Lights out factories operate with full automation and minimal human intervention, optimizing continuous production and reducing labor costs. Batch production involves manufacturing products in specific groups or quantities, allowing flexibility and customization but often resulting in longer lead times. Explore the advantages and applications of each manufacturing method to determine the best fit for your operations.
Why it is important
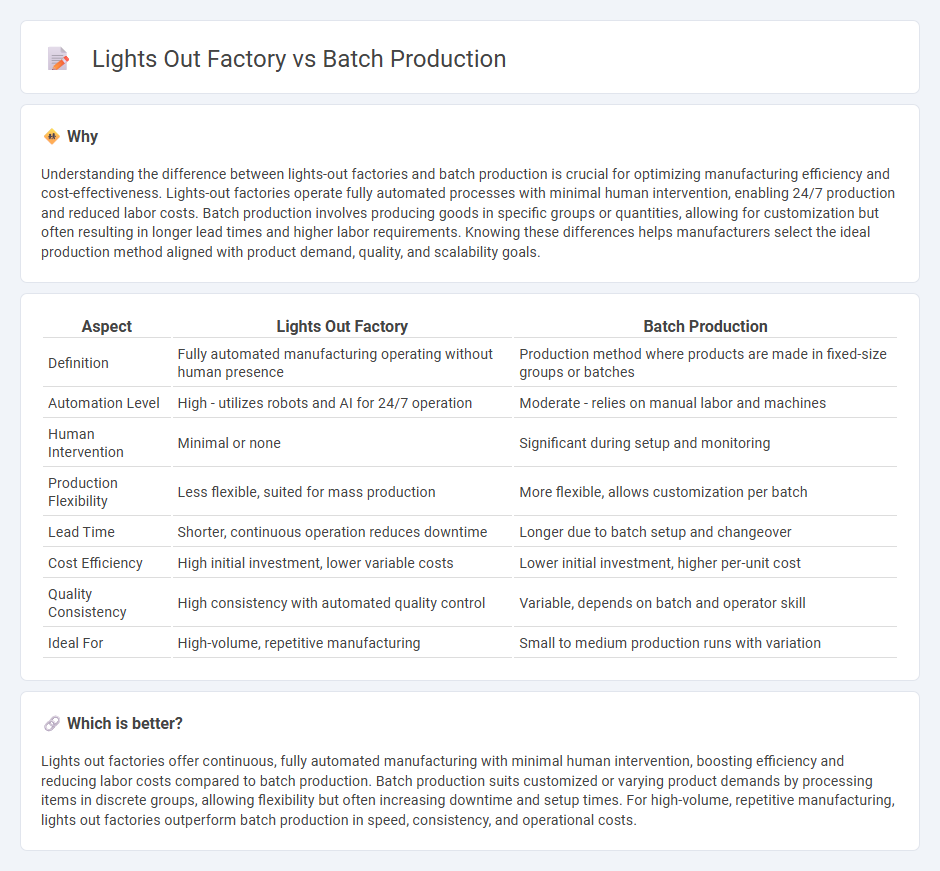
Understanding the difference between lights-out factories and batch production is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Lights-out factories operate fully automated processes with minimal human intervention, enabling 24/7 production and reduced labor costs. Batch production involves producing goods in specific groups or quantities, allowing for customization but often resulting in longer lead times and higher labor requirements. Knowing these differences helps manufacturers select the ideal production method aligned with product demand, quality, and scalability goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Lights Out Factory | Batch Production |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated manufacturing operating without human presence | Production method where products are made in fixed-size groups or batches |
| Automation Level | High - utilizes robots and AI for 24/7 operation | Moderate - relies on manual labor and machines |
| Human Intervention | Minimal or none | Significant during setup and monitoring |
| Production Flexibility | Less flexible, suited for mass production | More flexible, allows customization per batch |
| Lead Time | Shorter, continuous operation reduces downtime | Longer due to batch setup and changeover |
| Cost Efficiency | High initial investment, lower variable costs | Lower initial investment, higher per-unit cost |
| Quality Consistency | High consistency with automated quality control | Variable, depends on batch and operator skill |
| Ideal For | High-volume, repetitive manufacturing | Small to medium production runs with variation |
Which is better?
Lights out factories offer continuous, fully automated manufacturing with minimal human intervention, boosting efficiency and reducing labor costs compared to batch production. Batch production suits customized or varying product demands by processing items in discrete groups, allowing flexibility but often increasing downtime and setup times. For high-volume, repetitive manufacturing, lights out factories outperform batch production in speed, consistency, and operational costs.
Connection
Lights-out factories utilize automated systems that enable continuous, unattended manufacturing processes, which align seamlessly with batch production methods designed for producing specific quantities of products in set runs. The integration of robotic automation in lights-out facilities enhances the efficiency and scalability of batch production by minimizing human intervention, reducing errors, and optimizing equipment utilization. This synergy supports flexible manufacturing schedules, lowers operational costs, and improves product consistency across batch cycles.
Key Terms
Automation
Batch production involves manufacturing products in specified groups or quantities, relying on periodic human intervention and manual setup adjustments. Lights-out factories achieve full automation by operating without human presence, utilizing advanced robotics, AI, and IoT systems to maintain continuous production and reduce downtime. Explore how integrating automation can transform production efficiency by visiting our detailed analysis.
Production Scheduling
Batch production relies on predefined production schedules that group similar products to optimize machine setup and minimize downtime, while lights-out factories leverage automated, continuous production scheduling driven by real-time data and AI algorithms to maximize efficiency without human intervention. Batch scheduling requires manual adjustments and careful coordination to handle variability and demand fluctuations, whereas lights-out operations achieve seamless adaptability through intelligent scheduling and predictive maintenance. Explore advanced production scheduling techniques to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs in both manufacturing models.
Human Intervention
Batch production relies heavily on human intervention for machine operation, quality control, and workflow adjustments, making labor costs and human error significant considerations. In contrast, lights out factories operate with minimal to no human presence, utilizing automation and robotics to maintain consistent production and reduce downtime. Explore the benefits and challenges of each approach to determine the ideal manufacturing strategy for your business.
Source and External Links
What is batch production in manufacturing? - OneAdvanced - Batch production is a manufacturing method where groups of identical products are produced simultaneously through a series of stages, allowing flexibility to change batch specifications and conduct quality checks between batches, making it suitable for small to medium-sized manufacturers.
Batch Production - Benefits, Examples, and Tips - MRPeasy - Batch production involves producing sets of identical goods together through different production stages and offers advantages like flexibility, product variants, and quality control, but also has downsides like high work-in-progress inventory and idle time.
Batch Production: Definition, Advantages, Disadvantages - Batch production produces specific quantities before switching products, supporting new product introduction, easing inventory management, and allowing convenient maintenance scheduling during downtimes between batches.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com