Collaborative robots, or cobots, work alongside human operators to enhance manufacturing efficiency, precision, and safety, while digital twins create virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Cobots excel in automating repetitive tasks, whereas digital twins optimize entire production processes through data analysis and simulation. Explore the distinctive advantages of collaborative robots and digital twins to transform your manufacturing operations.
Why it is important
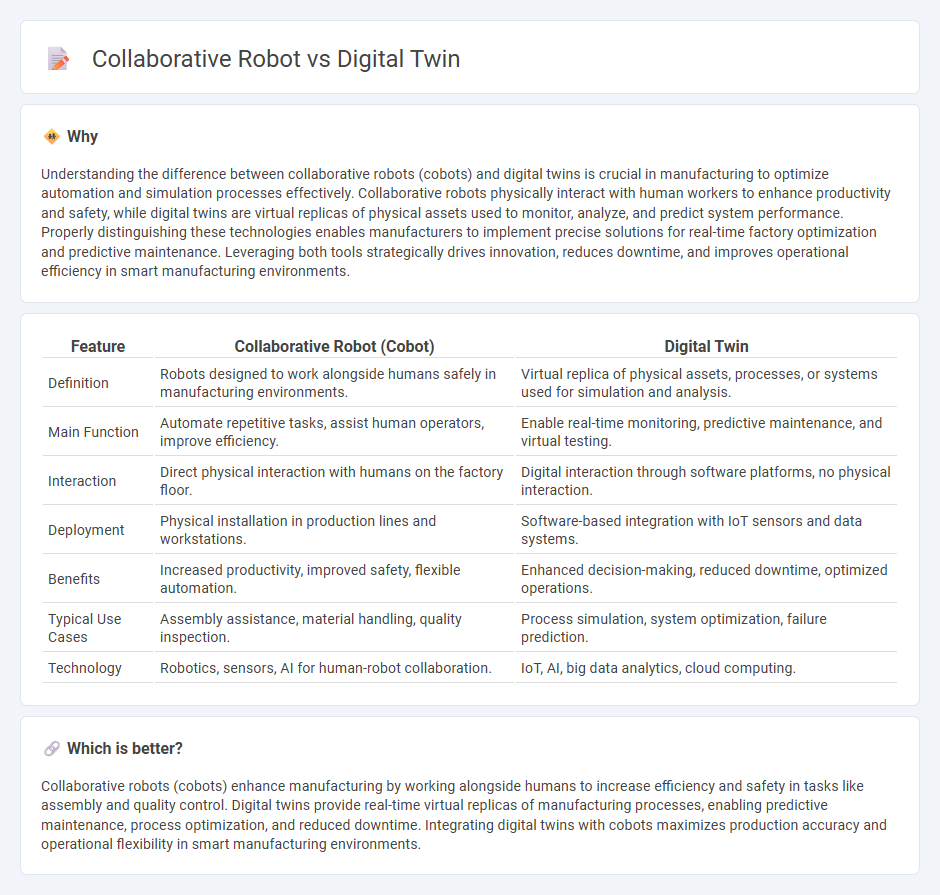
Understanding the difference between collaborative robots (cobots) and digital twins is crucial in manufacturing to optimize automation and simulation processes effectively. Collaborative robots physically interact with human workers to enhance productivity and safety, while digital twins are virtual replicas of physical assets used to monitor, analyze, and predict system performance. Properly distinguishing these technologies enables manufacturers to implement precise solutions for real-time factory optimization and predictive maintenance. Leveraging both tools strategically drives innovation, reduces downtime, and improves operational efficiency in smart manufacturing environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Collaborative Robot (Cobot) | Digital Twin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Robots designed to work alongside humans safely in manufacturing environments. | Virtual replica of physical assets, processes, or systems used for simulation and analysis. |
| Main Function | Automate repetitive tasks, assist human operators, improve efficiency. | Enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and virtual testing. |
| Interaction | Direct physical interaction with humans on the factory floor. | Digital interaction through software platforms, no physical interaction. |
| Deployment | Physical installation in production lines and workstations. | Software-based integration with IoT sensors and data systems. |
| Benefits | Increased productivity, improved safety, flexible automation. | Enhanced decision-making, reduced downtime, optimized operations. |
| Typical Use Cases | Assembly assistance, material handling, quality inspection. | Process simulation, system optimization, failure prediction. |
| Technology | Robotics, sensors, AI for human-robot collaboration. | IoT, AI, big data analytics, cloud computing. |
Which is better?
Collaborative robots (cobots) enhance manufacturing by working alongside humans to increase efficiency and safety in tasks like assembly and quality control. Digital twins provide real-time virtual replicas of manufacturing processes, enabling predictive maintenance, process optimization, and reduced downtime. Integrating digital twins with cobots maximizes production accuracy and operational flexibility in smart manufacturing environments.
Connection
Collaborative robots (cobots) utilize digital twins to simulate and optimize their movements and tasks in a virtual environment before deployment on manufacturing floors. Digital twins provide real-time data analytics and performance insights, enabling cobots to adapt dynamically to changes in production processes. This integration enhances precision, efficiency, and reduces downtime in smart manufacturing systems.
Key Terms
Simulation
Digital twins create virtual replicas of physical systems, enabling real-time simulation and predictive analysis that optimize performance and maintenance. Collaborative robots, or cobots, leverage simulation to enhance programming accuracy and ensure safe interaction with humans in dynamic environments. Explore how integrating digital twin technology with cobot simulation elevates automation and operational efficiency.
Human-robot interaction
Digital twins enable real-time simulation and monitoring of collaborative robots, enhancing human-robot interaction by predicting and optimizing robot behavior. Collaborative robots (cobots) are designed to work safely alongside humans, improving efficiency through shared tasks and adaptive control systems. Explore the latest advancements to understand how digital twins and cobots revolutionize human-robot collaboration.
Real-time monitoring
Digital twins provide real-time monitoring by creating a virtual replica of physical assets, enabling precise analysis and predictive maintenance. Collaborative robots (cobots) utilize embedded sensors to gather immediate operational data, enhancing safety and efficiency in shared human-robot workspaces. Explore how integrating digital twins with cobots revolutionizes real-time monitoring in industrial automation.
Source and External Links
Definition of a Digital Twin - A digital twin is a synchronized, data-driven virtual model of a real-world entity or process designed to optimize decision-making through continuous, bidirectional data exchange between the digital and physical components.
What Is a Digital Twin? - Digital twins are dynamic virtual replicas of physical systems that use real-time and historical data to simulate, analyze, and improve performance across the object's lifecycle, bridging the physical and digital worlds for actionable insights.
Digital twin - A digital twin is a living digital model that emulates the behavior and lifecycle of its physical counterpart, enabling simulation, monitoring, and predictive maintenance to enhance industrial and operational processes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com