Industrial Internet integrates advanced sensors, big data analytics, and cloud computing to optimize manufacturing processes, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Human-Machine Interface (HMI) focuses on the direct interaction between operators and machinery, enhancing usability and control through intuitive displays and controls. Discover how combining Industrial Internet with HMI transforms modern manufacturing efficiency and worker productivity.
Why it is important
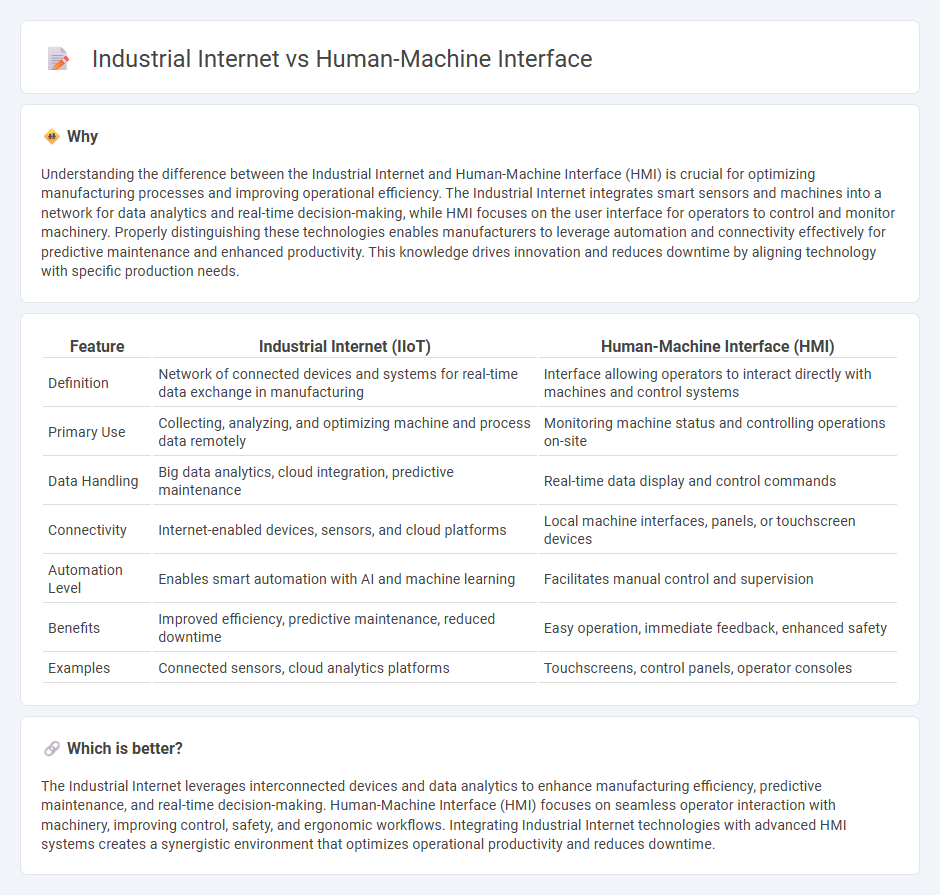
Understanding the difference between the Industrial Internet and Human-Machine Interface (HMI) is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes and improving operational efficiency. The Industrial Internet integrates smart sensors and machines into a network for data analytics and real-time decision-making, while HMI focuses on the user interface for operators to control and monitor machinery. Properly distinguishing these technologies enables manufacturers to leverage automation and connectivity effectively for predictive maintenance and enhanced productivity. This knowledge drives innovation and reduces downtime by aligning technology with specific production needs.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Industrial Internet (IIoT) | Human-Machine Interface (HMI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network of connected devices and systems for real-time data exchange in manufacturing | Interface allowing operators to interact directly with machines and control systems |
| Primary Use | Collecting, analyzing, and optimizing machine and process data remotely | Monitoring machine status and controlling operations on-site |
| Data Handling | Big data analytics, cloud integration, predictive maintenance | Real-time data display and control commands |
| Connectivity | Internet-enabled devices, sensors, and cloud platforms | Local machine interfaces, panels, or touchscreen devices |
| Automation Level | Enables smart automation with AI and machine learning | Facilitates manual control and supervision |
| Benefits | Improved efficiency, predictive maintenance, reduced downtime | Easy operation, immediate feedback, enhanced safety |
| Examples | Connected sensors, cloud analytics platforms | Touchscreens, control panels, operator consoles |
Which is better?
The Industrial Internet leverages interconnected devices and data analytics to enhance manufacturing efficiency, predictive maintenance, and real-time decision-making. Human-Machine Interface (HMI) focuses on seamless operator interaction with machinery, improving control, safety, and ergonomic workflows. Integrating Industrial Internet technologies with advanced HMI systems creates a synergistic environment that optimizes operational productivity and reduces downtime.
Connection
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) enhances manufacturing efficiency by integrating Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) with real-time data analytics and machine connectivity. HMIs serve as critical touchpoints for operators to monitor and control industrial equipment, facilitating seamless communication between humans and automated systems. This synergy accelerates predictive maintenance, reduces downtime, and optimizes production workflows in smart factories.
Key Terms
**Human-Machine Interface (HMI):**
Human-Machine Interface (HMI) serves as the critical communication platform between operators and industrial machines, enhancing real-time data visualization and control capabilities through intuitive graphical interfaces. Advanced HMIs integrate touchscreens, voice commands, and augmented reality to improve operational efficiency and reduce human errors in complex manufacturing environments. Explore the latest trends and technologies in HMI to optimize your industrial processes and workforce interaction.
Touchscreen Panels
Human-Machine Interface (HMI) touchscreen panels serve as essential components in industrial automation by enabling direct operator control and monitoring of machinery through intuitive graphical interfaces. Industrial Internet technologies integrate these HMIs with networked sensors and cloud-based analytics to enhance real-time data exchange, predictive maintenance, and operational efficiency. Explore how the convergence of HMI touchscreen panels and Industrial Internet solutions transforms manufacturing processes for smarter factories.
SCADA Systems
SCADA systems serve as critical human-machine interfaces (HMI) in industrial internet environments, enabling real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes through centralized data acquisition. These systems optimize operational efficiency by integrating sensors, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and networked communication within the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) framework. Discover how advanced SCADA solutions are transforming industrial automation and enhancing decision-making capabilities in complex industrial settings.
Source and External Links
Human Machine Interface (HMI) Software & Solutions - Human Machine Interface (HMI) refers to a dashboard or screen used to control machinery, enabling operators and managers to monitor and manage industrial processes efficiently by translating real-time data into easy-to-understand visual displays.
What is HMI? Human Machine Interface - An HMI is a user interface or dashboard connecting a person to a machine, typically used in industrial settings to display data, track production, monitor inputs/outputs, and provide control capabilities.
Touch Panel HMI - Human Machine Interfaces - An HMI is a digital product facilitating operator communication with automated equipment, featuring touch panels for easy configuration, communication ports, and display screens for machine monitoring, with advanced models supporting wireless connectivity and custom interfaces.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com