connection
Factory as a Service (FaaS) leverages cloud-based platforms to enable on-demand access to manufacturing resources, facilitating distributed manufacturing by connecting geographically dispersed production units through digital networks. Distributed manufacturing decentralizes production processes, allowing factories to produce goods closer to end-users, which reduces lead times and logistics costs. The integration of FaaS with distributed manufacturing creates a scalable, flexible ecosystem that optimizes resource utilization and enhances responsiveness to market demands.
Key Terms
**Distributed Manufacturing:**
Distributed manufacturing leverages multiple decentralized production sites to increase flexibility, reduce lead times, and lower logistics costs by producing goods closer to end customers. This model enables rapid scalability and customization, driven by digital technologies like additive manufacturing and IoT-enabled smart factories. Discover how distributed manufacturing revolutionizes production efficiency and supply chain resilience.
Decentralization
Distributed manufacturing leverages multiple decentralized production sites, reducing dependency on a single factory and enabling localized, flexible manufacturing closer to end consumers. Factory as a service (FaaS) provides on-demand access to advanced manufacturing capabilities without owning physical facilities, but typically centers around centralized resources and platforms. Explore how decentralization in these models transforms supply chains and manufacturing agility.
Local Production
Distributed manufacturing enables local production by using a network of smaller, decentralized facilities to produce goods closer to the end consumer, reducing transportation costs and lead times. Factory as a Service (FaaS) provides on-demand access to manufacturing infrastructure and expertise, allowing businesses to scale production locally without heavy upfront investments. Explore how leveraging distributed manufacturing and FaaS can revolutionize local production strategies and enhance supply chain resilience.
Source and External Links
Distributed manufacturing benefits: Revolutionizing production - Distributed manufacturing is a model using a network of smaller, geographically dispersed production facilities connected through digital technologies to enable localized, flexible production closer to consumers, reducing shipping costs and improving responsiveness to market demands.
Distributed Manufacturing: The Way of the Future? - Distributed manufacturing organizes production across many locations, often near end-users, leveraging approaches like localized, modular, and on-demand production, and focusing also on sustainability through recycling and upcycling.
What Is Distributed Manufacturing? - MRPeasy Blog - Distributed manufacturing is a business model where products are made in multiple smaller facilities over wide areas, centrally managed but producing customized products locally to reduce lead time, distribution cost, and enhance sustainability and risk diffusion.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com