Predictive maintenance uses data analytics and machine learning to forecast equipment failures before they occur, optimizing maintenance schedules and minimizing unplanned downtime. Condition-based maintenance relies on real-time sensor data to trigger maintenance actions only when specific equipment conditions indicate wear or malfunction. Explore detailed comparisons and benefits to enhance your manufacturing maintenance strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between predictive maintenance and condition-based maintenance is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and reducing downtime. Predictive maintenance uses data analytics and machine learning to forecast equipment failures before they occur, allowing proactive repairs. Condition-based maintenance relies on real-time monitoring of equipment status to trigger maintenance only when specific indicators show degradation. Choosing the right approach improves asset lifespan, minimizes costs, and enhances production reliability in manufacturing operations.
Comparison Table
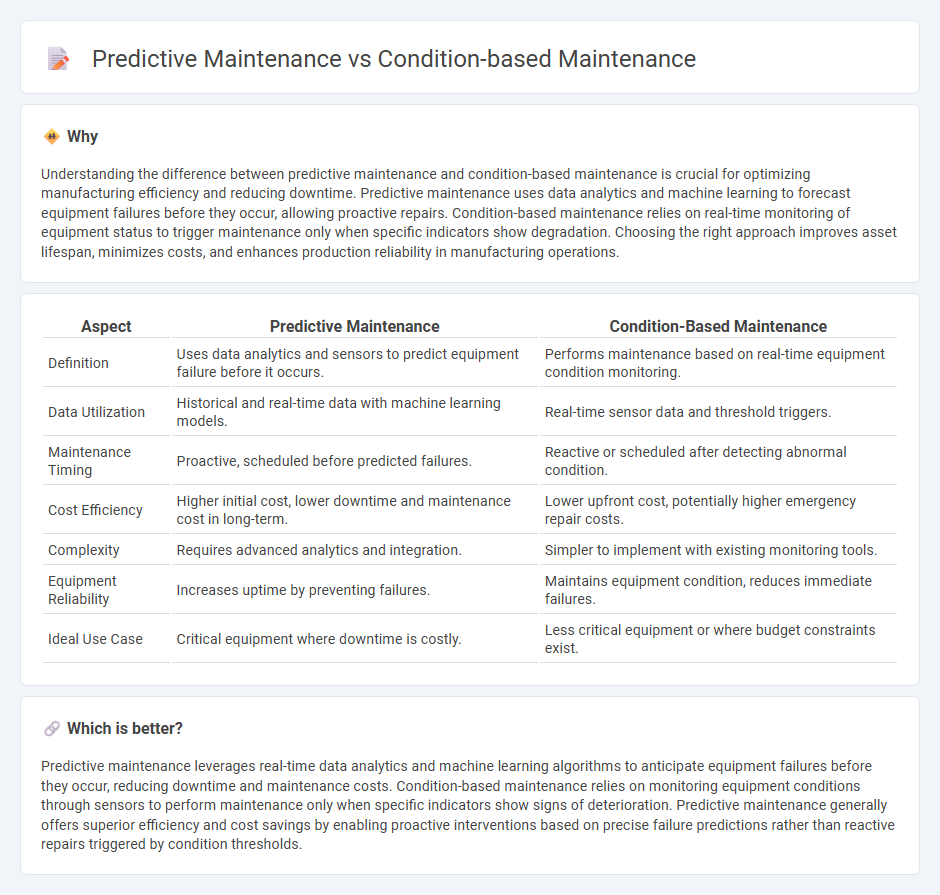
| Aspect | Predictive Maintenance | Condition-Based Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses data analytics and sensors to predict equipment failure before it occurs. | Performs maintenance based on real-time equipment condition monitoring. |
| Data Utilization | Historical and real-time data with machine learning models. | Real-time sensor data and threshold triggers. |
| Maintenance Timing | Proactive, scheduled before predicted failures. | Reactive or scheduled after detecting abnormal condition. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial cost, lower downtime and maintenance cost in long-term. | Lower upfront cost, potentially higher emergency repair costs. |
| Complexity | Requires advanced analytics and integration. | Simpler to implement with existing monitoring tools. |
| Equipment Reliability | Increases uptime by preventing failures. | Maintains equipment condition, reduces immediate failures. |
| Ideal Use Case | Critical equipment where downtime is costly. | Less critical equipment or where budget constraints exist. |
Which is better?
Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data analytics and machine learning algorithms to anticipate equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Condition-based maintenance relies on monitoring equipment conditions through sensors to perform maintenance only when specific indicators show signs of deterioration. Predictive maintenance generally offers superior efficiency and cost savings by enabling proactive interventions based on precise failure predictions rather than reactive repairs triggered by condition thresholds.
Connection
Predictive maintenance and condition-based maintenance are interconnected strategies focused on optimizing manufacturing equipment reliability by utilizing real-time data and analytics to anticipate failures before they occur. Predictive maintenance employs advanced sensors and machine learning algorithms to forecast equipment issues, while condition-based maintenance relies on continuous monitoring of equipment condition parameters such as vibration, temperature, and pressure. Together, these approaches enable manufacturers to reduce unplanned downtime, extend asset lifespan, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Key Terms
Real-time Monitoring
Condition-based maintenance relies on real-time monitoring of equipment parameters like vibration, temperature, and pressure to identify potential failures before they occur. Predictive maintenance enhances this approach by using advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to forecast future equipment issues based on historical and real-time data trends. Discover how real-time monitoring transforms maintenance strategies for improved operational efficiency and reduced downtime.
Data Analysis
Condition-based maintenance relies on real-time data from sensors to monitor equipment health and trigger maintenance only when specific thresholds are met, minimizing unnecessary interventions. Predictive maintenance uses advanced data analytics, machine learning algorithms, and historical data to forecast potential failures before they occur, enabling proactive scheduling of repairs. Explore detailed comparisons and methodologies to optimize maintenance strategies through data analysis.
Failure Prediction
Condition-based maintenance relies on real-time monitoring of equipment parameters to detect abnormalities and schedule repairs before failure occurs, whereas predictive maintenance uses advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to forecast future failures with higher accuracy. Failure prediction in predictive maintenance enhances decision-making by analyzing historical and sensor data to identify patterns, enabling proactive interventions that reduce downtime and maintenance costs. Explore our detailed insights to understand how these strategies improve operational efficiency through effective failure prediction.
Source and External Links
What is Condition-based Maintenance? - IBM - Condition-based maintenance (CBM) is a preventive maintenance strategy that uses real-time monitoring of equipment condition through sensors and data analysis to determine when maintenance is necessary, avoiding fixed schedules and reducing unexpected failures.
What is Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM)? CBM ... - eMaint - CBM improves asset reliability and safety by identifying failures before they occur, reducing costs and downtime by performing maintenance only when needed based on actual asset condition monitoring.
Condition-based Maintenance (CBM) Explained - Reliable Plant - CBM continuously monitors the real-time condition of assets, enabling maintenance teams to schedule interventions before failures happen, focusing on data-driven decision-making rather than fixed maintenance intervals.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com