Flexible manufacturing centers on adaptability, allowing production systems to quickly switch between different products to meet varying demand and customization needs. Continuous flow manufacturing emphasizes a streamlined, uninterrupted production process designed to minimize waste and maximize efficiency for high-volume output. Discover more about how these manufacturing strategies optimize operations and drive industry innovation.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between flexible manufacturing and continuous flow manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and meeting market demand. Flexible manufacturing allows for customization and quick adaptation to product changes, ideal for varying product types and volumes. Continuous flow manufacturing emphasizes a steady, uninterrupted production process, maximizing output for high-volume, standardized products. Choosing the appropriate method impacts cost, resource allocation, and overall operational agility in manufacturing systems.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Flexible Manufacturing | Continuous Flow Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
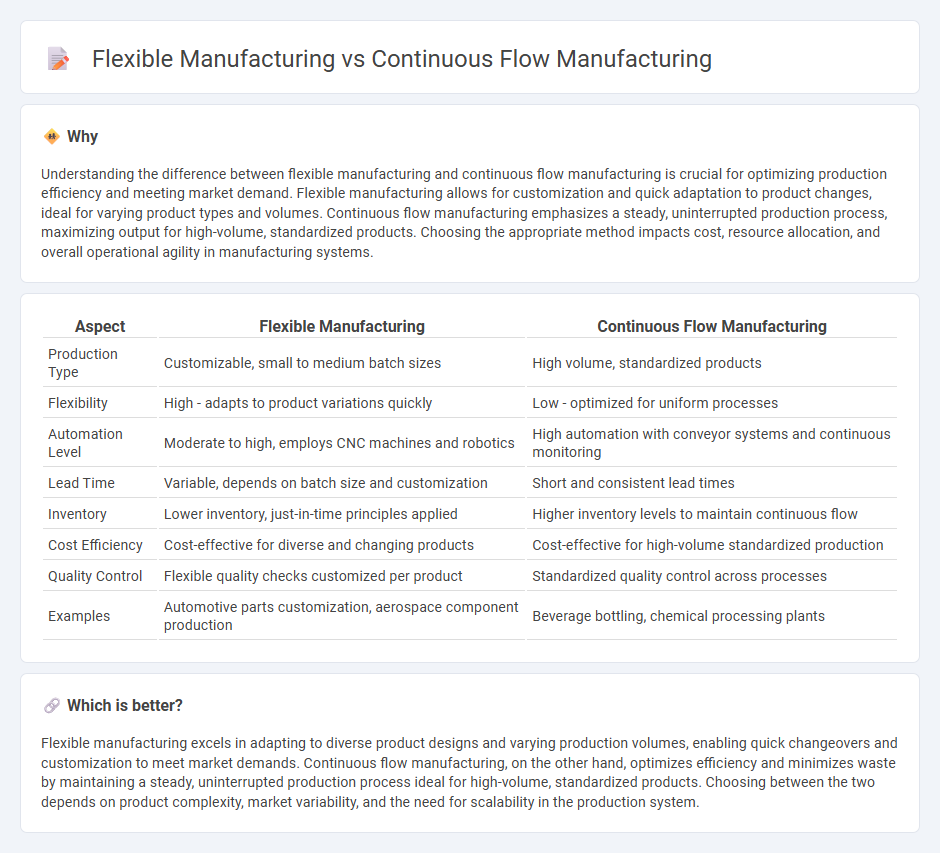
| Production Type | Customizable, small to medium batch sizes | High volume, standardized products |
| Flexibility | High - adapts to product variations quickly | Low - optimized for uniform processes |
| Automation Level | Moderate to high, employs CNC machines and robotics | High automation with conveyor systems and continuous monitoring |
| Lead Time | Variable, depends on batch size and customization | Short and consistent lead times |
| Inventory | Lower inventory, just-in-time principles applied | Higher inventory levels to maintain continuous flow |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for diverse and changing products | Cost-effective for high-volume standardized production |
| Quality Control | Flexible quality checks customized per product | Standardized quality control across processes |
| Examples | Automotive parts customization, aerospace component production | Beverage bottling, chemical processing plants |
Which is better?
Flexible manufacturing excels in adapting to diverse product designs and varying production volumes, enabling quick changeovers and customization to meet market demands. Continuous flow manufacturing, on the other hand, optimizes efficiency and minimizes waste by maintaining a steady, uninterrupted production process ideal for high-volume, standardized products. Choosing between the two depends on product complexity, market variability, and the need for scalability in the production system.
Connection
Flexible manufacturing enhances the adaptability of production systems to quickly switch between different product types, while continuous flow manufacturing focuses on maintaining a steady and uninterrupted production process. The integration of flexible manufacturing systems within continuous flow manufacturing enables rapid adjustments without disrupting the consistent movement of materials and products, thereby optimizing efficiency. This synergy reduces lead times, minimizes inventory levels, and improves overall responsiveness to market demand.
Key Terms
Source and External Links
Continuous-Flow Manufacturing (CFM) | Propel Glossary - Continuous Flow Manufacturing is a method where materials continuously move through production without batching, leveraging just-in-time manufacturing and automation to reduce delays and inventory.
Continuous Flow Production: A Complete Guide - Ease.io - This approach relies on precise process flow, specialized equipment, and integrated quality control to maintain nonstop production and optimize efficiency aligned with lean manufacturing principles.
Continuous Flow Manufacturing: A Guide to Streamlined Production - The method involves mapping value streams, optimizing factory layout, and training employees to ensure materials flow continuously through each process stage without interruption.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com