Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances manufacturing efficiency by automating repetitive administrative tasks, streamlining workflows in supply chain management and inventory control. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines precisely execute complex machining operations using programmed commands, revolutionizing product accuracy and production speed. Explore the distinct advantages of RPA and CNC technologies to optimize your manufacturing processes.
Why it is important
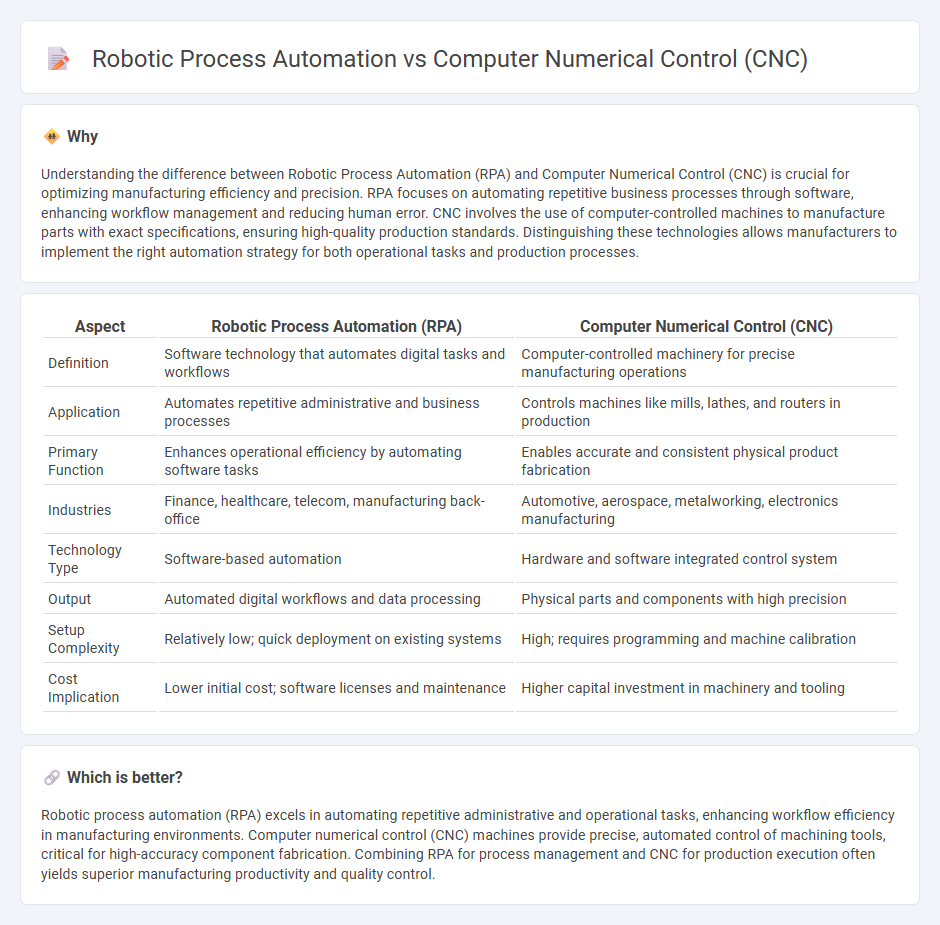
Understanding the difference between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Computer Numerical Control (CNC) is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and precision. RPA focuses on automating repetitive business processes through software, enhancing workflow management and reducing human error. CNC involves the use of computer-controlled machines to manufacture parts with exact specifications, ensuring high-quality production standards. Distinguishing these technologies allows manufacturers to implement the right automation strategy for both operational tasks and production processes.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Computer Numerical Control (CNC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software technology that automates digital tasks and workflows | Computer-controlled machinery for precise manufacturing operations |
| Application | Automates repetitive administrative and business processes | Controls machines like mills, lathes, and routers in production |
| Primary Function | Enhances operational efficiency by automating software tasks | Enables accurate and consistent physical product fabrication |
| Industries | Finance, healthcare, telecom, manufacturing back-office | Automotive, aerospace, metalworking, electronics manufacturing |
| Technology Type | Software-based automation | Hardware and software integrated control system |
| Output | Automated digital workflows and data processing | Physical parts and components with high precision |
| Setup Complexity | Relatively low; quick deployment on existing systems | High; requires programming and machine calibration |
| Cost Implication | Lower initial cost; software licenses and maintenance | Higher capital investment in machinery and tooling |
Which is better?
Robotic process automation (RPA) excels in automating repetitive administrative and operational tasks, enhancing workflow efficiency in manufacturing environments. Computer numerical control (CNC) machines provide precise, automated control of machining tools, critical for high-accuracy component fabrication. Combining RPA for process management and CNC for production execution often yields superior manufacturing productivity and quality control.
Connection
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Computer Numerical Control (CNC) are interconnected in manufacturing through their roles in automating precision tasks and enhancing operational efficiency. CNC machines execute programmed commands for manufacturing components with high accuracy, while RPA manages the data workflows and system integration that support CNC operations. Integrating RPA with CNC technology streamlines production processes, reduces human error, and increases overall manufacturing productivity.
Key Terms
G-code programming
CNC machines rely on G-code programming to precisely control toolpaths, speeds, and feed rates for manufacturing processes such as milling, turning, and drilling. Robotic Process Automation (RPA), in contrast, automates repetitive digital tasks using software robots without direct machining control or G-code integration. Explore deeper insights into programming techniques and their industry applications to understand the distinct roles of CNC and RPA in automation.
Industrial robots
Industrial robots equipped with CNC technology enable precise, programmable control of machining tools for complex manufacturing tasks, enhancing production accuracy and efficiency. Robotic process automation (RPA) in industrial settings primarily addresses software-driven tasks such as workflow optimization and data management, rather than physical operations. Discover detailed comparisons and explore how these technologies transform manufacturing processes.
Workflow automation
Computer numerical control (CNC) automates manufacturing workflows by precisely controlling machine tools through programmed instructions, enhancing production accuracy and efficiency. Robotic process automation (RPA) streamlines business workflows by automating repetitive digital tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and customer support, boosting operational productivity. Explore deeper insights on how CNC and RPA transform workflow automation across industries.
Source and External Links
What is Computer Numerical Control (CNC)? - TechTarget - CNC is a manufacturing method that automates the control and precision of machine tools through preprogrammed computer software, primarily using G-code to control movements and operations of tools like mills, lathes, and routers, enabling precise machining of metal and plastic parts.
What is Computer Numerical Control (CNC) - Techni Waterjet - CNC is a control system that automates the movement and function of machine tools using coded instructions, allowing one program to manufacture infinite parts with high consistency, unlike manual machining which requires more operator input for each part.
What is CNC Machining? | Goodwin University - CNC refers to computerized operation of machining tools where pre-programmed software dictates exact movements for tasks like cutting and shaping materials, streamlining production and enabling complex, precise manufacturing with minimal manual intervention.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com