Soft robotics emphasizes flexible, adaptive materials that mimic biological movements, ideal for delicate and complex tasks. CNC machining focuses on precise, automated cutting and shaping of rigid materials like metals and plastics, ensuring high accuracy in manufacturing components. Explore further to understand how these technologies reshape production processes.
Why it is important
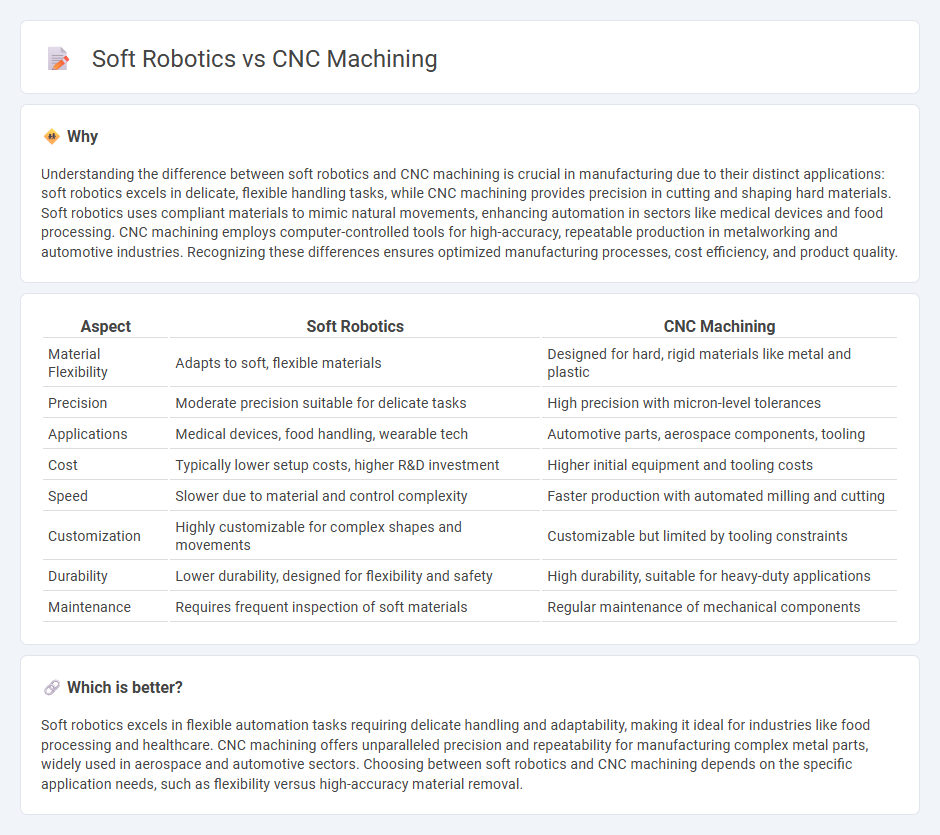
Understanding the difference between soft robotics and CNC machining is crucial in manufacturing due to their distinct applications: soft robotics excels in delicate, flexible handling tasks, while CNC machining provides precision in cutting and shaping hard materials. Soft robotics uses compliant materials to mimic natural movements, enhancing automation in sectors like medical devices and food processing. CNC machining employs computer-controlled tools for high-accuracy, repeatable production in metalworking and automotive industries. Recognizing these differences ensures optimized manufacturing processes, cost efficiency, and product quality.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Soft Robotics | CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Material Flexibility | Adapts to soft, flexible materials | Designed for hard, rigid materials like metal and plastic |
| Precision | Moderate precision suitable for delicate tasks | High precision with micron-level tolerances |
| Applications | Medical devices, food handling, wearable tech | Automotive parts, aerospace components, tooling |
| Cost | Typically lower setup costs, higher R&D investment | Higher initial equipment and tooling costs |
| Speed | Slower due to material and control complexity | Faster production with automated milling and cutting |
| Customization | Highly customizable for complex shapes and movements | Customizable but limited by tooling constraints |
| Durability | Lower durability, designed for flexibility and safety | High durability, suitable for heavy-duty applications |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent inspection of soft materials | Regular maintenance of mechanical components |
Which is better?
Soft robotics excels in flexible automation tasks requiring delicate handling and adaptability, making it ideal for industries like food processing and healthcare. CNC machining offers unparalleled precision and repeatability for manufacturing complex metal parts, widely used in aerospace and automotive sectors. Choosing between soft robotics and CNC machining depends on the specific application needs, such as flexibility versus high-accuracy material removal.
Connection
Soft robotics and CNC machining intersect through the precision manufacturing of flexible, adaptive components using computer-controlled milling and cutting techniques. CNC machining enables the production of intricate, soft robotic parts from specialized materials like silicone and elastomers, ensuring high accuracy and repeatability. This synergy enhances the development of advanced soft robotic systems with customizable mechanical properties tailored for applications in medical devices and automation.
Key Terms
Precision
CNC machining offers unparalleled precision through computer-controlled cutting tools that achieve tolerances as tight as +-0.001 mm, making it ideal for high-accuracy manufacturing. Soft robotics, using compliant materials and sensors, provides adaptive precision in delicate tasks but generally achieves lower repeatability compared to CNC systems. Explore further to understand how both technologies meet diverse precision requirements across industries.
Flexibility
CNC machining offers high precision and repeatability but lacks the adaptability required for complex, dynamic tasks, whereas soft robotics excels in flexibility by mimicking biological movements and adapting to unstructured environments. Soft robotic systems utilize compliant materials and advanced sensors to perform delicate operations that are challenging for rigid CNC machinery. Explore how integrating soft robotics can revolutionize manufacturing processes with enhanced flexibility and efficiency.
Material Compatibility
CNC machining excels in processing hard materials such as metals, plastics, and composites with high precision and rigidity, making it ideal for applications requiring durable and tightly toleranced parts. Soft robotics, utilizing flexible materials like silicone, elastomers, and hydrogels, offers enhanced adaptability and safer interactions with humans and delicate objects, albeit with less structural strength. Explore the material compatibility nuances to determine the best approach for your manufacturing needs.
Source and External Links
Online CNC Machining Service | Get a Quote - Protolabs - CNC machining is an automated process that transforms solid material blocks into precise parts using computer-controlled end mills, suitable for both prototyping and production.
Custom Online CNC Machining Services - Xometry - CNC machining replaces manual control with computer numerical control, enabling high precision and repeatability in metal and plastic part fabrication through automated, code-driven operations.
CNC machining: The manufacturing & design guide - CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing technology that produces accurate parts by removing material from a solid workpiece, driven directly by digital CAD files.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com