Smart factory technology integrates IoT, AI, and automation to optimize production efficiency, reduce downtime, and enable real-time data analysis in manufacturing processes. Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, revolutionizes production by building components layer-by-layer, allowing for rapid prototyping, customization, and material savings. Explore how these innovative approaches transform manufacturing for greater flexibility and sustainability.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between smart factory and additive manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and innovation. A smart factory integrates IoT, AI, and automation for real-time monitoring and adaptive control, enhancing overall factory performance. Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, focuses on layer-by-layer material deposition to create complex parts with less waste and rapid prototyping capabilities. Distinguishing these concepts enables businesses to strategically invest in the right technologies to improve supply chain agility and product customization.
Comparison Table
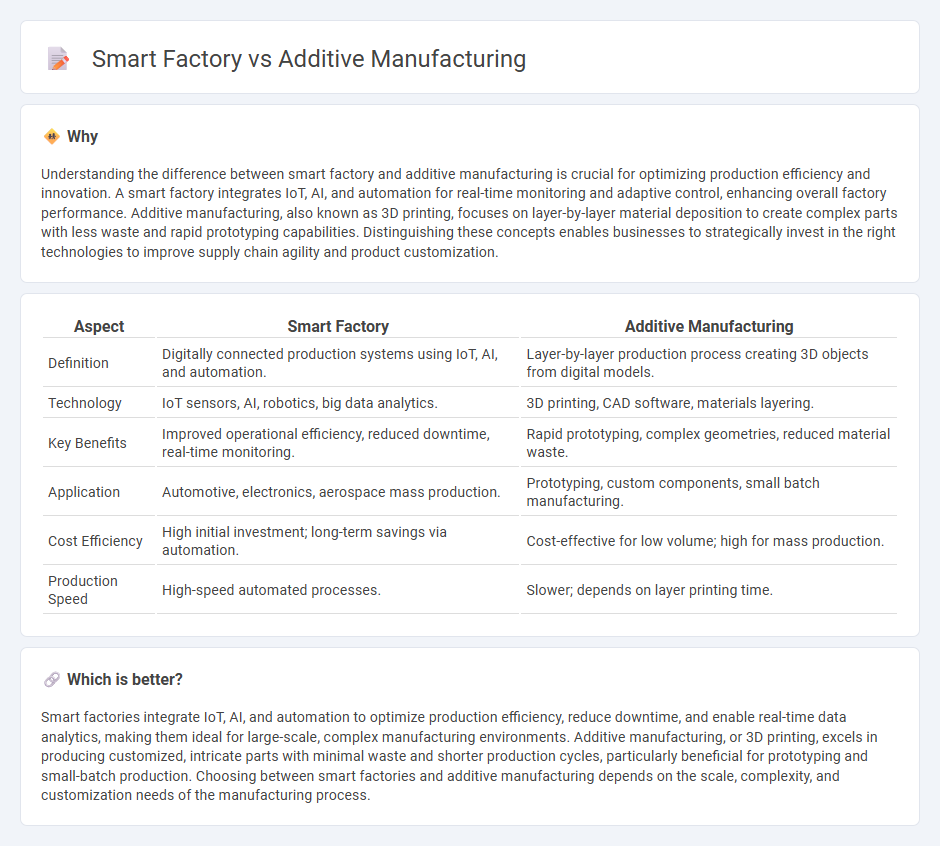
| Aspect | Smart Factory | Additive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digitally connected production systems using IoT, AI, and automation. | Layer-by-layer production process creating 3D objects from digital models. |
| Technology | IoT sensors, AI, robotics, big data analytics. | 3D printing, CAD software, materials layering. |
| Key Benefits | Improved operational efficiency, reduced downtime, real-time monitoring. | Rapid prototyping, complex geometries, reduced material waste. |
| Application | Automotive, electronics, aerospace mass production. | Prototyping, custom components, small batch manufacturing. |
| Cost Efficiency | High initial investment; long-term savings via automation. | Cost-effective for low volume; high for mass production. |
| Production Speed | High-speed automated processes. | Slower; depends on layer printing time. |
Which is better?
Smart factories integrate IoT, AI, and automation to optimize production efficiency, reduce downtime, and enable real-time data analytics, making them ideal for large-scale, complex manufacturing environments. Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, excels in producing customized, intricate parts with minimal waste and shorter production cycles, particularly beneficial for prototyping and small-batch production. Choosing between smart factories and additive manufacturing depends on the scale, complexity, and customization needs of the manufacturing process.
Connection
Smart factories leverage advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and machine learning to enhance the efficiency and flexibility of manufacturing processes, integrating additive manufacturing as a crucial component. Additive manufacturing enables on-demand production and rapid prototyping, which aligns with the smart factory's goal of reducing lead times and improving customization. The real-time data monitoring and automated control systems in smart factories optimize additive manufacturing workflows, resulting in higher precision and reduced waste.
Key Terms
Additive Manufacturing:
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, enables the creation of complex, customized parts layer by layer using materials such as plastics, metals, and ceramics, reducing waste and production time compared to traditional manufacturing methods. It is widely used in aerospace, healthcare, and automotive industries for rapid prototyping and on-demand production. Explore the latest advancements and applications of additive manufacturing to unlock its full potential in modern industry.
3D Printing
Additive manufacturing leverages 3D printing technology to create complex, custom parts layer by layer, optimizing material usage and reducing production time. Smart factories integrate additive manufacturing within automated, interconnected systems, enhancing real-time data analytics, precision, and flexibility in production processes. Explore how combining 3D printing with smart factory innovations transforms modern manufacturing efficiency and customization.
Layer-by-Layer Fabrication
Layer-by-layer fabrication defines additive manufacturing by building objects through successive material deposition, enabling complex geometries and customized production. In contrast, smart factories integrate digital technologies and automation for real-time monitoring and optimization across manufacturing processes, including additive methods. Explore the synergy between additive manufacturing and smart factory concepts to enhance efficient, flexible production systems.
Source and External Links
Additive manufacturing, explained | MIT Sloan - Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, creates objects by building them layer by layer from digital designs, using materials like polymers, metals, and ceramics, starting from prototyping in the 1980s to functional applications today in industries like aerospace.
Additive manufacturing | NIST - Additive manufacturing fabricates 3D products layer-by-layer from digital files, allowing complex designs with less waste, and is used across various fields such as aerospace and biomedical implants, relying on precise measurement and standards for industrial adoption.
The 7 categories of Additive Manufacturing - Loughborough University - Additive manufacturing comprises multiple processes grouped into seven categories by ASTM F42 standards, including vat photopolymerisation, material jetting, and binder jetting, each differing in layer-building methods and materials used.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com