Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time feedback systems to continuously monitor and adjust production processes, enhancing precision and reducing waste. Continuous manufacturing emphasizes an uninterrupted, streamlined production flow that boosts efficiency and scalability while maintaining consistent quality. Explore the benefits and applications of closed-loop versus continuous manufacturing to optimize your production strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Closed-loop manufacturing and Continuous manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and product quality in industrial processes. Closed-loop manufacturing uses real-time feedback to automatically adjust operations, minimizing errors and waste. Continuous manufacturing maintains an uninterrupted production flow, enhancing scalability and reducing downtime. Recognizing these distinctions enables manufacturers to select appropriate strategies aligned with their operational goals and regulatory requirements.
Comparison Table
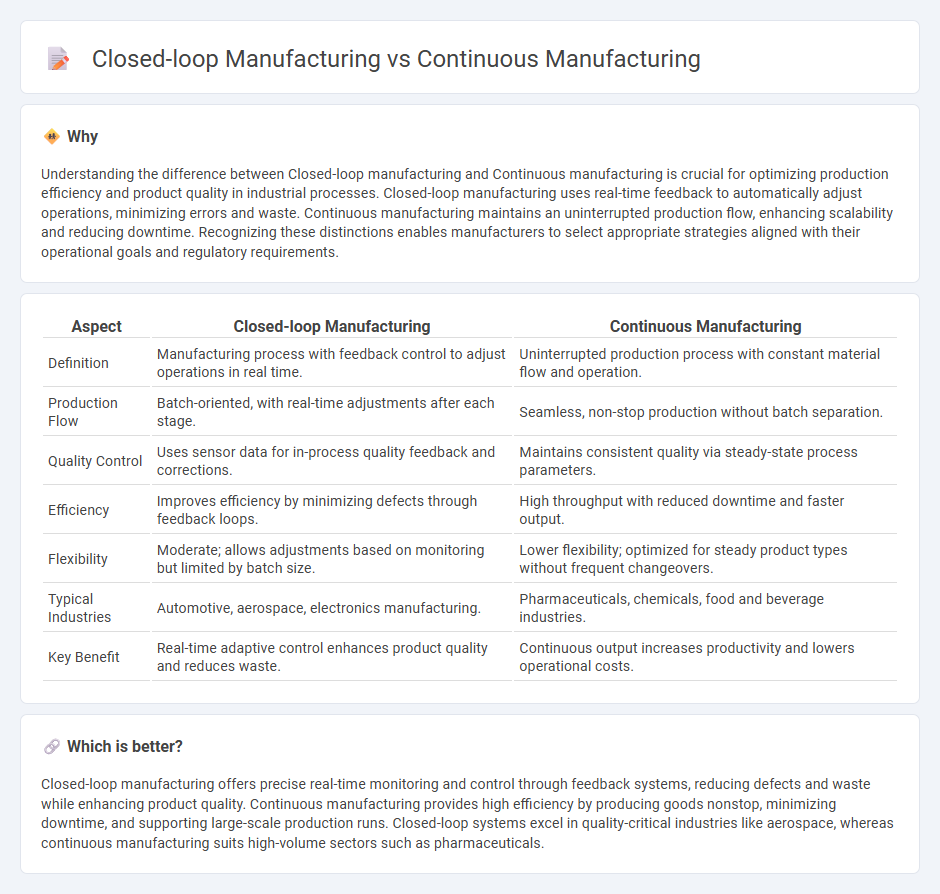
| Aspect | Closed-loop Manufacturing | Continuous Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturing process with feedback control to adjust operations in real time. | Uninterrupted production process with constant material flow and operation. |
| Production Flow | Batch-oriented, with real-time adjustments after each stage. | Seamless, non-stop production without batch separation. |
| Quality Control | Uses sensor data for in-process quality feedback and corrections. | Maintains consistent quality via steady-state process parameters. |
| Efficiency | Improves efficiency by minimizing defects through feedback loops. | High throughput with reduced downtime and faster output. |
| Flexibility | Moderate; allows adjustments based on monitoring but limited by batch size. | Lower flexibility; optimized for steady product types without frequent changeovers. |
| Typical Industries | Automotive, aerospace, electronics manufacturing. | Pharmaceuticals, chemicals, food and beverage industries. |
| Key Benefit | Real-time adaptive control enhances product quality and reduces waste. | Continuous output increases productivity and lowers operational costs. |
Which is better?
Closed-loop manufacturing offers precise real-time monitoring and control through feedback systems, reducing defects and waste while enhancing product quality. Continuous manufacturing provides high efficiency by producing goods nonstop, minimizing downtime, and supporting large-scale production runs. Closed-loop systems excel in quality-critical industries like aerospace, whereas continuous manufacturing suits high-volume sectors such as pharmaceuticals.
Connection
Closed-loop manufacturing and continuous manufacturing are interconnected through real-time feedback systems that monitor and control production processes to ensure consistent quality and efficiency. Closed-loop manufacturing employs sensors and automated adjustments to minimize defects, directly supporting the uninterrupted material flow characteristic of continuous manufacturing. This integration enhances overall operational agility by reducing downtime and maintaining constant product output.
Key Terms
Process flow
Continuous manufacturing streamlines production by maintaining an uninterrupted process flow, reducing downtime and variability in product quality through consistent material input and real-time monitoring. Closed-loop manufacturing enhances this by integrating feedback control systems that automatically adjust parameters based on sensor data, minimizing deviations and ensuring optimal process conditions throughout the operation. Explore the detailed differences and benefits of process flow optimization in both manufacturing approaches to improve operational efficiency.
Real-time feedback
Continuous manufacturing integrates real-time feedback systems that monitor and adjust production parameters instantly, ensuring consistent product quality and minimizing waste. Closed-loop manufacturing further advances this by using real-time data to automatically correct deviations without human intervention, enhancing precision and efficiency in complex production environments. Explore how real-time feedback transforms manufacturing processes for enhanced reliability and productivity.
Automation
Continuous manufacturing leverages automated processes to maintain uninterrupted production flow, enhancing efficiency and reducing variability. Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time feedback systems and automated adjustments to optimize quality control and minimize defects. Explore the advantages of automation in these manufacturing strategies for improved industrial performance.
Source and External Links
Continuous Manufacturing and How To Do It - Katana Cloud Inventory - Continuous manufacturing is a 24/7 production line where raw materials (liquids, powders, gases) are processed continuously in one location, producing products without interruption and allowing real-time monitoring to optimize the process, commonly used in industries like oil refining, metal smelting, and increasingly pharmaceuticals.
Embracing continuous manufacturing in the pharmaceutical industry - Continuous manufacturing in pharma involves uninterrupted 24/7 production feeding materials continuously, reducing inventory needs and improving time to market while offering real-time data advantages over traditional batch processing.
Continuous production - Wikipedia - Continuous production is a flow production method where materials undergo uninterrupted chemical, mechanical, or heat treatment, operating 24/7 except for infrequent maintenance, and is distinguished from batch production by its ongoing process flow.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com