Cobots enhance manufacturing efficiency by collaborating directly with human workers, improving precision and safety on the production line. AMRs optimize material transport through dynamic navigation and autonomous decision-making, reducing downtime and increasing throughput. Explore how these technologies transform modern manufacturing processes and boost operational productivity.
Why it is important
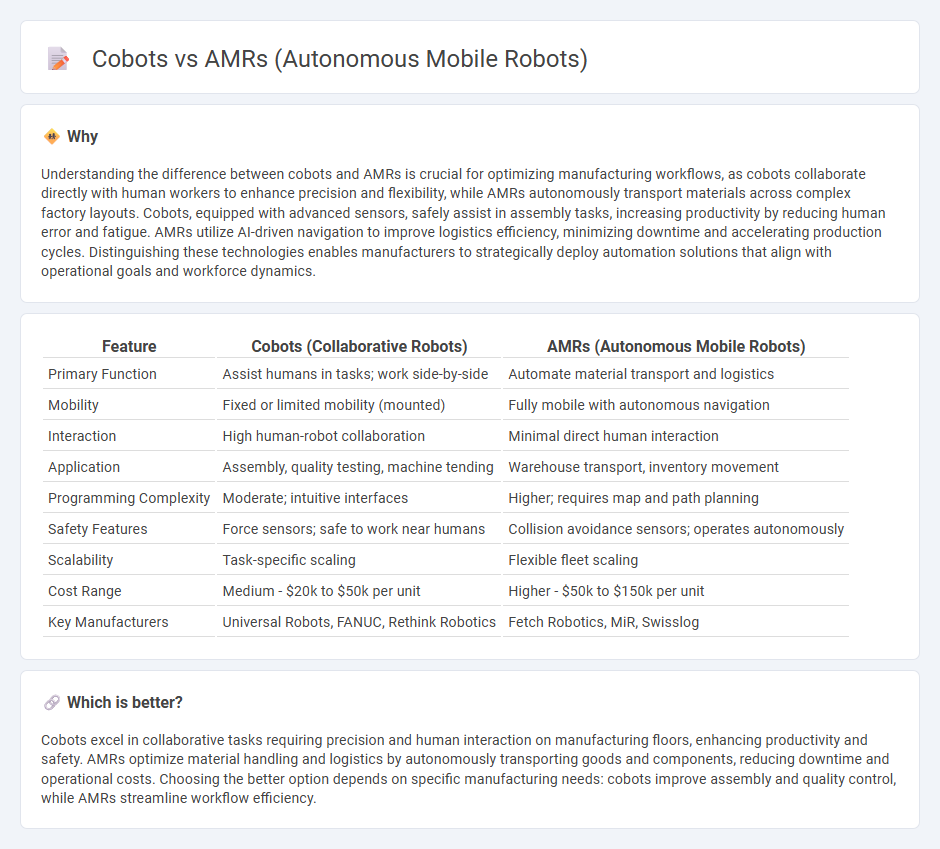
Understanding the difference between cobots and AMRs is crucial for optimizing manufacturing workflows, as cobots collaborate directly with human workers to enhance precision and flexibility, while AMRs autonomously transport materials across complex factory layouts. Cobots, equipped with advanced sensors, safely assist in assembly tasks, increasing productivity by reducing human error and fatigue. AMRs utilize AI-driven navigation to improve logistics efficiency, minimizing downtime and accelerating production cycles. Distinguishing these technologies enables manufacturers to strategically deploy automation solutions that align with operational goals and workforce dynamics.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Cobots (Collaborative Robots) | AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Assist humans in tasks; work side-by-side | Automate material transport and logistics |
| Mobility | Fixed or limited mobility (mounted) | Fully mobile with autonomous navigation |
| Interaction | High human-robot collaboration | Minimal direct human interaction |
| Application | Assembly, quality testing, machine tending | Warehouse transport, inventory movement |
| Programming Complexity | Moderate; intuitive interfaces | Higher; requires map and path planning |
| Safety Features | Force sensors; safe to work near humans | Collision avoidance sensors; operates autonomously |
| Scalability | Task-specific scaling | Flexible fleet scaling |
| Cost Range | Medium - $20k to $50k per unit | Higher - $50k to $150k per unit |
| Key Manufacturers | Universal Robots, FANUC, Rethink Robotics | Fetch Robotics, MiR, Swisslog |
Which is better?
Cobots excel in collaborative tasks requiring precision and human interaction on manufacturing floors, enhancing productivity and safety. AMRs optimize material handling and logistics by autonomously transporting goods and components, reducing downtime and operational costs. Choosing the better option depends on specific manufacturing needs: cobots improve assembly and quality control, while AMRs streamline workflow efficiency.
Connection
Cobots and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) enhance manufacturing efficiency by collaborating in shared workflows, where cobots perform precise assembly tasks while AMRs handle material transport autonomously. Integration of cobots with AMRs enables seamless synchronization through IoT connectivity and data exchange, optimizing production line flexibility and reducing downtime. Advanced sensor systems and AI-driven coordination allow these robotics technologies to dynamically adapt to changing manufacturing environments, driving Industry 4.0 transformation.
Key Terms
Navigation
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) leverage advanced sensors and AI-driven algorithms to independently navigate complex environments, optimizing route efficiency and obstacle avoidance in dynamic settings. Cobots rely on human operators for guidance and operate within predefined spaces, enhancing safety and collaboration without full autonomy in navigation. Discover more about how navigation technologies shape the future of AMRs and cobots.
Human-robot collaboration
AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots) and cobots (collaborative robots) both enhance human-robot collaboration but serve different roles in industrial environments; AMRs autonomously navigate complex spaces to transport materials, while cobots operate alongside humans, assisting with tasks requiring dexterity and precision. The integration of AMRs minimizes manual labor and optimizes workflow efficiency through real-time data processing and adaptive path planning, whereas cobots improve productivity by safely sharing workspaces and augmenting human capabilities without extensive safety barriers. Explore further to understand how combining AMRs and cobots can revolutionize human-robot collaboration for smarter manufacturing.
Task flexibility
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) excel in dynamic navigation and autonomous task execution across varying environments, offering significant adaptability in logistics and warehouse operations. Collaborative robots (cobots) provide enhanced task flexibility through direct human-robot interaction, enabling precise manipulation and assembly in manufacturing. Explore further to understand which robotic solution best fits your specific operational needs and flexibility requirements.
Source and External Links
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs): A Guide - AMRs are robots that navigate and operate independently in their environment using sensors and mapping to avoid obstacles and complete tasks like transporting goods without human intervention.
AMR vs AGV: Key Differences Explained - Unlike AGVs that follow fixed paths, AMRs use intelligent navigation to move flexibly in dynamic environments without requiring major infrastructure changes.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) - AMRs are designed to autonomously transport loads in warehouses using dynamic routing, obstacle detection, and integration with existing infrastructure for efficient material flow.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com