Factory as a Service (FaaS) revolutionizes manufacturing by providing on-demand access to production resources through cloud-based platforms, enabling businesses to scale operations without heavy capital investment. Smart factories leverage IoT, AI, and automation technologies to create highly efficient, interconnected production environments that optimize real-time data for enhanced decision-making and reduced downtime. Explore the differences and benefits of these innovative manufacturing models to determine the best fit for your business objectives.
Why it is important
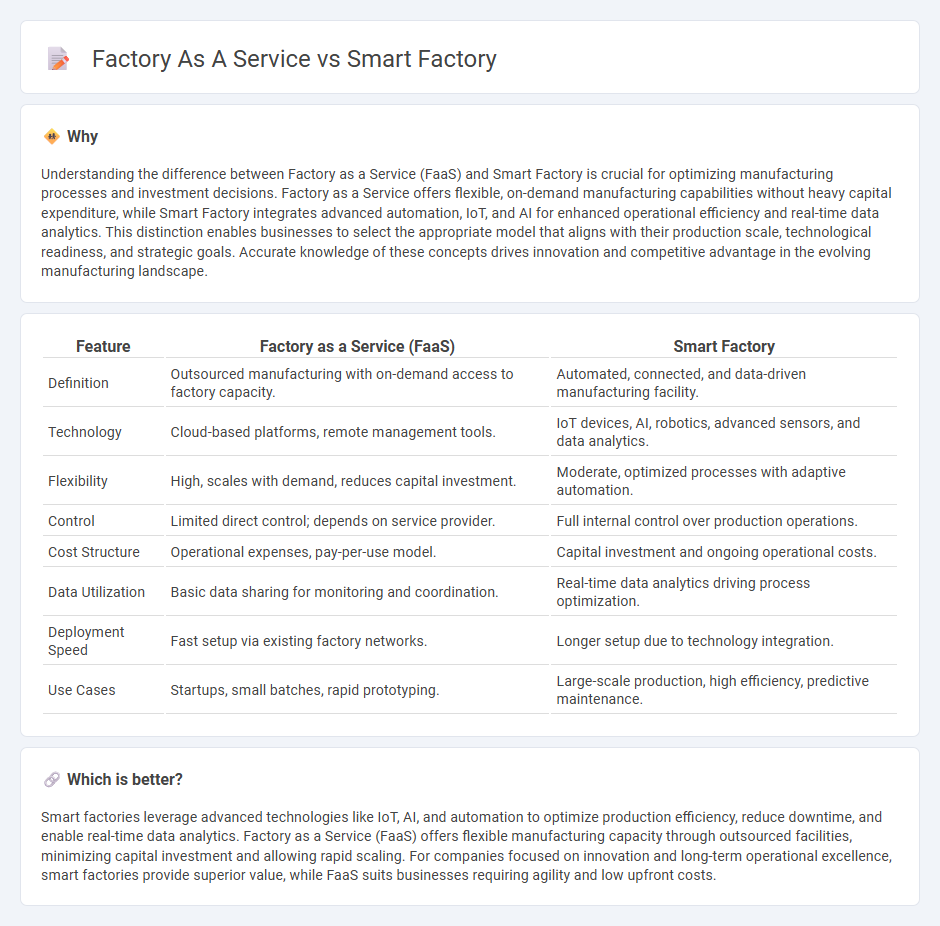
Understanding the difference between Factory as a Service (FaaS) and Smart Factory is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes and investment decisions. Factory as a Service offers flexible, on-demand manufacturing capabilities without heavy capital expenditure, while Smart Factory integrates advanced automation, IoT, and AI for enhanced operational efficiency and real-time data analytics. This distinction enables businesses to select the appropriate model that aligns with their production scale, technological readiness, and strategic goals. Accurate knowledge of these concepts drives innovation and competitive advantage in the evolving manufacturing landscape.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Factory as a Service (FaaS) | Smart Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Outsourced manufacturing with on-demand access to factory capacity. | Automated, connected, and data-driven manufacturing facility. |
| Technology | Cloud-based platforms, remote management tools. | IoT devices, AI, robotics, advanced sensors, and data analytics. |
| Flexibility | High, scales with demand, reduces capital investment. | Moderate, optimized processes with adaptive automation. |
| Control | Limited direct control; depends on service provider. | Full internal control over production operations. |
| Cost Structure | Operational expenses, pay-per-use model. | Capital investment and ongoing operational costs. |
| Data Utilization | Basic data sharing for monitoring and coordination. | Real-time data analytics driving process optimization. |
| Deployment Speed | Fast setup via existing factory networks. | Longer setup due to technology integration. |
| Use Cases | Startups, small batches, rapid prototyping. | Large-scale production, high efficiency, predictive maintenance. |
Which is better?
Smart factories leverage advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and automation to optimize production efficiency, reduce downtime, and enable real-time data analytics. Factory as a Service (FaaS) offers flexible manufacturing capacity through outsourced facilities, minimizing capital investment and allowing rapid scaling. For companies focused on innovation and long-term operational excellence, smart factories provide superior value, while FaaS suits businesses requiring agility and low upfront costs.
Connection
Factory as a Service (FaaS) integrates cloud-based platforms with smart factory technologies, enabling real-time data exchange and remote management of automated production systems. Smart factories leverage IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and robotics to optimize manufacturing processes, which FaaS supports through scalable infrastructure and seamless connectivity. This synergy enhances operational efficiency, reduces downtime, and drives intelligent decision-making in modern manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
**Smart Factory:**
Smart Factory integrates advanced IoT, AI, and robotics to optimize manufacturing efficiency, reduce downtime, and enable real-time data-driven decision-making. It leverages predictive maintenance and automated quality control to enhance productivity and operational flexibility while minimizing costs. Explore how Smart Factory technology transforms traditional manufacturing processes for industry 4.0 advancements.
Automation
Smart factories leverage advanced automation technologies such as IoT sensors, AI-driven robotics, and real-time data analytics to optimize manufacturing processes and increase efficiency. Factory as a Service (FaaS) offers on-demand access to automated production capabilities, allowing businesses to scale operations flexibly without investing heavily in automation infrastructure. Explore how these automation strategies transform manufacturing dynamics and improve operational agility.
IoT (Internet of Things)
Smart factories leverage IoT technologies to create interconnected, automated manufacturing environments that optimize production efficiency through real-time data analytics and machine-to-machine communication. Factory as a Service (FaaS) integrates IoT-enabled modular production units offered on-demand, providing scalable and flexible manufacturing solutions without the need for heavy upfront investments in infrastructure. Explore how IoT-driven innovations in smart factories and FaaS are revolutionizing industry operations and supply chain management.
Source and External Links
What is Smart Factory and Smart Manufacturing? - Oracle - A smart factory uses interconnected systems and machinery to generate real-time data that improves production processes and maintenance, aiming to speed up processes and eliminate errors while integrating physical and digital systems.
Smart Factory Guide | L2L - A smart factory is a digitally connected facility that integrates machines, people, and processes under Industry 4.0 principles to improve efficiency, quality, safety, and reduce costs through data analytics and cyber-physical systems.
Smart Factory - your way to networked production - TRUMPF - The Smart Factory is an environment where people, machines, automation, and software collaborate seamlessly, demonstrated in advanced plants like TRUMPF's Chicago, Ditzingen, and Taicang sites with fully integrated production chains and smart logistics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com