Lights-out manufacturing leverages fully automated production systems that operate without human intervention, maximizing efficiency and reducing labor costs. Green manufacturing focuses on eco-friendly processes, minimizing waste, energy consumption, and carbon emissions to promote sustainability. Explore the key differences and benefits of these advanced manufacturing approaches to understand their impact on the industry.
Why it is important
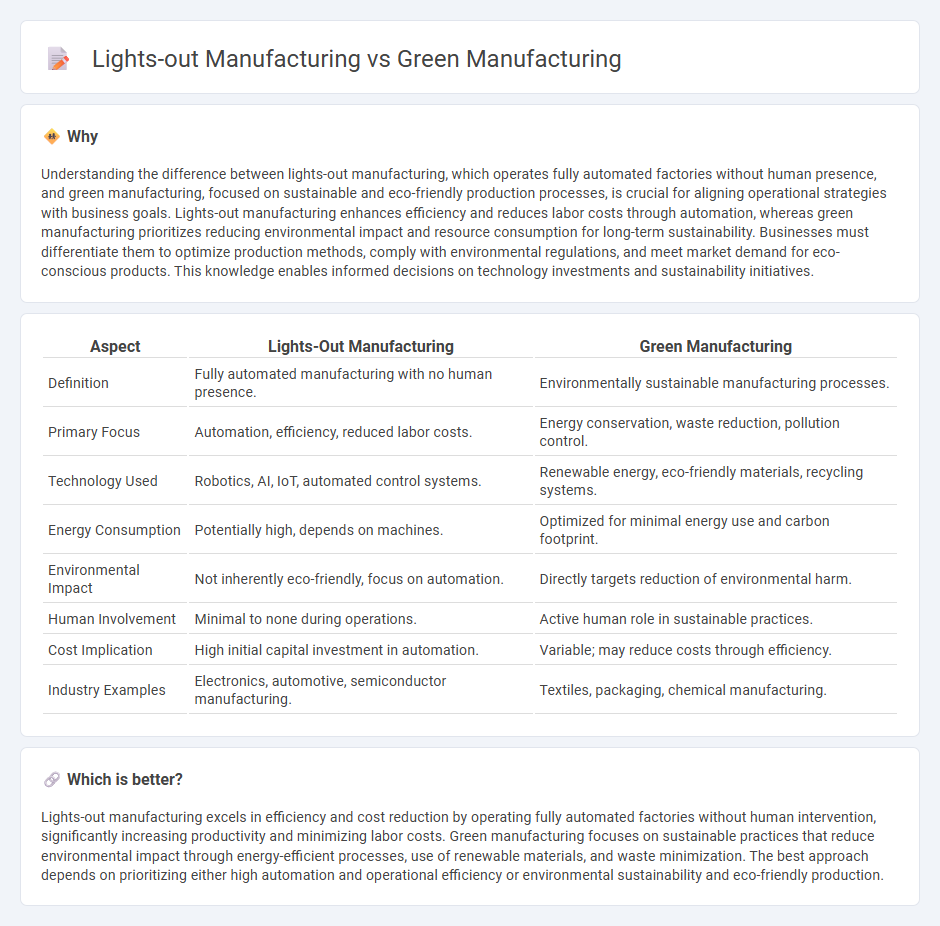
Understanding the difference between lights-out manufacturing, which operates fully automated factories without human presence, and green manufacturing, focused on sustainable and eco-friendly production processes, is crucial for aligning operational strategies with business goals. Lights-out manufacturing enhances efficiency and reduces labor costs through automation, whereas green manufacturing prioritizes reducing environmental impact and resource consumption for long-term sustainability. Businesses must differentiate them to optimize production methods, comply with environmental regulations, and meet market demand for eco-conscious products. This knowledge enables informed decisions on technology investments and sustainability initiatives.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Lights-Out Manufacturing | Green Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated manufacturing with no human presence. | Environmentally sustainable manufacturing processes. |
| Primary Focus | Automation, efficiency, reduced labor costs. | Energy conservation, waste reduction, pollution control. |
| Technology Used | Robotics, AI, IoT, automated control systems. | Renewable energy, eco-friendly materials, recycling systems. |
| Energy Consumption | Potentially high, depends on machines. | Optimized for minimal energy use and carbon footprint. |
| Environmental Impact | Not inherently eco-friendly, focus on automation. | Directly targets reduction of environmental harm. |
| Human Involvement | Minimal to none during operations. | Active human role in sustainable practices. |
| Cost Implication | High initial capital investment in automation. | Variable; may reduce costs through efficiency. |
| Industry Examples | Electronics, automotive, semiconductor manufacturing. | Textiles, packaging, chemical manufacturing. |
Which is better?
Lights-out manufacturing excels in efficiency and cost reduction by operating fully automated factories without human intervention, significantly increasing productivity and minimizing labor costs. Green manufacturing focuses on sustainable practices that reduce environmental impact through energy-efficient processes, use of renewable materials, and waste minimization. The best approach depends on prioritizing either high automation and operational efficiency or environmental sustainability and eco-friendly production.
Connection
Lights-out manufacturing minimizes human intervention by using automated systems, reducing energy consumption and waste. Green manufacturing emphasizes sustainable practices, including energy efficiency and reduced emissions. Integrating lights-out technologies supports green manufacturing goals by lowering the environmental footprint of production processes.
Key Terms
**Green Manufacturing:**
Green manufacturing emphasizes sustainable production processes that reduce environmental impact by minimizing waste, optimizing energy use, and utilizing eco-friendly materials. Companies adopting green manufacturing often implement renewable energy sources and circular economy principles to achieve carbon footprint reduction and regulatory compliance. Explore more insights on how green manufacturing drives innovation and sustainability in modern industries.
Sustainability
Green manufacturing emphasizes reducing environmental impact through energy efficiency, waste minimization, and the use of renewable materials. Lights-out manufacturing relies on fully automated, unmanned production processes to increase efficiency and reduce energy consumption during non-operational hours, contributing indirectly to sustainability. Explore further to understand how these strategies complement each other in advancing sustainable industrial practices.
Energy Efficiency
Green manufacturing prioritizes reducing environmental impact through energy-efficient processes, renewable energy use, and waste minimization, aiming to lower carbon footprints and promote sustainability. Lights-out manufacturing emphasizes fully automated production systems that operate without human presence, significantly cutting energy consumption during off-hours and optimizing resource utilization. Explore the innovative strategies integrating both approaches to maximize energy efficiency in modern industry.
Source and External Links
What Is Green Manufacturing? - IBM - Green manufacturing is the creation of products in a way that reduces the carbon footprint, conserves energy and natural resources, and minimizes negative environmental impacts through practices like using renewable energy and sustainable materials.
What is Green Manufacturing? (Plus 5 Steps to a Greener Future) - Green manufacturing focuses on producing goods using eco-friendly processes and technologies to cut energy use, waste, and emissions, while maximizing resource efficiency and sustainability.
Sustainable Manufacturing | US EPA - Sustainable manufacturing involves creating products through economically-sound processes that minimize environmental impacts, conserve resources, and enhance safety for employees and communities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com