Cobotics integrates collaborative robots with human workers to enhance manufacturing efficiency and safety, while digital twins create virtual replicas of physical assets for real-time monitoring and simulation. The synergy between cobotics and digital twins drives smart factory innovations by optimizing workflows and predictive maintenance. Discover how combining these technologies transforms modern manufacturing processes.
Why it is important
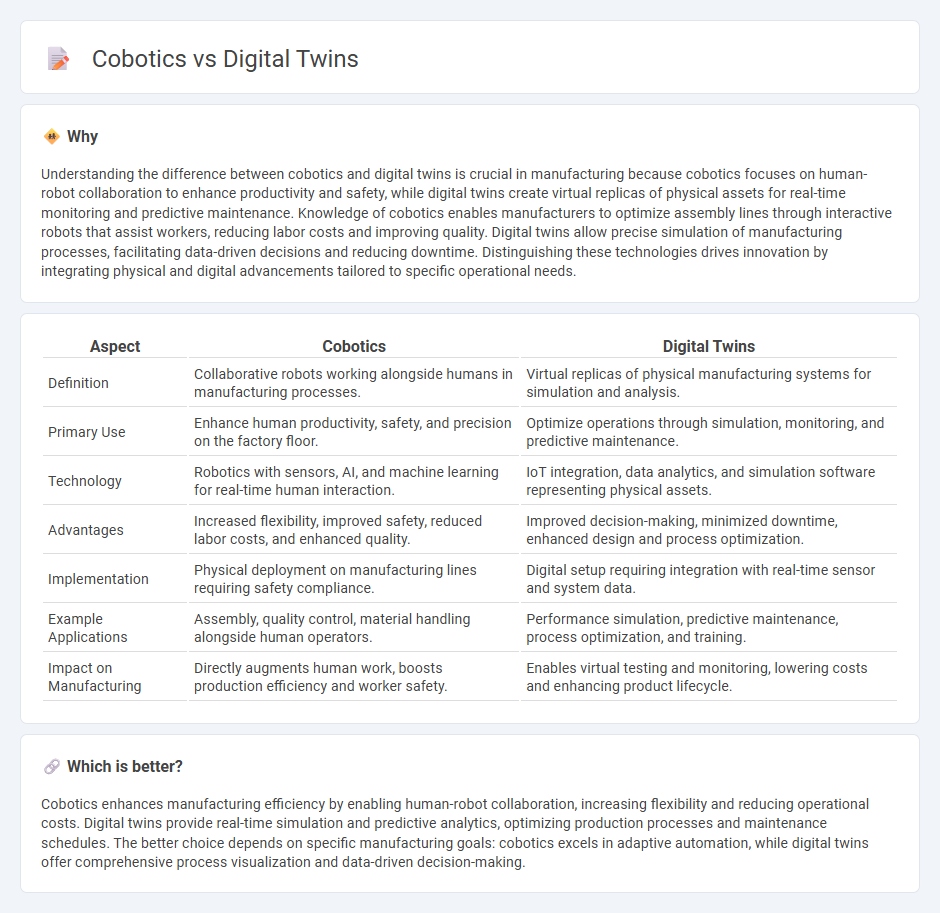
Understanding the difference between cobotics and digital twins is crucial in manufacturing because cobotics focuses on human-robot collaboration to enhance productivity and safety, while digital twins create virtual replicas of physical assets for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Knowledge of cobotics enables manufacturers to optimize assembly lines through interactive robots that assist workers, reducing labor costs and improving quality. Digital twins allow precise simulation of manufacturing processes, facilitating data-driven decisions and reducing downtime. Distinguishing these technologies drives innovation by integrating physical and digital advancements tailored to specific operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cobotics | Digital Twins |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaborative robots working alongside humans in manufacturing processes. | Virtual replicas of physical manufacturing systems for simulation and analysis. |
| Primary Use | Enhance human productivity, safety, and precision on the factory floor. | Optimize operations through simulation, monitoring, and predictive maintenance. |
| Technology | Robotics with sensors, AI, and machine learning for real-time human interaction. | IoT integration, data analytics, and simulation software representing physical assets. |
| Advantages | Increased flexibility, improved safety, reduced labor costs, and enhanced quality. | Improved decision-making, minimized downtime, enhanced design and process optimization. |
| Implementation | Physical deployment on manufacturing lines requiring safety compliance. | Digital setup requiring integration with real-time sensor and system data. |
| Example Applications | Assembly, quality control, material handling alongside human operators. | Performance simulation, predictive maintenance, process optimization, and training. |
| Impact on Manufacturing | Directly augments human work, boosts production efficiency and worker safety. | Enables virtual testing and monitoring, lowering costs and enhancing product lifecycle. |
Which is better?
Cobotics enhances manufacturing efficiency by enabling human-robot collaboration, increasing flexibility and reducing operational costs. Digital twins provide real-time simulation and predictive analytics, optimizing production processes and maintenance schedules. The better choice depends on specific manufacturing goals: cobotics excels in adaptive automation, while digital twins offer comprehensive process visualization and data-driven decision-making.
Connection
Cobotics integrates human-robot collaboration by enabling robots to assist workers in real-time, while digital twins create virtual replicas of manufacturing processes for simulation and optimization. The connection lies in digital twins providing a dynamic, data-driven environment where cobots' actions and workflows can be tested and refined before physical implementation. This synergy enhances flexibility, increases productivity, and reduces errors in smart manufacturing systems.
Key Terms
Simulation
Digital twins create dynamic virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling precise simulation and real-time monitoring to optimize performance and predict maintenance needs. Cobotics focuses on the simulation of human-robot interactions, enhancing collaboration and safety in shared workspaces through virtual modeling of robotic behaviors and ergonomics. Explore the latest advancements in simulation technology to understand how digital twins and cobotics revolutionize industrial processes.
Human-Robot Collaboration
Digital twins create virtual replicas of physical robots enabling real-time simulation and performance monitoring, which enhances precision in human-robot collaboration (HRC). Cobotics emphasizes interactive robots designed to work safely alongside humans, improving task efficiency and flexibility in manufacturing and service industries. Explore how integrating digital twins with cobotic systems can revolutionize collaborative workflows and optimize human-robot interactions.
Real-time Data
Digital twins leverage real-time data by creating virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling continuous monitoring and predictive maintenance through dynamic simulations. Cobotics integrates real-time sensor data to enhance human-robot collaboration, improving precision and responsiveness in manufacturing environments. Explore how real-time data drives both digital twins and cobotics to transform industrial processes and operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
Definition of a Digital Twin - A digital twin is an integrated, data-driven virtual representation of a real-world entity or process, synchronized with its physical counterpart at a specified frequency to enable understanding, decision-making, and intervention.
What Is a Digital Twin? - A digital twin is a virtual model that accurately mirrors a physical object or system throughout its lifecycle, using real-time data and simulations to analyze performance and drive improvements.
Digital twin - A digital twin is a digital counterpart of a physical product, system, or process, used for simulation, monitoring, testing, and maintenance by emulating the physical entity's behavior with real-time data.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com