Lights-out manufacturing relies on fully automated production processes that operate without human intervention, maximizing efficiency and reducing labor costs. Continuous flow manufacturing emphasizes seamless, uninterrupted production by minimizing work-in-progress inventory and bottlenecks, boosting throughput and product quality. Explore the core benefits and applications of these advanced manufacturing strategies to optimize your industrial operations.
Why it is important
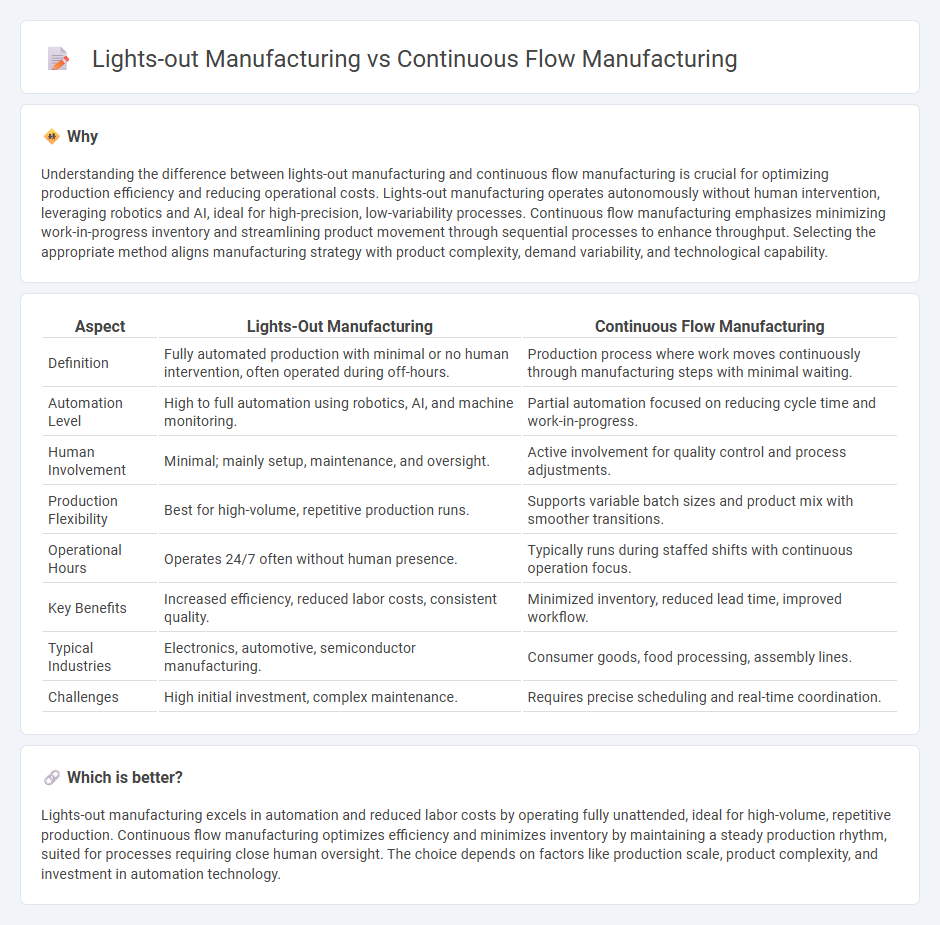
Understanding the difference between lights-out manufacturing and continuous flow manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and reducing operational costs. Lights-out manufacturing operates autonomously without human intervention, leveraging robotics and AI, ideal for high-precision, low-variability processes. Continuous flow manufacturing emphasizes minimizing work-in-progress inventory and streamlining product movement through sequential processes to enhance throughput. Selecting the appropriate method aligns manufacturing strategy with product complexity, demand variability, and technological capability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Lights-Out Manufacturing | Continuous Flow Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated production with minimal or no human intervention, often operated during off-hours. | Production process where work moves continuously through manufacturing steps with minimal waiting. |
| Automation Level | High to full automation using robotics, AI, and machine monitoring. | Partial automation focused on reducing cycle time and work-in-progress. |
| Human Involvement | Minimal; mainly setup, maintenance, and oversight. | Active involvement for quality control and process adjustments. |
| Production Flexibility | Best for high-volume, repetitive production runs. | Supports variable batch sizes and product mix with smoother transitions. |
| Operational Hours | Operates 24/7 often without human presence. | Typically runs during staffed shifts with continuous operation focus. |
| Key Benefits | Increased efficiency, reduced labor costs, consistent quality. | Minimized inventory, reduced lead time, improved workflow. |
| Typical Industries | Electronics, automotive, semiconductor manufacturing. | Consumer goods, food processing, assembly lines. |
| Challenges | High initial investment, complex maintenance. | Requires precise scheduling and real-time coordination. |
Which is better?
Lights-out manufacturing excels in automation and reduced labor costs by operating fully unattended, ideal for high-volume, repetitive production. Continuous flow manufacturing optimizes efficiency and minimizes inventory by maintaining a steady production rhythm, suited for processes requiring close human oversight. The choice depends on factors like production scale, product complexity, and investment in automation technology.
Connection
Lights-out manufacturing relies heavily on continuous flow manufacturing principles to maintain uninterrupted production without human intervention. Continuous flow manufacturing optimizes processes by streamlining work-in-progress and minimizing bottlenecks, which enables automated systems in lights-out manufacturing to operate efficiently. Together, they enhance productivity, reduce downtime, and lower operational costs in smart factories.
Key Terms
Automation
Continuous flow manufacturing emphasizes streamlined, automated processes to ensure steady production with minimal delays, leveraging automation technologies for efficiency. Lights-out manufacturing advances automation by operating facilities entirely without human intervention, using robotics, AI, and IoT to enable round-the-clock, unattended production. Explore how these automation strategies transform industrial productivity and reduce operational costs.
Human Intervention
Continuous flow manufacturing relies on consistent human intervention to monitor processes, manage quality control, and address unexpected issues, ensuring smooth production cycles. Lights-out manufacturing minimizes human presence by utilizing automated systems and robotics to operate machinery autonomously, reducing labor costs and human error. Explore how varying degrees of human involvement impact efficiency and innovation in modern manufacturing environments.
Production Efficiency
Continuous flow manufacturing optimizes production efficiency by minimizing work-in-progress inventory and reducing cycle times through synchronized operations on the assembly line. Lights-out manufacturing enhances efficiency further by enabling fully automated production processes that operate without human intervention, increasing throughput and decreasing downtime. Explore the advantages and applications of both methods to boost your manufacturing efficiency.
Source and External Links
Continuous-Flow Manufacturing (CFM) | Propel Glossary - Continuous Flow Manufacturing is a method where materials move continuously through the production line, enabling seamless, uninterrupted production with principles such as just-in-time manufacturing and automation to reduce lead times and minimize inventory.
Continuous Flow Production: A Complete Guide - Ease.io - This manufacturing approach focuses on nonstop production with zero downtime by optimizing process flow, using advanced equipment and automation, and implementing rigorous real-time quality control to ensure consistent, high-quality output.
Continuous Flow Manufacturing: A Guide to Streamlined Production - Continuous Flow Manufacturing requires assessing current processes, mapping value streams, designing optimized factory layouts, and training employees to create efficient, uninterrupted production flows that minimize waste and improve productivity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com