Digital twinning creates precise virtual replicas of physical manufacturing processes, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance to optimize efficiency. Augmented reality overlays digital information onto the physical environment, enhancing worker training, assembly accuracy, and troubleshooting on the factory floor. Explore how these transformative technologies reshape manufacturing productivity and innovation.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between digital twinning and augmented reality is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes and enhancing operational efficiency. Digital twinning creates a virtual replica of physical assets for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, while augmented reality overlays digital information onto the physical environment to assist workers. Choosing the right technology impacts cost savings, production downtime, and quality control in manufacturing plants. Manufacturers leveraging the correct tool can achieve precision in process optimization and workforce training.
Comparison Table
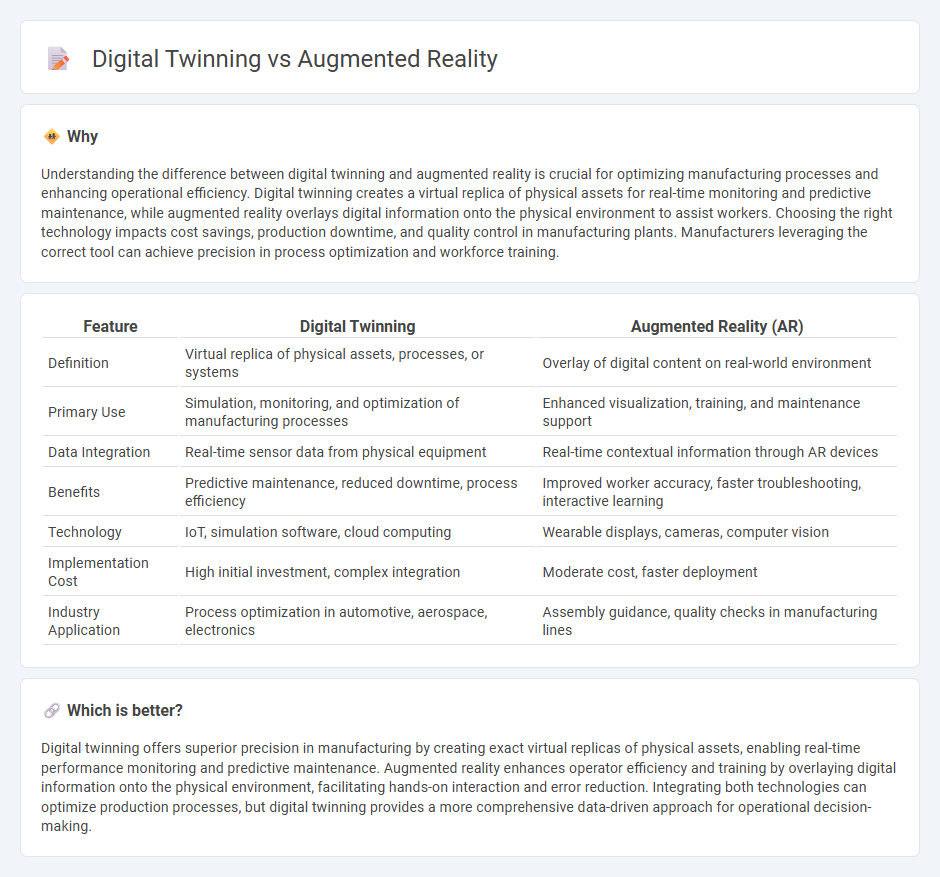
| Feature | Digital Twinning | Augmented Reality (AR) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual replica of physical assets, processes, or systems | Overlay of digital content on real-world environment |
| Primary Use | Simulation, monitoring, and optimization of manufacturing processes | Enhanced visualization, training, and maintenance support |
| Data Integration | Real-time sensor data from physical equipment | Real-time contextual information through AR devices |
| Benefits | Predictive maintenance, reduced downtime, process efficiency | Improved worker accuracy, faster troubleshooting, interactive learning |
| Technology | IoT, simulation software, cloud computing | Wearable displays, cameras, computer vision |
| Implementation Cost | High initial investment, complex integration | Moderate cost, faster deployment |
| Industry Application | Process optimization in automotive, aerospace, electronics | Assembly guidance, quality checks in manufacturing lines |
Which is better?
Digital twinning offers superior precision in manufacturing by creating exact virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling real-time performance monitoring and predictive maintenance. Augmented reality enhances operator efficiency and training by overlaying digital information onto the physical environment, facilitating hands-on interaction and error reduction. Integrating both technologies can optimize production processes, but digital twinning provides a more comprehensive data-driven approach for operational decision-making.
Connection
Digital twinning integrates with augmented reality by creating real-time, interactive 3D models of manufacturing processes and equipment, enhancing visualization and decision-making. This fusion enables operators to monitor system performance, predict maintenance needs, and simulate scenarios in a virtual environment that mirrors physical assets. Implementing these technologies drives efficiency, reduces downtime, and supports proactive maintenance strategies in smart factories.
Key Terms
Visualization
Augmented reality (AR) enhances visualization by overlaying digital elements onto the real world, creating immersive and interactive experiences for users across industries such as healthcare and manufacturing. Digital twinning provides detailed, real-time virtual replicas of physical assets or environments, enabling precise monitoring and simulation to optimize performance and predict maintenance needs. Explore further to understand how these technologies revolutionize visualization and operational efficiency.
Simulation
Augmented reality (AR) enhances real-world environments by overlaying digital simulations, allowing interactive visualization of complex systems in real time. Digital twinning creates precise virtual replicas of physical assets to simulate performance, predict outcomes, and optimize operations through continuous data synchronization. Explore further to understand how AR and digital twinning are transforming simulation in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and urban planning.
Real-time Data
Augmented reality enhances user experience by overlaying real-time data onto physical environments, enabling interactive visualization and immediate decision-making. Digital twinning involves creating a dynamic virtual model that continuously syncs with real-world assets, providing comprehensive real-time data analysis for predictive maintenance and operational optimization. Explore how integrating augmented reality with digital twinning can revolutionize real-time data utilization in industries.
Source and External Links
What is Augmented Reality? | IBM - Augmented reality (AR) integrates digital information into the user's real environment in real time, overlaying 3D models, images, or videos to enrich perception without replacing reality, using devices like smartphones, tablets, or smart glasses equipped with cameras and sensors.
Augmented reality - Wikipedia - AR, also called mixed reality, overlays real-time 3D computer graphics onto a physical environment through displays such as handheld or head-mounted devices, blending digital and physical worlds to alter perception with applications spanning from gaming to medicine.
Augmented reality | Definition, Examples, & Facts - Britannica - Augmented reality overlays computer-generated data on video or photographic displays to enhance real-world views, with origins in military HUDs and uses today ranging from gaming overlays to smartphone apps providing information about surroundings via GPS and cameras.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com