Cobotics integrates collaborative robots into production lines, enhancing efficiency and safety alongside human workers. Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction and process optimization to maximize value and minimize costs. Explore how combining cobotics with lean principles drives the future of smart manufacturing.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between cobotics and lean manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and workforce safety. Cobotics involves collaborative robots working alongside humans to enhance precision and reduce labor-intensive tasks, while lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste and streamlining processes. Implementing cobotics can complement lean principles by automating repetitive tasks without disrupting workflow. Companies that grasp these distinctions can strategically integrate technology to boost productivity and maintain competitive advantage.
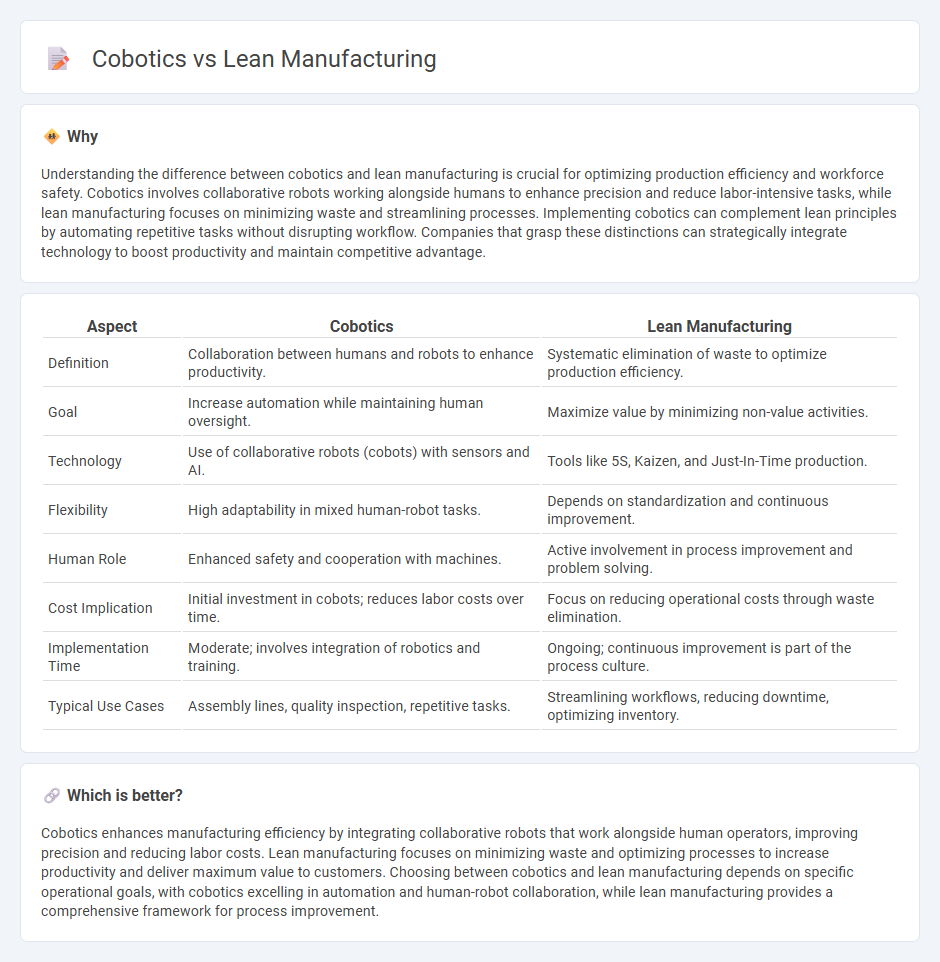
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cobotics | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaboration between humans and robots to enhance productivity. | Systematic elimination of waste to optimize production efficiency. |
| Goal | Increase automation while maintaining human oversight. | Maximize value by minimizing non-value activities. |
| Technology | Use of collaborative robots (cobots) with sensors and AI. | Tools like 5S, Kaizen, and Just-In-Time production. |
| Flexibility | High adaptability in mixed human-robot tasks. | Depends on standardization and continuous improvement. |
| Human Role | Enhanced safety and cooperation with machines. | Active involvement in process improvement and problem solving. |
| Cost Implication | Initial investment in cobots; reduces labor costs over time. | Focus on reducing operational costs through waste elimination. |
| Implementation Time | Moderate; involves integration of robotics and training. | Ongoing; continuous improvement is part of the process culture. |
| Typical Use Cases | Assembly lines, quality inspection, repetitive tasks. | Streamlining workflows, reducing downtime, optimizing inventory. |
Which is better?
Cobotics enhances manufacturing efficiency by integrating collaborative robots that work alongside human operators, improving precision and reducing labor costs. Lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste and optimizing processes to increase productivity and deliver maximum value to customers. Choosing between cobotics and lean manufacturing depends on specific operational goals, with cobotics excelling in automation and human-robot collaboration, while lean manufacturing provides a comprehensive framework for process improvement.
Connection
Cobotics integrates collaborative robots into lean manufacturing processes to enhance efficiency by automating repetitive tasks while maintaining human oversight. This synergy reduces waste, improves production flow, and supports continuous improvement principles inherent in lean methodologies. Leveraging cobots enables manufacturers to optimize resource use and achieve higher product quality with minimal downtime.
Key Terms
**Lean Manufacturing:**
Lean manufacturing emphasizes eliminating waste and improving efficiency through streamlined processes, continuous improvement, and just-in-time production. Key principles include value stream mapping, 5S methodology, and Kaizen events to enhance productivity and reduce costs. Discover how lean manufacturing can transform your operational performance and drive sustainable growth.
Value Stream Mapping
Lean manufacturing utilizes Value Stream Mapping (VSM) to identify and eliminate waste, improving process efficiency and product flow for maximum customer value. Cobotics enhances this by integrating collaborative robots within the value stream, automating repetitive tasks while maintaining human flexibility and intervention. Explore how combining VSM with cobotic automation can revolutionize your production system.
Waste Reduction (Muda)
Lean manufacturing targets waste reduction (Muda) by streamlining processes and eliminating non-value-added activities through methods like value stream mapping and 5S implementation. Cobotics enhances this approach by integrating collaborative robots that efficiently perform repetitive tasks, reducing human error and cycle time while enabling workers to focus on value-adding activities. Explore how combining lean principles with cobotic solutions drives superior waste minimization and operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
Lean manufacturing - Wikipedia - Lean manufacturing is a methodology focused on reducing production times and waste, inspired by the Toyota Production System, emphasizing efficiency, continuous improvement, and elimination of non-value-adding activities through principles such as just-in-time inventory and quality control.
What is Lean Manufacturing? | Definition from TechTarget - Lean manufacturing minimizes waste and maximizes productivity by following principles like continuous improvement (Kaizen), and is widely applied across many industries, with origins rooted in the Toyota Production System.
Lean Manufacturing: Understanding a New Manufacturing System - Lean manufacturing originated in the 1950s at Toyota, emphasizing multi-skilled teams, quality control, minimal inventory, and rapid correction of defects to increase efficiency and product quality.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com