Lights-out manufacturing employs fully automated, unattended production processes to maximize efficiency and reduce labor costs. Flexible manufacturing systems adapt quickly to changing product designs and volumes, enhancing responsiveness and customization capabilities. Explore the distinct advantages and applications of both methods to optimize your industrial operations.
Why it is important
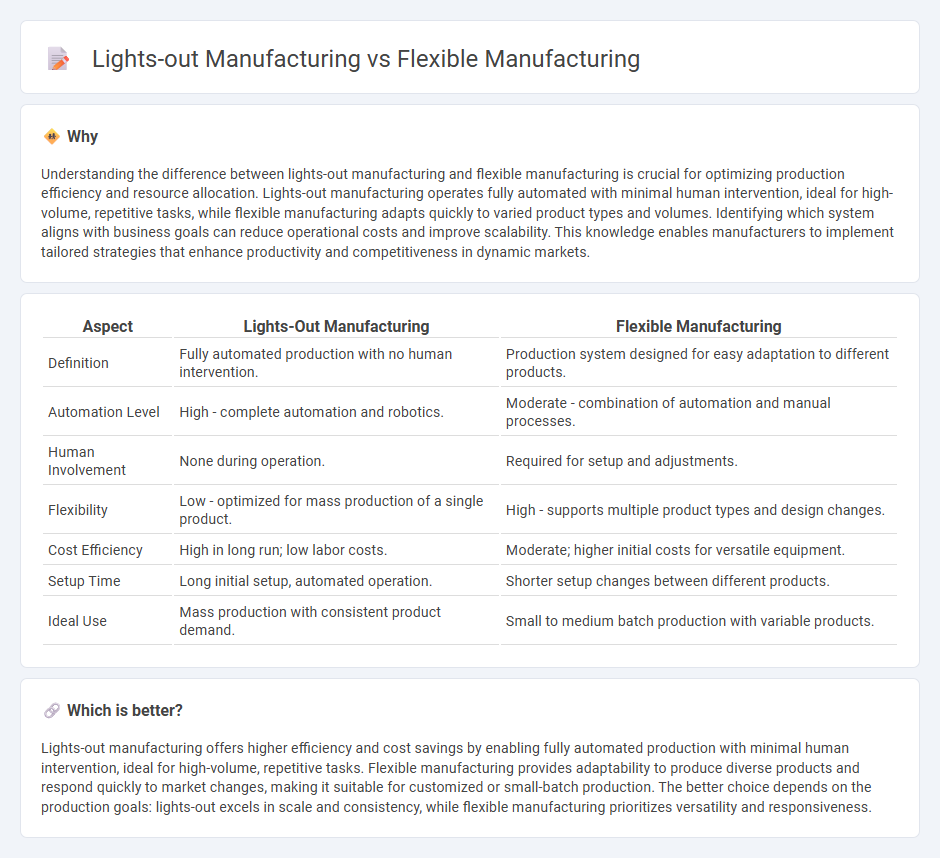
Understanding the difference between lights-out manufacturing and flexible manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and resource allocation. Lights-out manufacturing operates fully automated with minimal human intervention, ideal for high-volume, repetitive tasks, while flexible manufacturing adapts quickly to varied product types and volumes. Identifying which system aligns with business goals can reduce operational costs and improve scalability. This knowledge enables manufacturers to implement tailored strategies that enhance productivity and competitiveness in dynamic markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Lights-Out Manufacturing | Flexible Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated production with no human intervention. | Production system designed for easy adaptation to different products. |
| Automation Level | High - complete automation and robotics. | Moderate - combination of automation and manual processes. |
| Human Involvement | None during operation. | Required for setup and adjustments. |
| Flexibility | Low - optimized for mass production of a single product. | High - supports multiple product types and design changes. |
| Cost Efficiency | High in long run; low labor costs. | Moderate; higher initial costs for versatile equipment. |
| Setup Time | Long initial setup, automated operation. | Shorter setup changes between different products. |
| Ideal Use | Mass production with consistent product demand. | Small to medium batch production with variable products. |
Which is better?
Lights-out manufacturing offers higher efficiency and cost savings by enabling fully automated production with minimal human intervention, ideal for high-volume, repetitive tasks. Flexible manufacturing provides adaptability to produce diverse products and respond quickly to market changes, making it suitable for customized or small-batch production. The better choice depends on the production goals: lights-out excels in scale and consistency, while flexible manufacturing prioritizes versatility and responsiveness.
Connection
Lights-out manufacturing relies heavily on automation and robotics to operate without human intervention, creating a foundation for flexible manufacturing systems. Flexible manufacturing adjusts quickly to changes in product design and volume, enabled by the automated processes inherent in lights-out setups. Integrating these approaches enhances production efficiency, reduces labor costs, and improves responsiveness to market demands.
Key Terms
Automation
Flexible manufacturing integrates automation with human oversight, enabling quick shifts in production schedules and customization of products, optimizing efficiency and responsiveness. Lights-out manufacturing relies fully on automated systems operating without human intervention, maximizing productivity around the clock and minimizing labor costs. Explore the technology advancements driving these contrasting automation approaches in manufacturing.
Human Intervention
Flexible manufacturing integrates human intervention to adapt production processes in real-time, enhancing customization and problem-solving capabilities. Lights-out manufacturing operates autonomously with minimal or no human presence, optimizing efficiency and reducing labor costs through advanced robotics and automation. Explore how human roles evolve within these contrasting manufacturing paradigms and their impact on industrial productivity.
Production Adaptability
Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) enable rapid reconfiguration of production lines to handle diverse product designs and volumes, enhancing adaptability to changing market demands. Lights-out manufacturing operates autonomously without human intervention, optimizing efficiency but often with less flexibility for customization or sudden production changes. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how each system impacts production adaptability and responsiveness.
Source and External Links
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) - Autodesk - Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) are computer-controlled setups designed to quickly adapt to changes in product design, production sequence, or machine availability, enabling manufacturers to maintain efficiency and respond to disruptions without major retooling.
Flexible manufacturing system - Wikipedia - An FMS combines automated work machines, material handling systems, and central computer control to provide routing flexibility (changing the order of operations) and machine flexibility (using different machines for the same task), resulting in reduced costs, improved quality, and faster production times.
What is Flexible Manufacturing - Big Sky Engineering, Inc. - Flexible manufacturing allows companies to rapidly switch between producing different parts or products, adjust production schedules, and scale output up or down, all while minimizing the need for significant equipment changes or retooling.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com