Industrial symbiosis maximizes resource efficiency by facilitating direct exchange of materials and energy between interconnected manufacturing facilities, reducing waste across supply chains. The circular economy expands on this concept by promoting systemic redesign for long-term sustainability, focusing on product lifecycle extension, reuse, and recycling at a macroeconomic scale. Explore how integrating these strategies can revolutionize manufacturing sustainability.
Why it is important
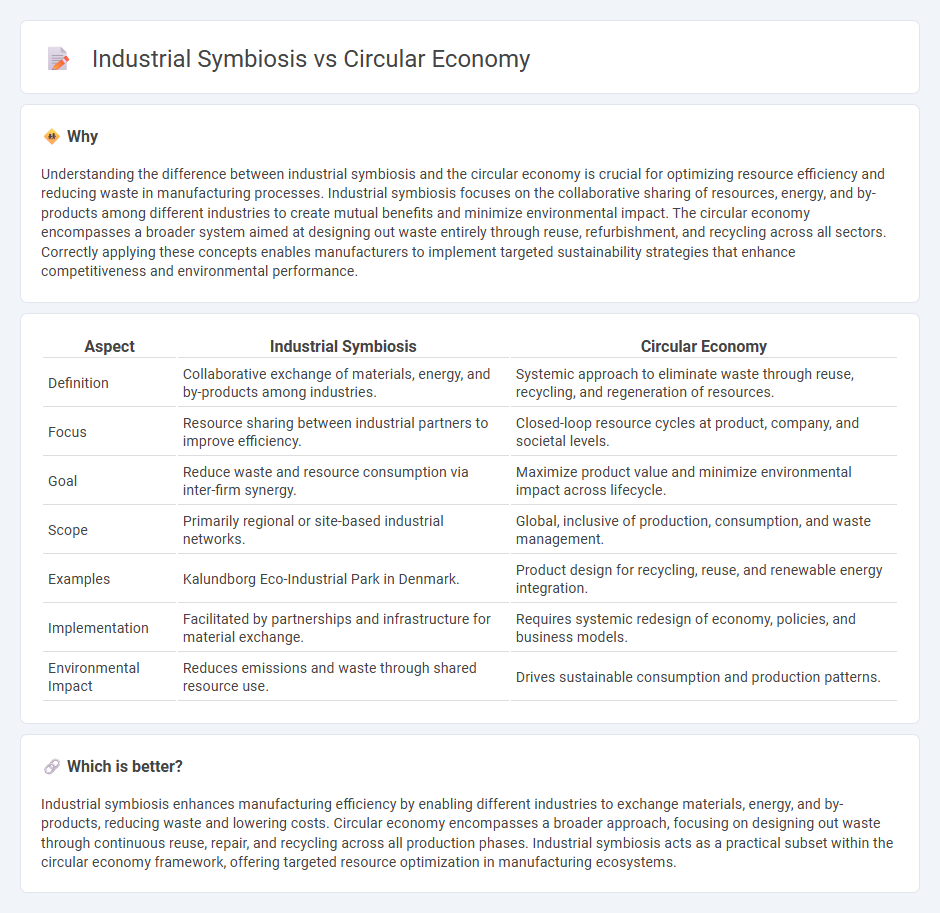
Understanding the difference between industrial symbiosis and the circular economy is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and reducing waste in manufacturing processes. Industrial symbiosis focuses on the collaborative sharing of resources, energy, and by-products among different industries to create mutual benefits and minimize environmental impact. The circular economy encompasses a broader system aimed at designing out waste entirely through reuse, refurbishment, and recycling across all sectors. Correctly applying these concepts enables manufacturers to implement targeted sustainability strategies that enhance competitiveness and environmental performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Industrial Symbiosis | Circular Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaborative exchange of materials, energy, and by-products among industries. | Systemic approach to eliminate waste through reuse, recycling, and regeneration of resources. |
| Focus | Resource sharing between industrial partners to improve efficiency. | Closed-loop resource cycles at product, company, and societal levels. |
| Goal | Reduce waste and resource consumption via inter-firm synergy. | Maximize product value and minimize environmental impact across lifecycle. |
| Scope | Primarily regional or site-based industrial networks. | Global, inclusive of production, consumption, and waste management. |
| Examples | Kalundborg Eco-Industrial Park in Denmark. | Product design for recycling, reuse, and renewable energy integration. |
| Implementation | Facilitated by partnerships and infrastructure for material exchange. | Requires systemic redesign of economy, policies, and business models. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces emissions and waste through shared resource use. | Drives sustainable consumption and production patterns. |
Which is better?
Industrial symbiosis enhances manufacturing efficiency by enabling different industries to exchange materials, energy, and by-products, reducing waste and lowering costs. Circular economy encompasses a broader approach, focusing on designing out waste through continuous reuse, repair, and recycling across all production phases. Industrial symbiosis acts as a practical subset within the circular economy framework, offering targeted resource optimization in manufacturing ecosystems.
Connection
Industrial symbiosis enhances the circular economy by facilitating the exchange of materials, energy, and by-products among manufacturing firms to minimize waste and optimize resource efficiency. Manufacturing clusters engaged in industrial symbiosis reduce raw material consumption and landfill disposal through collaborative reuse and recycling processes. This synergy supports sustainable production cycles, lowering environmental impact while boosting economic resilience within industrial ecosystems.
Key Terms
Resource Efficiency
Circular economy promotes resource efficiency by minimizing waste through continuous reuse, recycling, and remanufacturing of materials within closed-loop systems. Industrial symbiosis enhances resource efficiency by facilitating collaboration between industries where the waste or by-products of one process become the raw materials for another, optimizing resource utilization across sectors. Explore how integrating circular economy principles and industrial symbiosis can significantly boost sustainable resource efficiency in various industries.
Waste Valorization
Circular economy emphasizes the overall system redesign to minimize waste through continuous reuse, recycling, and resource efficiency. Industrial symbiosis specifically focuses on inter-industry cooperation, exchanging by-products and waste materials to create value and reduce environmental impact. Explore how waste valorization strategies transform waste streams into valuable resources, enhancing sustainability in both models.
Closed-Loop Systems
Circular economy emphasizes resource efficiency by minimizing waste through reusing, recycling, and regenerating materials within closed-loop systems. Industrial symbiosis specifically involves collaboration between different industries to utilize each other's by-products and energy flows, maximizing resource productivity in a shared closed-loop environment. Explore in-depth how closed-loop systems drive sustainability in both circular economy and industrial symbiosis for transformative environmental impacts.
Source and External Links
Circular economy - Wikipedia - A circular economy is a resource production and consumption model that emphasizes sharing, leasing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and recycling materials and products to extend their life cycle and reduce waste, contrasting with the traditional linear economy and aiming to address climate change and resource depletion.
What is a circular economy? | Ellen MacArthur Foundation - The circular economy is a system where materials never become waste and nature is regenerated, based on principles to eliminate waste and pollution, keep products and materials in use at their highest value, and regenerate natural systems, transforming the traditional take-make-waste approach.
What is Circular Economy & How Does It Work? : Complete Guide - Circular economy is an industrial system designed to be restorative and regenerative, allowing materials to be reused, repaired, and recycled continuously, reducing waste and emissions while improving environmental sustainability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com